Lead-glazed ceramic contains a coating that can release harmful lead particles, posing significant health risks when used for food or drink storage. Unglazed ceramic, free from such coatings, is a safer alternative as it prevents lead contamination and maintains natural porosity for breathability. Choosing unglazed ceramic ensures non-toxic use while preserving the material's durability and eco-friendliness.
Table of Comparison
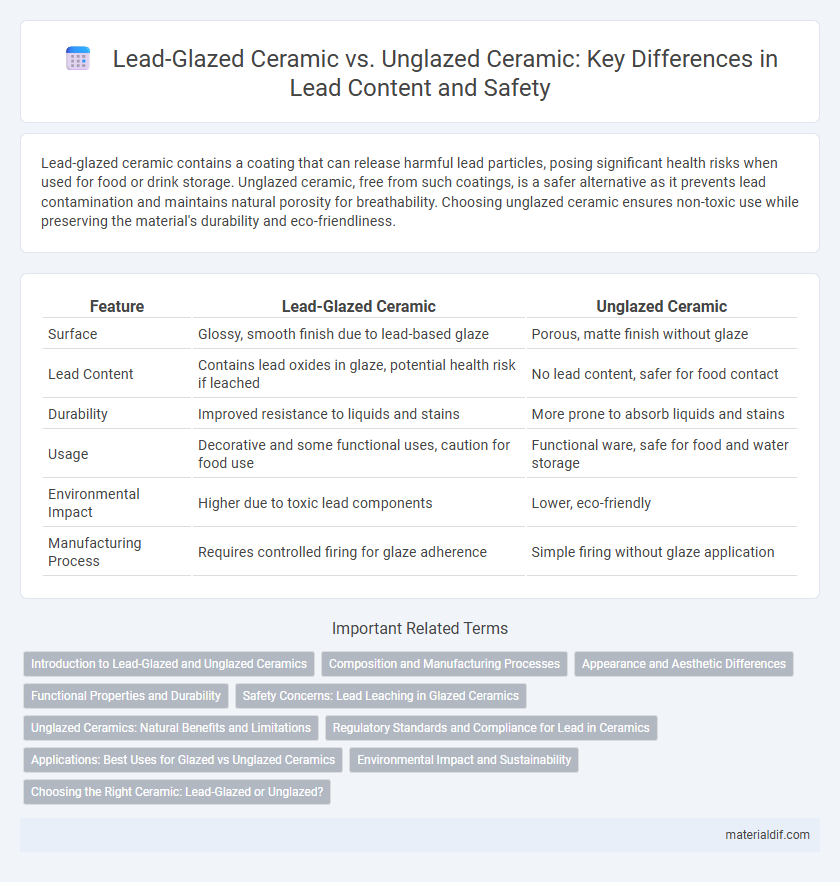
| Feature | Lead-Glazed Ceramic | Unglazed Ceramic |
|---|---|---|
| Surface | Glossy, smooth finish due to lead-based glaze | Porous, matte finish without glaze |
| Lead Content | Contains lead oxides in glaze, potential health risk if leached | No lead content, safer for food contact |
| Durability | Improved resistance to liquids and stains | More prone to absorb liquids and stains |
| Usage | Decorative and some functional uses, caution for food use | Functional ware, safe for food and water storage |
| Environmental Impact | Higher due to toxic lead components | Lower, eco-friendly |
| Manufacturing Process | Requires controlled firing for glaze adherence | Simple firing without glaze application |
Introduction to Lead-Glazed and Unglazed Ceramics
Lead-glazed ceramics feature a glassy coating infused with lead oxide, providing a smooth, glossy surface that enhances durability and prevents liquid absorption. Unglazed ceramics lack this protective layer, resulting in a porous, matte finish that is more susceptible to staining and wear. Understanding the key differences in composition and surface properties is essential for selecting the appropriate ceramic type for health, safety, and functionality.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Lead-glazed ceramics incorporate a glassy coating containing lead oxide, which lowers the melting point and enhances durability and shine, while unglazed ceramics lack this coating, retaining a porous, matte surface. Manufacturing lead-glazed ceramics involves applying the lead-based glaze before firing at lower temperatures, whereas unglazed ceramics require higher firing temperatures to achieve hardness and are left untreated to maintain their natural texture. The lead composition in glazes raises concerns regarding toxicity and regulatory restrictions, influencing production and usage standards across markets.
Appearance and Aesthetic Differences
Lead-glazed ceramic exhibits a glossy, smooth surface with vibrant colors and intricate patterns, enhancing its visual appeal and richness in design. Unglazed ceramic has a matte, textured finish with natural earthy tones, offering a rustic and organic aesthetic. The contrast between the shiny, reflective quality of lead-glazed ceramics and the subdued, raw look of unglazed ceramics defines their distinct decorative uses.
Functional Properties and Durability
Lead-glazed ceramics provide a smooth, non-porous surface that enhances resistance to staining and water absorption, significantly improving durability in everyday use. Unglazed ceramics, while more porous, offer greater resistance to thermal shock and mechanical abrasion, making them suitable for heavy-duty functional applications. The lead glaze, however, may raise concerns about chemical leaching, whereas unglazed ceramics ensure a safer option with longer-term stability under harsh conditions.
Safety Concerns: Lead Leaching in Glazed Ceramics
Lead-glazed ceramics pose significant safety concerns due to the potential for lead to leach into food and beverages, especially when the glaze is cracked or worn. Unglazed ceramics, lacking lead-based coatings, do not have this risk and are generally considered safer for everyday use. Regulatory agencies recommend testing glazed ceramics for lead content to prevent poisoning and ensure consumer protection.
Unglazed Ceramics: Natural Benefits and Limitations
Unglazed ceramics offer natural breathability and superior moisture absorption compared to lead-glazed ceramics, making them ideal for storing dry foods and promoting freshness. Their porous surface enhances heat retention and provides a non-toxic alternative free from potential lead contamination risks. However, unglazed ceramics are more prone to staining and require careful maintenance to prevent bacterial buildup and prolong durability.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance for Lead in Ceramics
Lead-glazed ceramics must comply with strict regulatory standards limit lead leaching to protect consumer health, such as the U.S. FDA's permissible lead levels in tableware and the European Union's REACH regulations. Unglazed ceramics generally pose lower lead exposure risks but still require adherence to regional safety standards to ensure no contamination during manufacturing. Manufacturers must perform rigorous testing following protocols like ASTM C738 to certify ceramics meet lead content and migration limits.
Applications: Best Uses for Glazed vs Unglazed Ceramics
Lead-glazed ceramics are ideal for decorative items and functional pottery that require a smooth, non-porous surface, making them suitable for tableware and ornamental pieces where moisture resistance and vibrant finishes are essential. Unglazed ceramics excel in applications such as plant pots, floor tiles, and cookware where breathability and natural texture enhance functionality and aesthetic appeal. Choosing between glazed and unglazed ceramics depends on the balance needed between durability, moisture retention, and the intended use environment.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Lead-glazed ceramics pose significant environmental risks due to the leaching of toxic heavy metals like lead into soil and water, contributing to pollution and health hazards. Unglazed ceramics, often made from natural clay without hazardous coatings, offer a more sustainable alternative by minimizing chemical contamination and supporting safer disposal or recycling processes. Choosing unglazed ceramics reduces ecological footprints and aligns better with sustainable manufacturing and waste management practices.
Choosing the Right Ceramic: Lead-Glazed or Unglazed?
Lead-glazed ceramics provide a smooth, colorful finish but carry health risks due to potential lead leaching, making them unsuitable for food storage or children's items. Unglazed ceramics offer a natural, porous surface that is safer for culinary use and better for environmental sustainability. Choosing between lead-glazed and unglazed ceramics hinges on intended use, with unglazed preferred for health-conscious applications and lead-glazed used mostly for decorative purposes.
Lead-glazed ceramic vs Unglazed ceramic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com