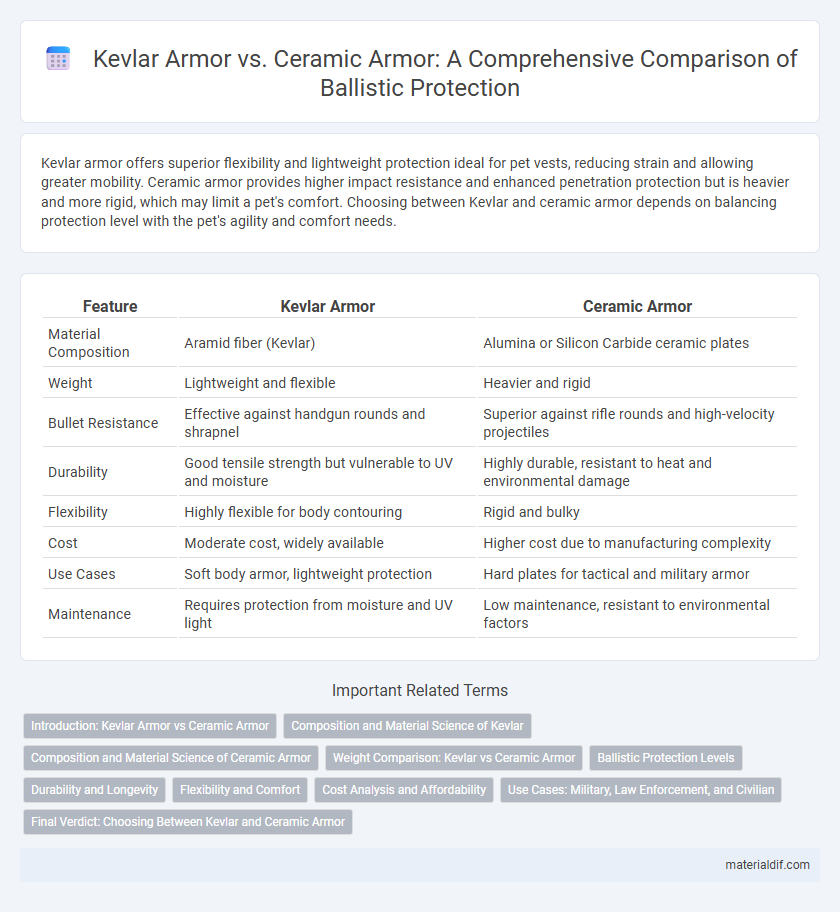
Kevlar armor offers superior flexibility and lightweight protection ideal for pet vests, reducing strain and allowing greater mobility. Ceramic armor provides higher impact resistance and enhanced penetration protection but is heavier and more rigid, which may limit a pet's comfort. Choosing between Kevlar and ceramic armor depends on balancing protection level with the pet's agility and comfort needs.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kevlar Armor | Ceramic Armor |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Aramid fiber (Kevlar) | Alumina or Silicon Carbide ceramic plates |
| Weight | Lightweight and flexible | Heavier and rigid |
| Bullet Resistance | Effective against handgun rounds and shrapnel | Superior against rifle rounds and high-velocity projectiles |
| Durability | Good tensile strength but vulnerable to UV and moisture | Highly durable, resistant to heat and environmental damage |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible for body contouring | Rigid and bulky |
| Cost | Moderate cost, widely available | Higher cost due to manufacturing complexity |
| Use Cases | Soft body armor, lightweight protection | Hard plates for tactical and military armor |
| Maintenance | Requires protection from moisture and UV light | Low maintenance, resistant to environmental factors |
Introduction: Kevlar Armor vs Ceramic Armor
Kevlar armor and ceramic armor are two leading materials used in personal protective equipment, each offering distinct advantages in ballistic resistance and weight. Kevlar, a synthetic aramid fiber, excels in flexibility and impact dispersion, making it ideal for lightweight body armor, while ceramic armor provides superior hardness and penetration resistance against rifle rounds. Comparing their molecular structures and performance metrics highlights Kevlar's durability under blunt force and ceramic's effectiveness in stopping high-velocity projectiles.
Composition and Material Science of Kevlar
Kevlar armor is composed of para-aramid synthetic fibers known for their exceptional tensile strength-to-weight ratio, making it highly effective in ballistic protection by absorbing and dispersing impact energy. The material's molecular structure consists of long, rigid poly-aramid chains aligned to form strong hydrogen bonds, resulting in high thermal stability and resistance to abrasion. In contrast to ceramic armor, which relies on hard, brittle materials like alumina or silicon carbide to shatter projectiles, Kevlar's flexible fiber weave provides lightweight, durable resistance against blunt force and multiple hits.
Composition and Material Science of Ceramic Armor
Ceramic armor primarily consists of hard, brittle materials such as alumina, silicon carbide, or boron carbide, which provide superior hardness and compressive strength to effectively shatter and erode incoming projectiles. The microstructure of ceramic armor features tightly bonded crystalline phases that help dissipate kinetic energy through cracking and fragmentation, contrasting with the fiber-reinforced aramid structure of Kevlar. While Kevlar relies on energy absorption through tensile strength, ceramic armor's material science emphasizes high hardness and fracture toughness to achieve enhanced ballistic resistance in multilayer composite systems.
Weight Comparison: Kevlar vs Ceramic Armor
Kevlar armor is significantly lighter than ceramic armor, providing enhanced mobility and reduced fatigue for wearers. While ceramic armor offers superior ballistic protection, its weight often exceeds that of Kevlar composites by up to 30-50%. The lightweight nature of Kevlar makes it ideal for applications requiring extended wear and agility without compromising basic ballistic resistance.
Ballistic Protection Levels
Kevlar armor offers high flexibility and superior resistance against lower velocity projectiles, commonly rated at NIJ Level IIIA, providing protection against handgun rounds and fragmentation. Ceramic armor typically achieves higher ballistic protection levels such as NIJ Level III and IV, effectively stopping rifle rounds and armor-piercing bullets due to its hardness and ability to shatter projectiles. Combining Kevlar with ceramic strike plates provides enhanced ballistic protection by leveraging Kevlar's energy absorption and ceramic's projectile fragmentation capabilities.
Durability and Longevity
Kevlar armor offers exceptional flexibility and impact resistance due to its aramid fiber composition, making it highly durable against blunt force trauma and repeated wear. Ceramic armor excels in hardness and ballistic protection but is more prone to cracking and degradation over time under extreme stress. Combining Kevlar with ceramic plates enhances longevity by balancing Kevlar's toughness with ceramic's resistance to penetration.
Flexibility and Comfort
Kevlar armor offers superior flexibility and comfort compared to ceramic armor due to its woven aramid fibers, which allow for better mobility and reduced bulk. Its lightweight nature ensures ease of wear during extended use, making it ideal for personnel requiring agility. Ceramic armor, while highly protective against high-velocity threats, tends to be rigid and heavier, limiting flexibility and comfort during prolonged wear.
Cost Analysis and Affordability
Kevlar armor generally offers a cost-effective solution for personal protection due to its lower material and manufacturing expenses compared to ceramic armor. Ceramic armor, while providing superior ballistic resistance against high-velocity projectiles, incurs higher costs because of expensive raw materials and complex fabrication processes. The affordability of Kevlar makes it a preferred choice in applications where budget constraints exist without compromising moderate-level protection.
Use Cases: Military, Law Enforcement, and Civilian
Kevlar armor offers superior flexibility and lighter weight, making it ideal for military personnel and law enforcement officers requiring mobility during extended operations. Ceramic armor provides enhanced ballistic protection against rifle rounds, suited for frontline combat and high-risk tactical scenarios. Civilians benefit from Kevlar armor for discreet everyday protection, while ceramic vests are preferred in situations demanding maximum stopping power.
Final Verdict: Choosing Between Kevlar and Ceramic Armor
Kevlar armor offers superior flexibility and lightweight protection against ballistic threats, making it ideal for mobility-focused applications. Ceramic armor provides enhanced resistance against high-velocity rounds and armor-piercing ammunition, excelling in durability but often at the cost of increased weight. The final verdict depends on mission requirements: Kevlar suits agile operations, while ceramic plates are preferable for maximum penetration defense.
Kevlar armor vs Ceramic armor Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com