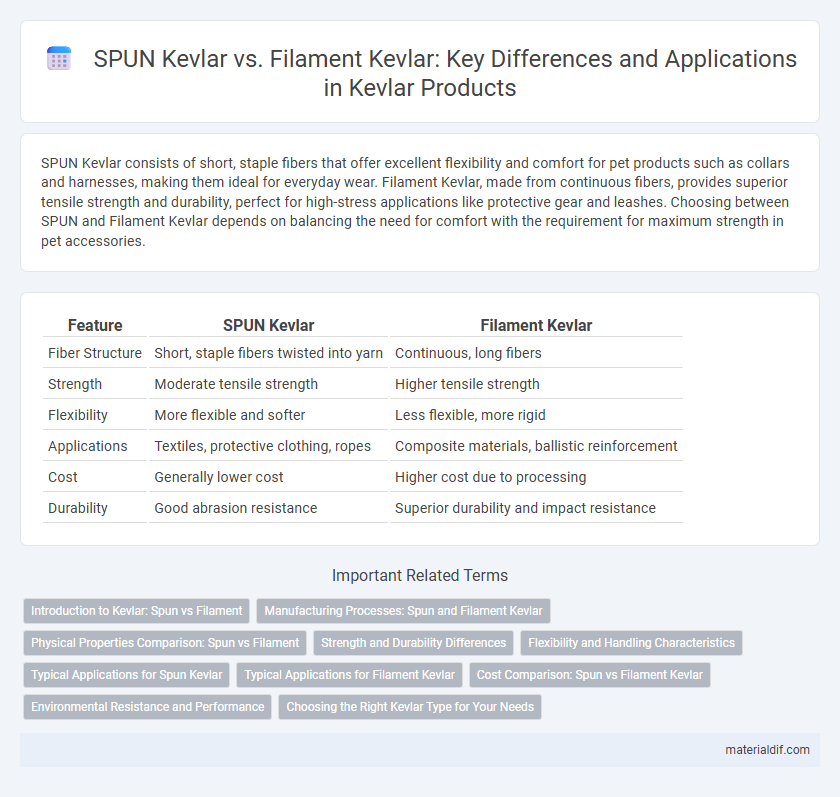
SPUN Kevlar consists of short, staple fibers that offer excellent flexibility and comfort for pet products such as collars and harnesses, making them ideal for everyday wear. Filament Kevlar, made from continuous fibers, provides superior tensile strength and durability, perfect for high-stress applications like protective gear and leashes. Choosing between SPUN and Filament Kevlar depends on balancing the need for comfort with the requirement for maximum strength in pet accessories.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | SPUN Kevlar | Filament Kevlar |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Structure | Short, staple fibers twisted into yarn | Continuous, long fibers |
| Strength | Moderate tensile strength | Higher tensile strength |
| Flexibility | More flexible and softer | Less flexible, more rigid |
| Applications | Textiles, protective clothing, ropes | Composite materials, ballistic reinforcement |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Superior durability and impact resistance |
Introduction to Kevlar: Spun vs Filament
Kevlar is a high-strength synthetic fiber widely used for its exceptional durability and resistance to impact. Spun Kevlar consists of staple fibers twisted into yarns, offering enhanced flexibility and comfort in textile applications. Filament Kevlar features continuous long fibers providing superior tensile strength and abrasion resistance, making it ideal for ballistic protection and industrial uses.
Manufacturing Processes: Spun and Filament Kevlar
Spun Kevlar is produced by twisting short Kevlar fibers together, resulting in a yarn that offers flexibility and ease of weaving, ideal for textile applications. Filament Kevlar, on the other hand, is made from continuous, long fibers extruded directly from the polymer solution, providing higher tensile strength and superior durability for industrial and ballistic uses. The manufacturing process of spun Kevlar emphasizes fiber alignment and twist control for softness, while filament Kevlar's process focuses on fiber continuity and molecular orientation to maximize strength.
Physical Properties Comparison: Spun vs Filament
Spun Kevlar fibers exhibit enhanced flexibility and higher abrasion resistance due to their staple fiber construction, making them ideal for textile applications requiring comfort and durability. Filament Kevlar fibers offer superior tensile strength and dimensional stability, attributed to their continuous filament structure, which is crucial in ballistic and composite materials. Both forms maintain excellent chemical resistance and thermal stability, but filament Kevlar's uniformity provides greater strength-to-weight ratio compared to spun Kevlar.
Strength and Durability Differences
Spun Kevlar consists of short fibers twisted into yarn, offering flexibility but lower tensile strength compared to filament Kevlar, which uses continuous fibers for superior strength and durability. Filament Kevlar exhibits enhanced resistance to abrasion and impact, making it ideal for high-performance ballistic and protective gear. The continuous fiber structure of filament Kevlar results in higher load-bearing capacity and longer service life under stress conditions.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Spun Kevlar fibers exhibit enhanced flexibility due to their short, staple form which allows for easier bending and smoother handling in textile applications. Filament Kevlar, composed of continuous long fibers, offers superior tensile strength but tends to be stiffer and less pliable, making it ideal for high-strength composite materials. The choice between spun and filament forms impacts product performance, with spun Kevlar favored in flexible fabrics and filament Kevlar preferred in rigid protective gear and technical components.
Typical Applications for Spun Kevlar
Spun Kevlar is commonly used in applications requiring flexibility and comfort, such as body armor liners, thermal and cut-resistant gloves, and protective clothing. Its shorter fiber length allows for enhanced fabric hand and drapability, making it ideal for garments and upholstery. Typical industries utilizing spun Kevlar include personal protection, automotive, and industrial safety gear.
Typical Applications for Filament Kevlar
Filament Kevlar is predominantly used in ballistic protection, including bulletproof vests and helmets, due to its high tensile strength and durability. Its continuous fiber structure enhances impact resistance, making it ideal for aerospace components and high-performance ropes. Industrial applications such as composite reinforcement and sporting goods also benefit from Filament Kevlar's superior mechanical properties.
Cost Comparison: Spun vs Filament Kevlar
Spun Kevlar is generally more cost-effective than filament Kevlar due to its simpler manufacturing process and lower-quality fiber production, making it suitable for applications where budget constraints are critical. Filament Kevlar, with its continuous fiber formation, offers superior strength and durability but comes with a higher price point reflecting its advanced performance characteristics. Choosing between spun and filament Kevlar depends on balancing cost against application-specific demands for tensile strength and abrasion resistance.
Environmental Resistance and Performance
Filament Kevlar offers superior environmental resistance compared to Spun Kevlar, exhibiting enhanced durability against UV exposure, moisture, and chemical degradation. Its continuous fiber structure contributes to higher tensile strength and consistent performance under harsh conditions. Spun Kevlar, while providing good abrasion resistance, tends to absorb more moisture, which can reduce its mechanical properties in wet or corrosive environments.
Choosing the Right Kevlar Type for Your Needs
Spun Kevlar consists of short fibers twisted into yarns, offering greater flexibility and comfort for textiles and protective clothing, whereas filament Kevlar is made from continuous fibers providing higher tensile strength and durability suited for industrial and ballistic applications. Selecting the right Kevlar type depends on specific performance requirements such as flexibility, abrasion resistance, and impact protection. For lightweight garments or soft body armor, spun Kevlar is ideal; filament Kevlar is preferred for heavy-duty gear and reinforcement materials demanding maximum strength.
SPUN Kevlar vs Filament Kevlar Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com