Pig lead offers higher density and easier handling for heavy-duty applications compared to sheet lead, which provides flexibility and ease of customization for detailed projects. The choice between pig lead and sheet lead depends on specific project requirements such as weight distribution, shape conformity, and ease of installation. For heavy shielding or ballast uses, pig lead is preferred, while sheet lead suits roofing, flashing, and precision fitting tasks.
Table of Comparison
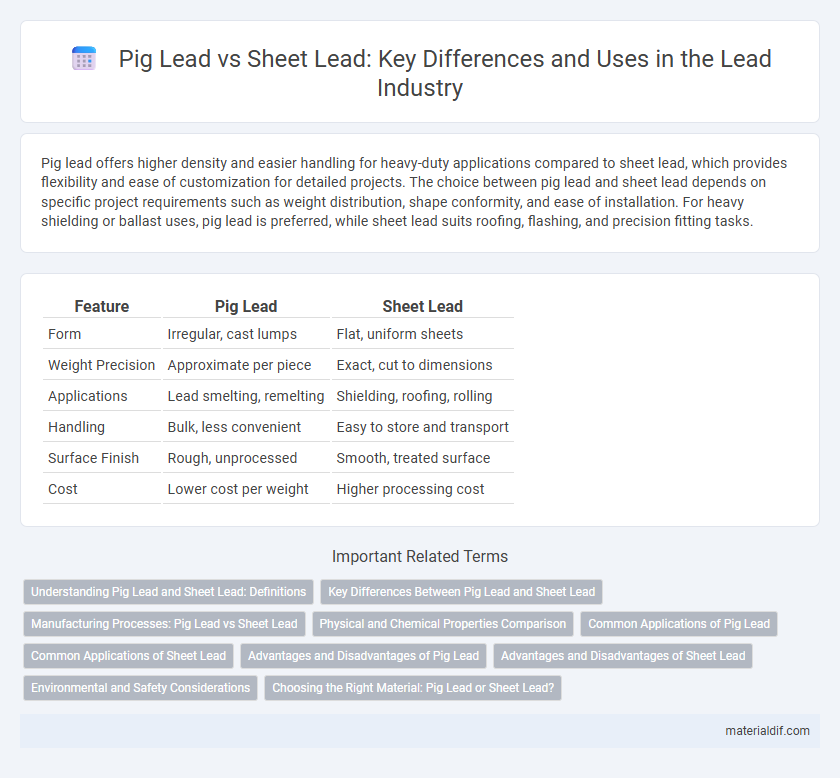
| Feature | Pig Lead | Sheet Lead |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Irregular, cast lumps | Flat, uniform sheets |
| Weight Precision | Approximate per piece | Exact, cut to dimensions |
| Applications | Lead smelting, remelting | Shielding, roofing, rolling |
| Handling | Bulk, less convenient | Easy to store and transport |
| Surface Finish | Rough, unprocessed | Smooth, treated surface |
| Cost | Lower cost per weight | Higher processing cost |
Understanding Pig Lead and Sheet Lead: Definitions
Pig lead refers to raw, unrefined lead typically cast into block-like shapes for ease of transport and further processing, offering high purity levels suitable for industrial uses. Sheet lead, on the other hand, is lead rolled into thin, flexible sheets commonly used for construction, radiation shielding, and soundproofing applications. Understanding these definitions is crucial for selecting the appropriate form of lead based on specific project requirements and performance characteristics.
Key Differences Between Pig Lead and Sheet Lead
Pig lead is raw, unrefined lead formed into small, irregularly shaped pieces, primarily used as a raw material for further processing, whereas sheet lead is a refined, flat, and uniform product manufactured through rolling processes for direct industrial applications. Pig lead typically contains higher impurities compared to sheet lead, which undergoes purification to meet standards required for roofing, radiation shielding, and chemical resistance. The distinct physical forms influence their handling, with pig lead favored for melting and remelting cycles, while sheet lead provides ease of installation and mechanical strength in construction and manufacturing sectors.
Manufacturing Processes: Pig Lead vs Sheet Lead
Pig lead is produced by smelting and casting molten lead into irregular, dense blocks that solidify quickly, optimizing bulk transport and storage. Sheet lead involves rolling heated lead billets into thin, uniform sheets through multiple passes in rolling mills, enhancing flexibility for applications requiring precise thickness and shape. The manufacturing process of pig lead emphasizes rapid solidification and mass production, while sheet lead production focuses on mechanical deformation and dimensional consistency.
Physical and Chemical Properties Comparison
Pig lead, characterized by its granular, irregular form, exhibits a density of approximately 11.34 g/cm3 and a melting point near 327.5degC, offering high malleability and corrosion resistance similar to sheet lead. Sheet lead, produced by rolling pig lead into flat, uniform sheets, shares the same chemical composition (Pb) and density but provides enhanced surface area for applications requiring flexibility and precise thickness. Both forms display excellent chemical stability and low reactivity with acids, making them valuable in radiation shielding, battery manufacturing, and construction uses.
Common Applications of Pig Lead
Pig lead is primarily used in industrial applications such as battery manufacturing, radiation shielding, and cable sheathing due to its relatively pure and malleable form. Unlike sheet lead, which is often employed in roofing and flashing, pig lead's granular shape allows for easier melting and alloying in metallurgical processes. Its versatility in producing lead-based components and compounds makes it essential in chemical and construction industries.
Common Applications of Sheet Lead
Sheet lead is widely used in roofing for waterproofing and as a weather-resistant barrier due to its flexibility and durability. It also finds applications in radiation shielding in medical and industrial settings, protecting against X-rays and gamma rays. Additionally, sheet lead is commonly employed in soundproofing and vibration damping in construction and automotive industries.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Pig Lead
Pig lead offers advantages such as high purity and ease of remelting, making it ideal for recycling and casting applications. Its form facilitates transportation and storage but presents disadvantages including higher handling risks due to its bulky shape and increased potential for contamination compared to sheet lead. Sheet lead provides superior surface coverage and uniform thickness, yet pig lead remains cost-effective for bulk lead procurement.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Sheet Lead
Sheet lead offers superior flexibility and ease of installation compared to pig lead, making it ideal for roofing and waterproofing tasks where precision is required. However, sheet lead is more expensive and less malleable for complex shapes than pig lead, which is commonly used in industrial applications for its adaptability. The durability of sheet lead in harsh weather conditions outweighs its cost, providing long-term protection with minimal maintenance.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Pig lead, commonly used in battery manufacturing, poses significant environmental risks due to its potential for heavy metal contamination in soil and water. Sheet lead, often utilized in construction and radiation shielding, requires careful handling to prevent lead dust and exposure, which can cause severe health issues including neurological damage. Proper disposal and recycling of both pig and sheet lead are critical to minimize toxic lead emissions and ensure worker safety.
Choosing the Right Material: Pig Lead or Sheet Lead?
Choosing the right material between pig lead and sheet lead depends on the specific application requirements, such as shape, malleability, and ease of handling. Pig lead, typically cast into blocks or ingots, is ideal for melting down and custom shaping, while sheet lead offers pre-formed, flat pieces suited for shielding, lining, or roofing purposes. Evaluating factors like weight distribution, installation method, and environmental exposure ensures optimal performance and cost-effectiveness.
Pig Lead vs Sheet Lead Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com