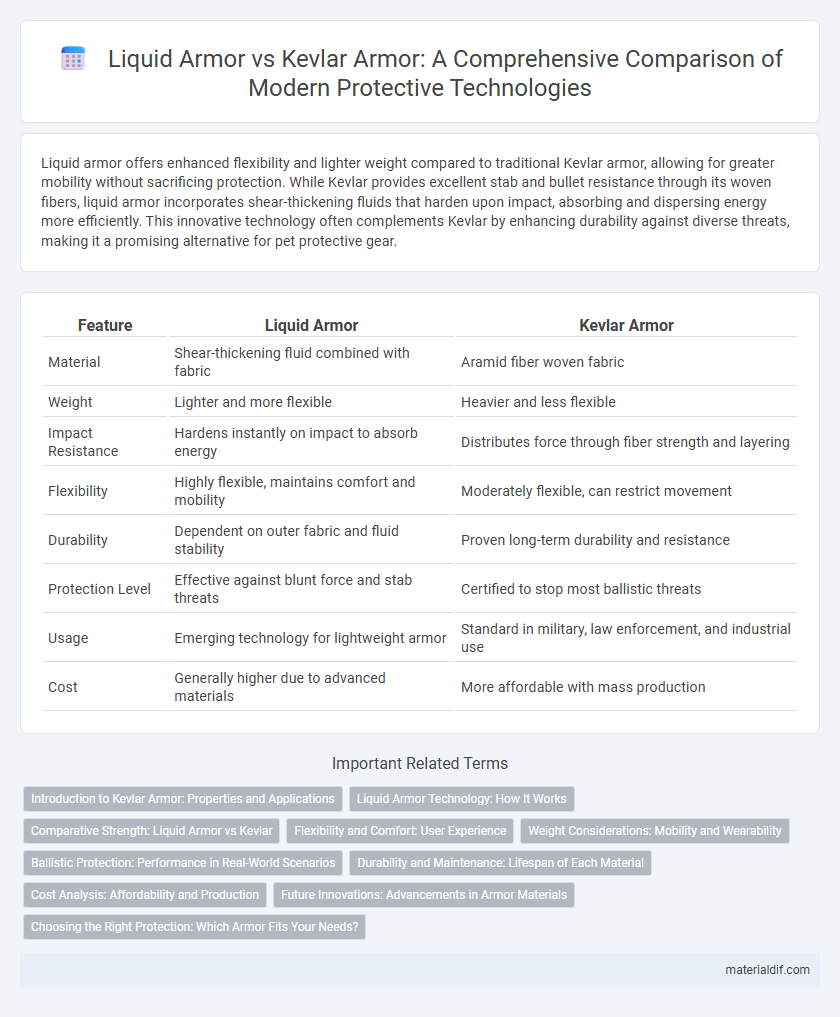
Liquid armor offers enhanced flexibility and lighter weight compared to traditional Kevlar armor, allowing for greater mobility without sacrificing protection. While Kevlar provides excellent stab and bullet resistance through its woven fibers, liquid armor incorporates shear-thickening fluids that harden upon impact, absorbing and dispersing energy more efficiently. This innovative technology often complements Kevlar by enhancing durability against diverse threats, making it a promising alternative for pet protective gear.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Liquid Armor | Kevlar Armor |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Shear-thickening fluid combined with fabric | Aramid fiber woven fabric |
| Weight | Lighter and more flexible | Heavier and less flexible |
| Impact Resistance | Hardens instantly on impact to absorb energy | Distributes force through fiber strength and layering |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, maintains comfort and mobility | Moderately flexible, can restrict movement |
| Durability | Dependent on outer fabric and fluid stability | Proven long-term durability and resistance |
| Protection Level | Effective against blunt force and stab threats | Certified to stop most ballistic threats |
| Usage | Emerging technology for lightweight armor | Standard in military, law enforcement, and industrial use |
| Cost | Generally higher due to advanced materials | More affordable with mass production |
Introduction to Kevlar Armor: Properties and Applications
Kevlar armor, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont, features exceptional tensile strength and lightweight properties, making it ideal for personal protective equipment. Its molecular structure allows it to absorb and disperse impact energy, providing reliable ballistic resistance in body armor and helmets. Kevlar's applications extend across military, law enforcement, and industrial safety, showcasing versatility in protection against bullets, shrapnel, and stab threats.
Liquid Armor Technology: How It Works
Liquid armor technology enhances traditional Kevlar armor by integrating shear-thickening fluids (STFs), which instantly harden upon impact to disperse energy more effectively. This fluid-embedded material remains flexible during normal movement, providing superior mobility while offering increased protection against ballistic threats. The STF's rapid viscosity change absorbs and redistributes force, reducing penetration and trauma compared to conventional Kevlar layers.
Comparative Strength: Liquid Armor vs Kevlar
Liquid armor utilizes shear-thickening fluids that harden upon impact, providing enhanced flexibility and shock absorption compared to traditional Kevlar fibers. Kevlar armor offers high tensile strength and resistance to penetration but can be rigid and less adaptive under dynamic stress. Recent studies show liquid armor can improve blunt force trauma protection while maintaining comparable ballistic performance to Kevlar, making it a promising material for future personal protective equipment.
Flexibility and Comfort: User Experience
Liquid armor offers superior flexibility compared to traditional Kevlar armor by adapting to body movements without sacrificing protection, enhancing wearer comfort during extended use. Kevlar armor tends to be stiffer and bulkier, which can restrict mobility and cause discomfort during dynamic activities or long wear times. Users report that liquid armor's lightweight, flexible properties significantly improve comfort and reduce fatigue, making it a preferred choice in scenarios requiring agility.
Weight Considerations: Mobility and Wearability
Liquid armor offers significant weight reduction compared to traditional Kevlar, enhancing mobility for users in combat or law enforcement scenarios. Its lightweight properties improve wearability, allowing for extended use without fatigue or restriction. Kevlar, while durable and effective, tends to be heavier, potentially limiting agility and comfort during prolonged wear.
Ballistic Protection: Performance in Real-World Scenarios
Liquid armor enhances ballistic protection by integrating shear-thickening fluids that harden upon impact, providing superior resistance to blunt trauma compared to traditional Kevlar armor. Kevlar remains highly effective against penetration due to its tightly woven fibers that absorb and disperse kinetic energy, but liquid armor offers improved flexibility and reduced weight, increasing wearer mobility. Real-world tests indicate that combining liquid armor with Kevlar layers results in enhanced multi-hit performance and reduced trauma, making it a promising advancement in personal ballistic protection.
Durability and Maintenance: Lifespan of Each Material
Liquid armor demonstrates enhanced durability by dispersing impact forces and self-healing minor damages, leading to a longer effective lifespan compared to traditional Kevlar armor. Kevlar, while inherently strong, suffers from fiber degradation over time due to UV exposure and moisture, requiring more frequent maintenance and replacement. Maintenance for liquid armor is generally lower, as its adaptive nature minimizes wear, preserving protective performance and extending service intervals in harsh environments.
Cost Analysis: Affordability and Production
Liquid armor presents a potentially cost-effective alternative to traditional Kevlar armor due to lower raw material expenses and simplified manufacturing processes, reducing overall production costs. Kevlar production involves complex chemical processes and energy-intensive steps, driving higher final product prices. Economies of scale in existing Kevlar manufacturing may currently offset some costs, but advancements in liquid armor technology aim to achieve greater affordability and mass production efficiency in future defense applications.
Future Innovations: Advancements in Armor Materials
Future innovations in armor materials focus on enhancing the flexibility and impact resistance of Kevlar by incorporating shear-thickening fluids found in liquid armor technology. Researchers are developing hybrid composites that combine Kevlar's high tensile strength with the adaptive viscosity properties of liquid armor, resulting in lightweight, durable protection against ballistic and stab threats. Advances in nanotechnology and polymer chemistry are paving the way for smart armor systems that dynamically respond to varying threat levels, offering superior protection and mobility for military and law enforcement personnel.
Choosing the Right Protection: Which Armor Fits Your Needs?
Liquid armor incorporates shear-thickening fluids that harden upon impact, offering superior flexibility and lightweight protection compared to traditional Kevlar armor. Kevlar armor, known for its high tensile strength and proven ballistic resistance, excels in stopping projectiles but can be bulkier and less flexible. Selecting the right protection depends on specific use cases, where liquid armor suits dynamic environments requiring mobility, while Kevlar remains reliable for maximum stopping power in high-threat scenarios.
Liquid armor vs Kevlar armor Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com