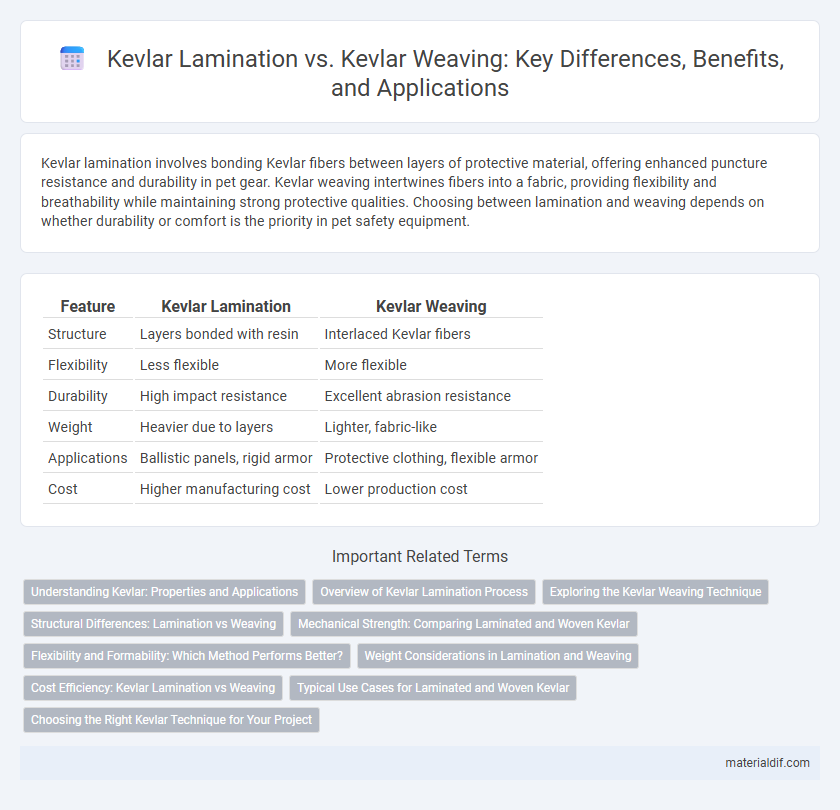
Kevlar lamination involves bonding Kevlar fibers between layers of protective material, offering enhanced puncture resistance and durability in pet gear. Kevlar weaving intertwines fibers into a fabric, providing flexibility and breathability while maintaining strong protective qualities. Choosing between lamination and weaving depends on whether durability or comfort is the priority in pet safety equipment.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kevlar Lamination | Kevlar Weaving |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Layers bonded with resin | Interlaced Kevlar fibers |
| Flexibility | Less flexible | More flexible |
| Durability | High impact resistance | Excellent abrasion resistance |
| Weight | Heavier due to layers | Lighter, fabric-like |
| Applications | Ballistic panels, rigid armor | Protective clothing, flexible armor |
| Cost | Higher manufacturing cost | Lower production cost |
Understanding Kevlar: Properties and Applications
Kevlar lamination enhances impact resistance and rigidity by bonding multiple layers of Kevlar fabric with resin, creating lightweight composite materials widely used in aerospace and body armor. Kevlar weaving, on the other hand, involves interlacing fibers to produce flexible, durable textiles ideal for ballistic vests and protective apparel, balancing strength and flexibility. Both methods leverage Kevlar's high tensile strength, thermal stability, and chemical resistance to meet specific application requirements.
Overview of Kevlar Lamination Process
Kevlar lamination involves bonding thin layers of Kevlar fabric together with adhesives or resins to create a composite material that enhances strength and durability while maintaining flexibility. This process offers improved resistance to abrasion, impact, and moisture compared to traditional Kevlar weaving, making it ideal for protective gear and industrial applications. Laminated Kevlar products exhibit uniform thickness and tailored performance characteristics by controlling the layering sequence and adhesive types.
Exploring the Kevlar Weaving Technique
Kevlar weaving involves interlacing strong Kevlar fibers in a crisscross pattern to create a flexible yet durable fabric, offering enhanced impact resistance and tensile strength compared to lamination. The weaving technique optimizes fiber alignment, allowing better energy dispersion and improved abrasion resistance, making it ideal for ballistic and protective gear applications. Unlike Kevlar lamination, which bonds fibers with resins, weaving maintains the inherent properties of Kevlar fibers without compromising flexibility or breathability.
Structural Differences: Lamination vs Weaving
Kevlar lamination involves bonding multiple layers of Kevlar fabric with adhesives to form a rigid, uniform composite, enhancing impact resistance and reducing flexibility. In contrast, Kevlar weaving interlaces individual fibers in a distinct pattern, providing superior tensile strength and flexibility due to the fiber arrangement. The structural difference lies in lamination creating a solid layered matrix, while weaving maintains fiber integrity through an interlocked textile structure.
Mechanical Strength: Comparing Laminated and Woven Kevlar
Laminated Kevlar offers enhanced mechanical strength through multiple bonded layers that provide superior impact resistance and stiffness under high stress conditions. Woven Kevlar provides exceptional tensile strength and flexibility due to its interlaced fiber construction, making it ideal for applications requiring durability combined with pliability. Comparing the two, laminated Kevlar excels in resisting punctures and delamination, while woven Kevlar delivers consistent load distribution and fatigue resistance.
Flexibility and Formability: Which Method Performs Better?
Kevlar weaving offers superior flexibility because the interlaced fibers can bend and move more freely, adapting better to complex shapes and contours. Kevlar lamination provides enhanced rigidity and structural integrity but limits formability due to the bonded layers restricting fiber movement. For applications requiring high flexibility and ease of shaping, woven Kevlar outperforms laminated Kevlar in maintaining both strength and adaptability.
Weight Considerations in Lamination and Weaving
Kevlar lamination offers a lighter overall weight by bonding thin layers with resin, optimizing strength-to-weight ratios crucial in aerospace and ballistic applications. In contrast, Kevlar weaving inherently increases weight due to the interlaced fiber structure, which adds bulk but enhances flexibility and tensile strength. Weight considerations favor lamination where minimal mass is critical, while weaving is preferred when durability and impact resistance are prioritized despite the added weight.
Cost Efficiency: Kevlar Lamination vs Weaving
Kevlar lamination offers a more cost-efficient solution compared to traditional Kevlar weaving due to reduced labor intensity and faster production times. Lamination processes minimize material waste and simplify manufacturing, leading to lower overall expenses in large-scale applications. Weaving, while providing superior flexibility and strength, involves higher costs related to intricate yarn handling and longer assembly durations.
Typical Use Cases for Laminated and Woven Kevlar
Kevlar lamination is typically used in applications requiring enhanced ballistic protection and rigidity, such as body armor panels, helmets, and vehicle armor, where layers are bonded to create a composite structure. Woven Kevlar excels in flexibility and durability, making it ideal for protective gloves, ropes, tires, and fabric reinforcements that demand high tensile strength and abrasion resistance. Choosing between laminated and woven Kevlar depends on the need for either structural integrity or flexibility in protective gear and industrial materials.
Choosing the Right Kevlar Technique for Your Project
Kevlar lamination offers superior impact resistance and is ideal for applications requiring rigidity and waterproof properties, while Kevlar weaving provides flexibility and breathability, suitable for protective clothing and lightweight gear. Selecting the appropriate Kevlar technique depends on project-specific needs, such as durability, flexibility, and environmental exposure. Understanding these material characteristics ensures optimized performance and longevity in ballistic protection, automotive components, or industrial uses.
Kevlar lamination vs Kevlar weaving Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com