Lead pipes pose significant health risks due to lead leaching into drinking water, potentially causing severe neurological damage, especially in children. Copper pipes offer a safer alternative, providing durability, corrosion resistance, and better water quality without the toxic risk of lead exposure. Choosing copper pipes over lead pipes ensures compliance with health regulations and promotes long-term safety for residential and commercial plumbing systems.
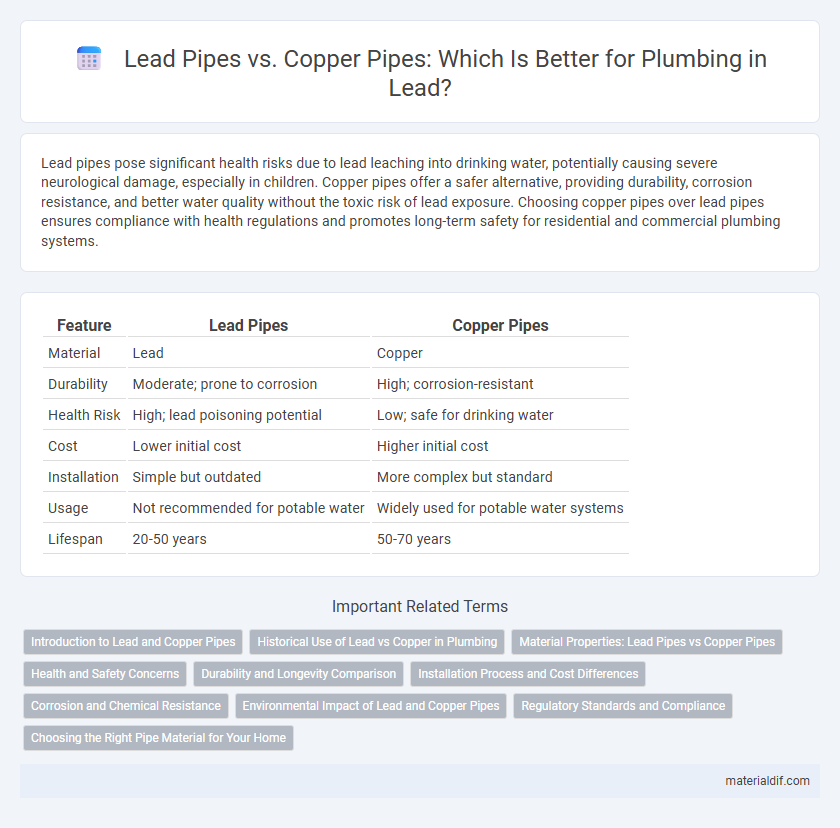
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Lead Pipes | Copper Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Lead | Copper |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to corrosion | High; corrosion-resistant |
| Health Risk | High; lead poisoning potential | Low; safe for drinking water |
| Cost | Lower initial cost | Higher initial cost |
| Installation | Simple but outdated | More complex but standard |
| Usage | Not recommended for potable water | Widely used for potable water systems |
| Lifespan | 20-50 years | 50-70 years |
Introduction to Lead and Copper Pipes
Lead pipes, historically used in plumbing due to their malleability and resistance to pinhole leaks, pose significant health risks because of lead's toxicity and potential for leaching into drinking water. Copper pipes offer superior durability, corrosion resistance, and biostatic properties that inhibit bacterial growth, making them a safer alternative widely adopted in modern plumbing systems. Understanding the material properties and health implications of lead and copper pipes is crucial for evaluating plumbing infrastructure and ensuring safe water delivery.
Historical Use of Lead vs Copper in Plumbing
Lead pipes were widely used in plumbing systems from ancient Rome through the early 20th century due to their malleability and resistance to corrosion. Copper pipes began replacing lead in the 20th century as awareness of lead's toxicity grew, offering a safer, more durable option that also resists bacterial growth. Modern plumbing standards prioritize copper and other non-toxic materials to prevent lead contamination and ensure water safety.
Material Properties: Lead Pipes vs Copper Pipes
Lead pipes exhibit high malleability and corrosion resistance but pose significant health risks due to lead leaching into water. Copper pipes offer superior durability, corrosion resistance, and antimicrobial properties, making them safer for potable water systems. Material strength and longevity favor copper, while lead's flexibility once made it popular despite its toxicity concerns.
Health and Safety Concerns
Lead pipes pose significant health risks due to the potential leaching of toxic lead into drinking water, which can cause neurological damage, especially in children and pregnant women. Copper pipes, while generally safer, can still contribute to copper exposure and corrosion if water chemistry is unbalanced. Regulatory standards strongly recommend replacing lead pipes to ensure safe, contaminant-free water supply and minimize long-term health hazards.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Lead pipes, once common in plumbing, exhibit significant corrosion over time that compromises structural integrity and poses health risks, resulting in a typical lifespan of 50 years or less. Copper pipes offer superior durability with resistance to corrosion, often lasting over 70 years, making them a preferred choice for long-term plumbing solutions. The longevity of copper pipes contributes to reduced maintenance and replacement costs compared to lead pipes, which require frequent inspection and potential replacement to ensure safety.
Installation Process and Cost Differences
Lead pipes require specialized techniques and safety precautions during installation due to health risks associated with lead exposure, making the process more complex and time-consuming. Copper pipes offer easier installation with the ability to use soldering or compression fittings, reducing labor costs and installation time. While lead pipes have a lower material cost, copper pipes generally present a more cost-effective solution overall when considering installation efficiency and long-term safety compliance.
Corrosion and Chemical Resistance
Lead pipes exhibit significant corrosion issues due to their susceptibility to chemical reactions with water, often resulting in lead leaching. Copper pipes offer superior corrosion resistance, forming a protective oxide layer that prevents metal degradation and contamination. Chemical resistance in copper pipes makes them a safer choice for potable water systems compared to lead pipes.
Environmental Impact of Lead and Copper Pipes
Lead pipes release toxic lead particles into water, posing severe environmental hazards and health risks such as neurotoxicity and water contamination. Copper pipes, while generally safer, can contribute to copper leaching in acidic water conditions, impacting aquatic ecosystems and water quality. Copper is more environmentally friendly due to higher recyclability and lower toxicity compared to lead's persistent environmental pollution.
Regulatory Standards and Compliance
Lead pipes are largely banned in modern plumbing due to stringent regulatory standards such as the Safe Drinking Water Act (SDWA) in the United States, which limits lead content to 15 parts per billion in drinking water. Copper pipes comply with these regulations and are preferred because they do not leach harmful substances, meeting NSF/ANSI 61 standards for potable water systems. Municipalities increasingly mandate copper or lead-free alternatives to ensure compliance with health and safety codes.
Choosing the Right Pipe Material for Your Home
Lead pipes pose significant health risks due to lead contamination in drinking water, making copper pipes a safer and more durable choice for home plumbing systems. Copper pipes offer excellent corrosion resistance, longevity, and antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of bacterial growth and ensuring water quality. Homeowners should prioritize copper plumbing to comply with modern building codes and protect family health.
Lead pipes vs Copper pipes Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com