Lead crystal offers exceptional brilliance and clarity due to its high refractive index, making it ideal for decorative glassware. Borosilicate glass is prized for its durability and thermal resistance, suitable for scientific and everyday use. The choice between lead crystal and borosilicate glass depends on whether aesthetic appeal or functional strength is prioritized.
Table of Comparison
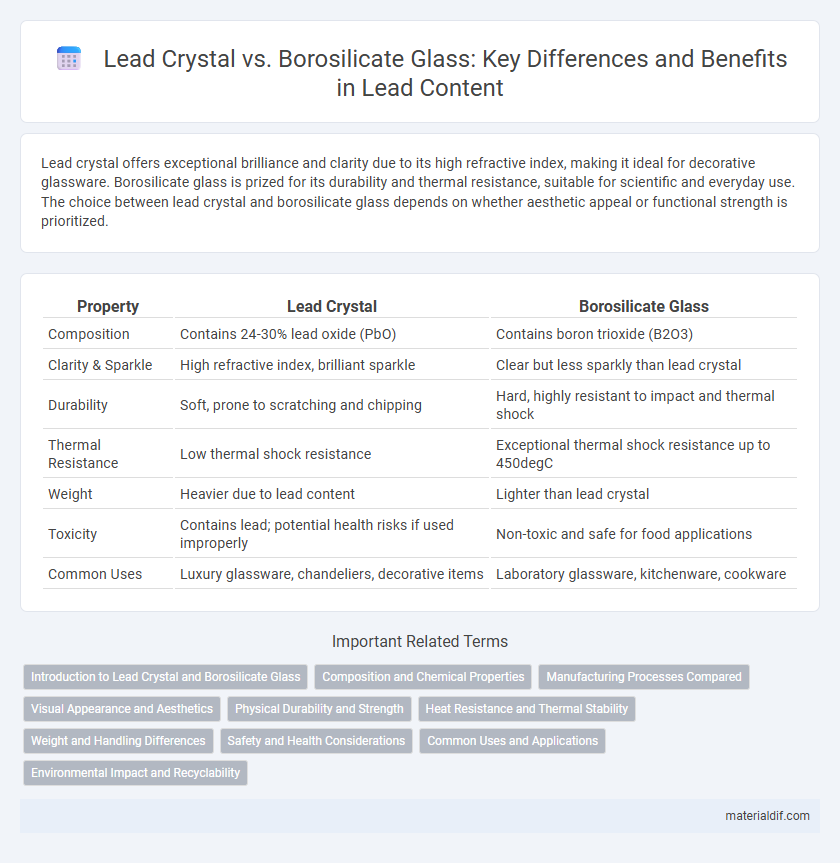
| Property | Lead Crystal | Borosilicate Glass |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Contains 24-30% lead oxide (PbO) | Contains boron trioxide (B2O3) |
| Clarity & Sparkle | High refractive index, brilliant sparkle | Clear but less sparkly than lead crystal |
| Durability | Soft, prone to scratching and chipping | Hard, highly resistant to impact and thermal shock |
| Thermal Resistance | Low thermal shock resistance | Exceptional thermal shock resistance up to 450degC |
| Weight | Heavier due to lead content | Lighter than lead crystal |
| Toxicity | Contains lead; potential health risks if used improperly | Non-toxic and safe for food applications |
| Common Uses | Luxury glassware, chandeliers, decorative items | Laboratory glassware, kitchenware, cookware |
Introduction to Lead Crystal and Borosilicate Glass
Lead crystal is a type of glass that contains lead oxide, typically between 18% to 30%, which enhances its refractive index and brilliance, making it highly prized for fine glassware and decorative items. Borosilicate glass consists primarily of silica and boron trioxide, offering superior thermal resistance and durability, commonly used in laboratory equipment and kitchenware. The contrasting compositions of lead crystal and borosilicate glass determine their optical properties, weight, and resistance to thermal shock.
Composition and Chemical Properties
Lead crystal contains lead oxide, typically between 24% and 32%, which enhances its density, brilliance, and refractive index. Borosilicate glass is composed primarily of silica and boron trioxide, offering superior thermal resistance and chemical durability. The high lead content in lead crystal increases its softness and susceptibility to chemical corrosion, while borosilicate glass resists alkalis and acids due to its stable borosilicate network.
Manufacturing Processes Compared
Lead crystal is manufactured by adding lead oxide to the glass mixture, which enhances its refractive properties and requires a slower, more intricate blowing and annealing process to ensure clarity and brilliance. Borosilicate glass is produced by combining silica and boron trioxide, resulting in a higher resistance to thermal shock and simplifying the manufacturing process through faster cooling times and less stringent annealing. The differences in raw materials and thermal properties directly influence production speed, energy consumption, and the final product's durability and appearance.
Visual Appearance and Aesthetics
Lead crystal exhibits exceptional brilliance and clarity due to its high refractive index, creating vibrant light dispersion and a sparkling effect. Borosilicate glass offers a more muted, transparent look with less sparkle, valued for its simplicity and durability rather than ornamentation. The visual appeal of lead crystal makes it favored in decorative and luxury tableware, while borosilicate glass suits minimalist and functional designs.
Physical Durability and Strength
Lead crystal offers exceptional clarity and weight but is softer and more prone to chipping compared to borosilicate glass, which boasts superior physical durability and resistance to thermal shock. Borosilicate glass contains silica and boron trioxide, enhancing its strength and making it ideal for items exposed to sudden temperature changes or heavy use. The high durability of borosilicate glass ensures longer lifespan and better resistance to mechanical stress than lead crystal, which, despite its brilliance, requires more delicate handling.
Heat Resistance and Thermal Stability
Lead crystal contains lead oxide that enhances its brilliance but reduces heat resistance, making it prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes. Borosilicate glass, composed mainly of silica and boron trioxide, offers superior thermal stability and can withstand high temperatures without breaking. Its low coefficient of thermal expansion makes borosilicate glass ideal for applications requiring resistance to thermal shock.
Weight and Handling Differences
Lead crystal is significantly heavier than borosilicate glass due to its high lead oxide content, providing a substantial, luxurious feel in hand. Borosilicate glass is lighter and more durable, allowing for easier handling and increased resistance to thermal shock. The weight difference impacts user experience, with lead crystal favored for elegance and borosilicate for practicality and everyday use.
Safety and Health Considerations
Lead crystal contains lead oxide which can leach into liquids, posing potential health risks such as lead poisoning with prolonged exposure. Borosilicate glass is free from lead, making it a safer alternative for food and beverage storage due to its chemical stability and non-toxic properties. Choosing borosilicate glass reduces the risk of harmful metal contamination and is preferred in health-conscious environments.
Common Uses and Applications
Lead crystal is widely used in fine glassware, decorative items, and luxury tableware due to its high refractive index and brilliance, enhancing aesthetic appeal in chandeliers, wine glasses, and vases. Borosilicate glass is preferred in laboratory equipment, cookware, and optical instruments because of its exceptional thermal resistance and durability under rapid temperature changes. Both materials serve distinct industries, with lead crystal excelling in decorative and collectible products, while borosilicate glass meets rigorous functional requirements in scientific and industrial applications.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Lead crystal contains lead oxide, which poses environmental hazards during production and disposal due to lead toxicity, making recycling more complex and limited. Borosilicate glass, composed mainly of silica and boron trioxide, offers better environmental compatibility with lower toxicity and higher recyclability rates. The recycling infrastructure for borosilicate glass is more developed, enabling effective reuse and reducing landfill waste compared to lead crystal.
Lead crystal vs borosilicate glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com