Kevlar reinforcement offers superior impact resistance and flexibility compared to glass fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for applications requiring durability under stress. Unlike glass fiber, Kevlar provides enhanced tensile strength while maintaining lightweight properties, which improves overall performance. Its exceptional energy absorption capabilities also contribute to increased safety and longevity in pet products.
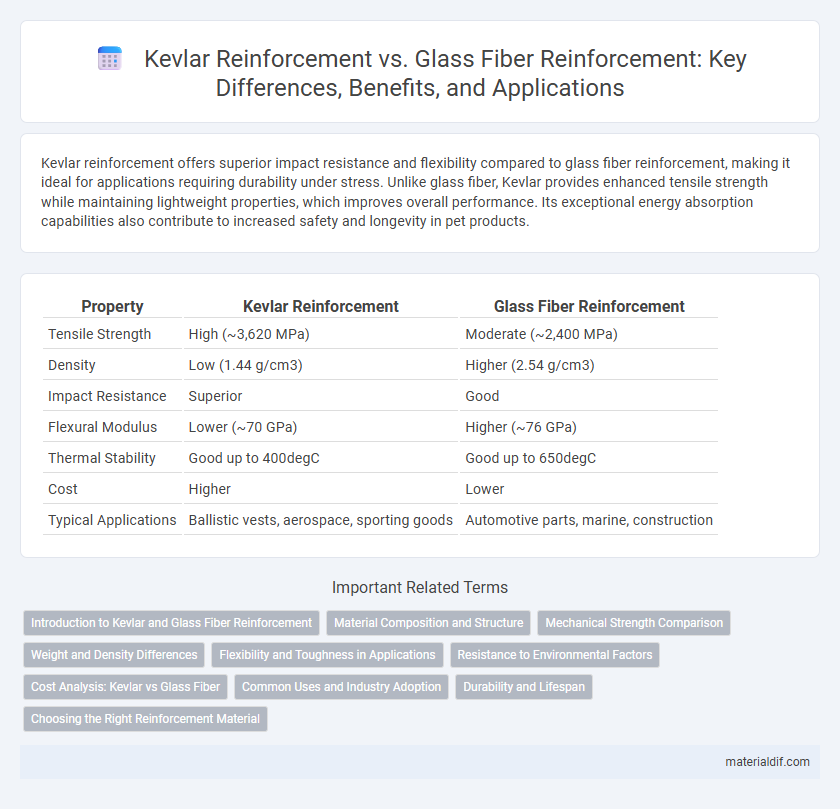
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kevlar Reinforcement | Glass Fiber Reinforcement |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (~3,620 MPa) | Moderate (~2,400 MPa) |
| Density | Low (1.44 g/cm3) | Higher (2.54 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Superior | Good |
| Flexural Modulus | Lower (~70 GPa) | Higher (~76 GPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Good up to 400degC | Good up to 650degC |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | Ballistic vests, aerospace, sporting goods | Automotive parts, marine, construction |
Introduction to Kevlar and Glass Fiber Reinforcement
Kevlar reinforcement offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for aerospace and ballistic applications. Glass fiber reinforcement provides excellent stiffness and affordability, commonly used in automotive and construction materials. Both materials serve critical roles in composite fabrication, with Kevlar favored for its lightweight durability and glass fiber chosen for cost-effective structural support.
Material Composition and Structure
Kevlar reinforcement consists of aromatic polyamide fibers with a highly crystalline structure, providing exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance. Glass fiber reinforcement is made from silica-based fibers with an amorphous structure, offering good stiffness but lower tensile strength compared to Kevlar. The molecular alignment in Kevlar results in superior energy absorption and durability, while glass fibers excel in compressive strength and cost-effectiveness.
Mechanical Strength Comparison
Kevlar reinforcement exhibits significantly higher tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for applications requiring superior durability and toughness. Kevlar fibers provide excellent energy absorption and fatigue resistance, resulting in enhanced mechanical performance under repeated stress. Glass fiber, while offering good compressive strength and stiffness, typically falls short of Kevlar's strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to crack propagation.
Weight and Density Differences
Kevlar reinforcement offers a significant advantage in weight reduction compared to glass fiber reinforcement due to its lower density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3 versus glass fiber's density around 2.5 g/cm3. This density difference results in Kevlar composites being lighter while maintaining high tensile strength and impact resistance, making them ideal for applications demanding weight efficiency. The reduced weight contributes to improved performance in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods, where minimizing mass without compromising durability is critical.
Flexibility and Toughness in Applications
Kevlar reinforcement offers superior flexibility compared to glass fiber reinforcement, making it ideal for applications requiring dynamic bending and impact resistance. Kevlar's toughness excels in absorbing energy and resisting damage under high stress, outperforming glass fibers in scenarios demanding durability and resilience. These properties make Kevlar the preferred choice in protective gear, flexible composites, and high-performance sporting equipment.
Resistance to Environmental Factors
Kevlar reinforcement exhibits superior resistance to environmental factors compared to glass fiber reinforcement, particularly in moisture absorption and chemical exposure. Kevlar fibers maintain structural integrity and mechanical properties in humid or corrosive conditions, whereas glass fibers tend to degrade or weaken due to hydrolysis and alkali attack. This makes Kevlar a preferred choice for applications requiring durability and long-term performance in harsh environments.
Cost Analysis: Kevlar vs Glass Fiber
Kevlar reinforcement typically involves higher initial material costs compared to glass fiber due to its superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability. Despite the upfront expense, Kevlar often reduces long-term costs by providing better impact resistance and longer service life, minimizing maintenance and replacement expenses. Glass fiber remains a cost-effective choice for applications with budget constraints but offers lower performance under high-stress or impact conditions.
Common Uses and Industry Adoption
Kevlar reinforcement outperforms glass fiber reinforcement in applications requiring high tensile strength and impact resistance, such as aerospace components, ballistic protection, and sporting goods. Industries favor Kevlar for its superior energy absorption and lightweight properties, leading to widespread adoption in military, automotive, and aerospace sectors. Glass fiber reinforcement remains popular in construction and marine industries due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, despite lower mechanical strength compared to Kevlar.
Durability and Lifespan
Kevlar reinforcement offers superior durability and lifespan compared to glass fiber reinforcement due to its exceptional resistance to impact, fatigue, and environmental degradation. Kevlar's high tensile strength and elasticity enable it to maintain structural integrity under repeated stress, extending the lifespan of composite materials in demanding applications. Glass fiber, while cost-effective, is more prone to micro-cracking and moisture absorption, which can reduce durability and accelerate material failure over time.
Choosing the Right Reinforcement Material
Kevlar reinforcement offers superior tensile strength and impact resistance compared to glass fiber, making it ideal for applications requiring high durability and lightweight performance. Glass fiber reinforcement provides cost-effective solutions with good stiffness and chemical resistance but generally exhibits lower fatigue endurance than Kevlar. Selecting the right reinforcement material depends on balancing mechanical properties, weight constraints, and budget to meet specific engineering demands.
Kevlar reinforcement vs Glass fiber reinforcement Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com