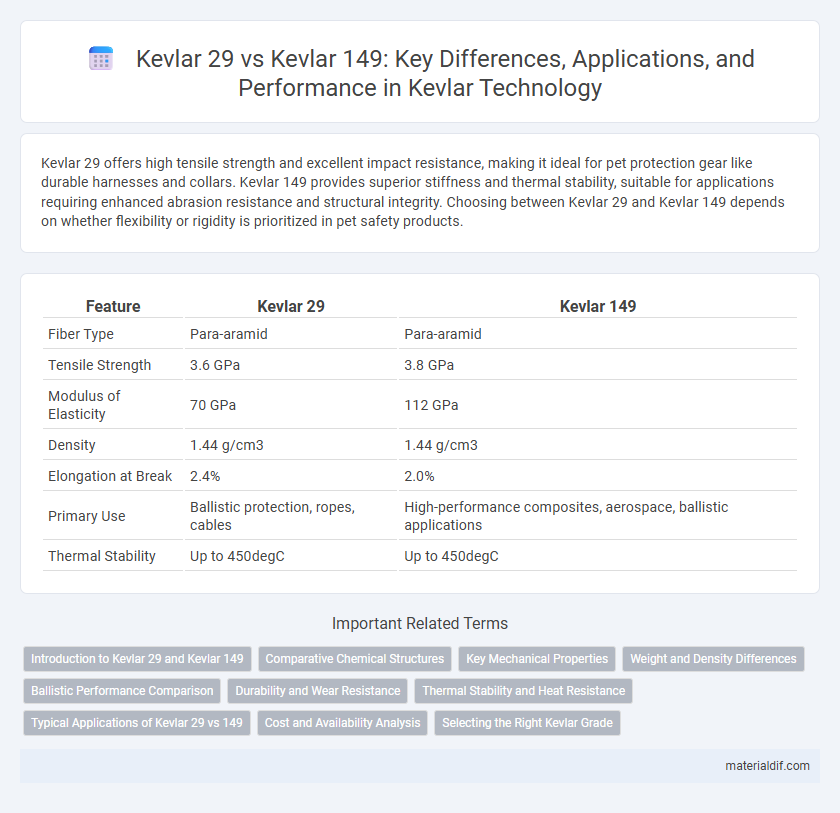
Kevlar 29 offers high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it ideal for pet protection gear like durable harnesses and collars. Kevlar 149 provides superior stiffness and thermal stability, suitable for applications requiring enhanced abrasion resistance and structural integrity. Choosing between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 149 depends on whether flexibility or rigidity is prioritized in pet safety products.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kevlar 29 | Kevlar 149 |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Type | Para-aramid | Para-aramid |
| Tensile Strength | 3.6 GPa | 3.8 GPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 70 GPa | 112 GPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Elongation at Break | 2.4% | 2.0% |
| Primary Use | Ballistic protection, ropes, cables | High-performance composites, aerospace, ballistic applications |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 450degC | Up to 450degC |
Introduction to Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 149
Kevlar 29 is a para-aramid synthetic fiber known for its high tensile strength and impact resistance, commonly used in ballistic and body armor applications. Kevlar 149 offers enhanced tensile modulus and improved dimensional stability, making it suitable for advanced composites and high-performance materials. Both Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 149 are integral to industries requiring lightweight, durable, and heat-resistant fibers.
Comparative Chemical Structures
Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 149 differ primarily in their chemical structures, with Kevlar 29 composed of poly(paraphenylene terephthalamide) providing balanced tensile strength and pliability ideal for body armor and ropes. Kevlar 149 features a more rigid polymer chain due to higher crystallinity and extended molecular alignment, offering superior tensile strength and thermal resistance suited for aerospace and ballistic applications. The variation in amide linkages and aromatic ring orientation between the two variants influences their mechanical properties and chemical resistance, optimizing each for specific industrial uses.
Key Mechanical Properties
Kevlar 29 offers superior tensile strength with an average of 3,620 MPa and a modulus of elasticity around 83 GPa, making it ideal for ballistic protection applications. Kevlar 149, however, provides a higher modulus of elasticity approximately 112 GPa, delivering enhanced stiffness and resistance to deformation under stress. Both fibers exhibit comparable density near 1.44 g/cm3, but Kevlar 149's increased rigidity makes it more suitable for composite reinforcement where structural integrity is critical.
Weight and Density Differences
Kevlar 29 has a density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3, making it lighter compared to Kevlar 149, which has a density around 1.50 g/cm3. The lower density of Kevlar 29 results in a lighter weight fiber ideal for applications requiring reduced mass without compromising strength. Kevlar 149's slightly higher density contributes to enhanced toughness and abrasion resistance, suited for heavy-duty uses despite the increased weight.
Ballistic Performance Comparison
Kevlar 29 offers superior ballistic resistance with high tensile strength and energy absorption, optimized for bulletproof vests and rigid ballistic armor applications. Kevlar 149, while also strong, is characterized by increased modulus and creep resistance, contributing to improved shape retention under stress but slightly lower ballistic energy dispersion. The enhanced performance of Kevlar 29 in ballistic impact scenarios makes it the preferred choice for high-stakes protective gear where maximum threat protection is critical.
Durability and Wear Resistance
Kevlar 29 is engineered for high tensile strength and excellent durability, making it suitable for ballistic and protective applications with superior impact resistance. Kevlar 149 offers enhanced wear resistance and greater flexibility, ideal for industrial uses requiring abrasion resistance and extended material lifespan. Both variants provide exceptional durability, but Kevlar 149 excels in environments with continuous friction and mechanical stress.
Thermal Stability and Heat Resistance
Kevlar 29 offers moderate thermal stability with a decomposition temperature around 500degC, making it suitable for general protective applications. Kevlar 149, designed for advanced performance, exhibits enhanced heat resistance and higher thermal endurance due to its superior polymer structure. This increased thermal stability enables Kevlar 149 to maintain strength and integrity under more extreme heat conditions compared to Kevlar 29.
Typical Applications of Kevlar 29 vs 149
Kevlar 29 is commonly used in ballistic vests, helmets, and general industrial applications due to its balanced tensile strength and flexibility. Kevlar 149, with higher tensile modulus and stiffness, is favored in aerospace components, ropes, and composite reinforcements where superior structural performance is critical. The choice between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 149 depends on the specific application requirements for strength, durability, and weight.
Cost and Availability Analysis
Kevlar 29 is more widely available and cost-effective, making it the preferred choice for mass-market applications such as ballistic vests and ropes due to its lower production expenses. Kevlar 149, designed for higher tensile strength and modulus, comes at a significantly higher cost and limited availability, restricting its use to specialized industries like aerospace and advanced composites. Manufacturers often balance performance needs against budget constraints, with Kevlar 29 dominating sectors where cost-efficiency and supply reliability are critical.
Selecting the Right Kevlar Grade
Kevlar 29 offers superior tensile strength and flexibility, making it ideal for ballistic protection and body armor applications, while Kevlar 149 provides enhanced modulus and dimensional stability, suitable for composite materials and aerospace components. Selecting the right Kevlar grade depends on balancing performance requirements such as impact resistance and structural rigidity against application-specific demands. Understanding the mechanical properties and environmental resistance of Kevlar 29 versus Kevlar 149 ensures optimal material performance and longevity in critical uses.
Kevlar 29 vs Kevlar 149 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com