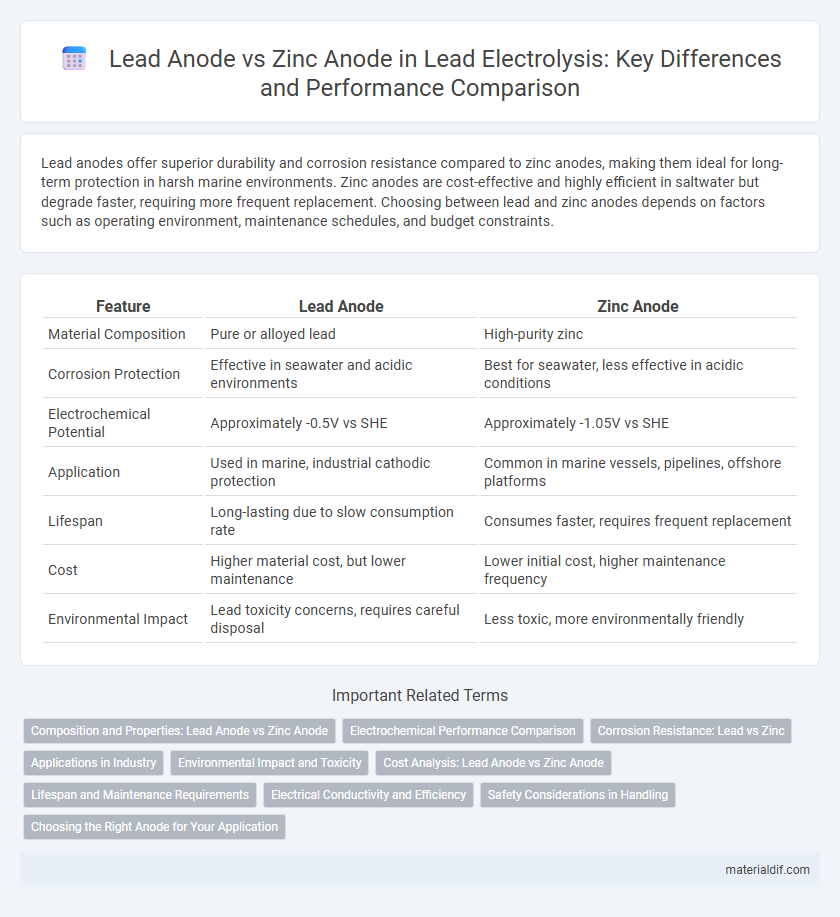
Lead anodes offer superior durability and corrosion resistance compared to zinc anodes, making them ideal for long-term protection in harsh marine environments. Zinc anodes are cost-effective and highly efficient in saltwater but degrade faster, requiring more frequent replacement. Choosing between lead and zinc anodes depends on factors such as operating environment, maintenance schedules, and budget constraints.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Anode | Zinc Anode |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Pure or alloyed lead | High-purity zinc |
| Corrosion Protection | Effective in seawater and acidic environments | Best for seawater, less effective in acidic conditions |
| Electrochemical Potential | Approximately -0.5V vs SHE | Approximately -1.05V vs SHE |
| Application | Used in marine, industrial cathodic protection | Common in marine vessels, pipelines, offshore platforms |
| Lifespan | Long-lasting due to slow consumption rate | Consumes faster, requires frequent replacement |
| Cost | Higher material cost, but lower maintenance | Lower initial cost, higher maintenance frequency |
| Environmental Impact | Lead toxicity concerns, requires careful disposal | Less toxic, more environmentally friendly |
Composition and Properties: Lead Anode vs Zinc Anode
Lead anodes consist primarily of lead, often alloyed with small amounts of calcium or antimony to enhance mechanical strength and corrosion resistance, making them highly effective in protecting steel structures in harsh environments. Zinc anodes are composed mainly of zinc with alloying elements like aluminum and indium, providing better performance in seawater due to their higher electrochemical potential and superior self-corrosion rates. Compared to lead anodes, zinc anodes exhibit greater efficiency in cathodic protection systems by offering increased current output and longer service life in marine applications.
Electrochemical Performance Comparison
Lead anodes exhibit higher corrosion resistance and longer service life compared to zinc anodes due to their stable electrochemical potential and dense oxide film formation. Zinc anodes provide higher initial driving voltage and are more effective in preventing galvanic corrosion in seawater environments but tend to degrade faster under prolonged exposure. Electrochemical performance of lead anodes makes them suitable for applications requiring durability, while zinc anodes are preferred for rapid protection in marine cathodic protection systems.
Corrosion Resistance: Lead vs Zinc
Lead anodes exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to zinc anodes due to their stable oxide layer formation, which effectively protects the metal surface in various environments. Zinc anodes, while reactive, tend to corrode faster in acidic and chloride-rich conditions, reducing their lifespan in marine applications. The enhanced durability of lead anodes makes them a preferred choice for long-term protection in harsh industrial and marine settings.
Applications in Industry
Lead anodes are widely utilized in industries requiring corrosion resistance in harsh environments, such as electroplating, battery manufacturing, and chemical processing. Zinc anodes are predominantly applied in marine and underground structures for cathodic protection due to their effective sacrificial properties and cost-efficiency. Industrial applications benefit from selecting lead or zinc anodes based on factors like conductivity, environmental compatibility, and longevity under specific operational conditions.
Environmental Impact and Toxicity
Lead anodes release highly toxic lead ions into the environment, posing severe risks to aquatic life and human health due to bioaccumulation and persistence in ecosystems. Zinc anodes, while still metallic pollutants, exhibit significantly lower toxicity and degrade more readily, reducing long-term environmental harm. Choosing zinc anodes over lead anodes contributes to safer corrosion prevention with less ecological contamination.
Cost Analysis: Lead Anode vs Zinc Anode
Lead anodes generally incur higher upfront material costs compared to zinc anodes due to lead's greater density and market price volatility. Zinc anodes offer cost advantages with lower initial investment and longer service life in seawater environments, potentially reducing replacement frequency and maintenance expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership requires balancing lead's superior durability against zinc's economic benefits in specific corrosion protection applications.
Lifespan and Maintenance Requirements
Lead anodes generally offer a longer lifespan compared to zinc anodes due to their superior corrosion resistance in various electrolytic environments. Maintenance of lead anodes is often less frequent, as they tend to degrade slower and maintain structural integrity under prolonged use. In contrast, zinc anodes, while effective, require more regular inspection and replacement especially in seawater applications where they dissolve faster.
Electrical Conductivity and Efficiency
Lead anodes exhibit lower electrical conductivity compared to zinc anodes, impacting overall efficiency in electrochemical applications. Zinc anodes provide higher conductivity, resulting in improved current distribution and enhanced protection in cathodic systems. The superior efficiency of zinc anodes makes them preferable for corrosion control in marine and industrial environments.
Safety Considerations in Handling
Lead anodes require careful handling due to their toxicity and potential health risks from lead exposure, necessitating the use of gloves and proper ventilation to avoid inhalation of dust or fumes. Zinc anodes, while less toxic, still require appropriate protective equipment to prevent skin irritation and respiratory issues during installation and disposal. Safe storage and disposal protocols for both anode types are essential to minimize environmental contamination and protect worker health.
Choosing the Right Anode for Your Application
Lead anodes offer superior corrosion resistance and longer service life compared to zinc anodes, making them ideal for harsh marine environments and heavy-duty cathodic protection systems. Zinc anodes provide effective sacrificial protection in seawater due to their higher electrochemical activity but have a shorter lifespan and can be less suitable in freshwater applications. Selecting the right anode depends on factors such as electrolyte type, operating conditions, budget, and maintenance frequency to optimize efficiency and durability.
Lead anode vs Zinc anode Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com