Kevlar 29 offers high tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for pet accessories requiring durability and flexibility. Kevlar 49 provides greater stiffness and higher modulus, suitable for applications demanding enhanced structural integrity. Choosing between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49 depends on the balance needed between flexibility and rigidity in pet products.
Table of Comparison
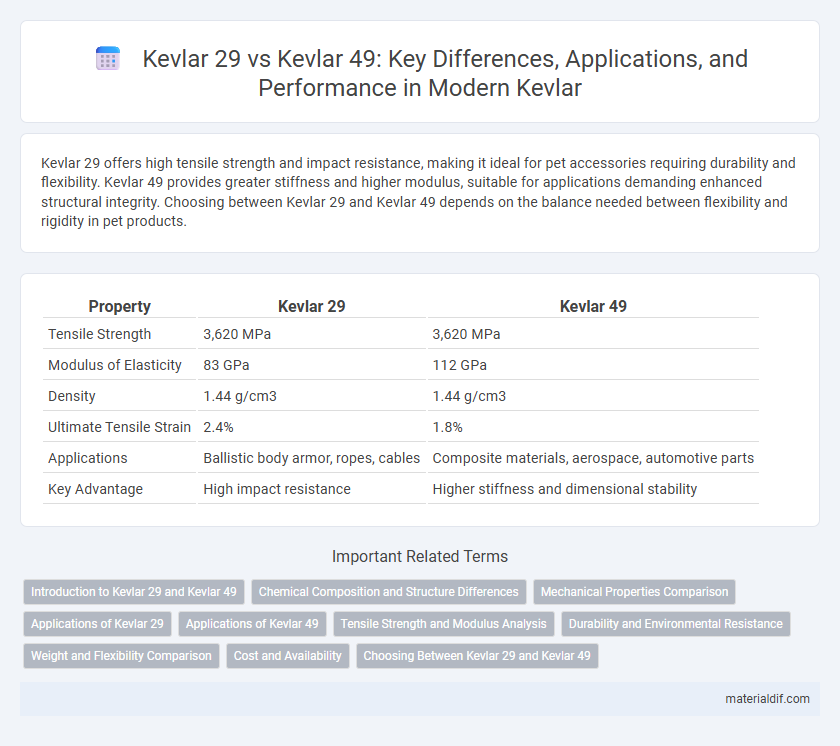
| Property | Kevlar 29 | Kevlar 49 |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | 3,620 MPa | 3,620 MPa |
| Modulus of Elasticity | 83 GPa | 112 GPa |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 1.44 g/cm3 |
| Ultimate Tensile Strain | 2.4% | 1.8% |
| Applications | Ballistic body armor, ropes, cables | Composite materials, aerospace, automotive parts |
| Key Advantage | High impact resistance | Higher stiffness and dimensional stability |
Introduction to Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49
Kevlar 29 is a para-aramid synthetic fiber primarily used in ballistic and personal armor applications due to its high tensile strength and impact resistance. Kevlar 49 offers enhanced mechanical properties including higher modulus and improved stiffness, making it ideal for aerospace and composite reinforcement. Both fibers provide exceptional durability, with Kevlar 49 optimized for structural uses while Kevlar 29 excels in protective gear.
Chemical Composition and Structure Differences
Kevlar 29 is composed primarily of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide with a lower molecular weight and a less rigid molecular structure, resulting in moderate tensile strength and flexibility. Kevlar 49, by contrast, features a higher molecular weight and a more rigid, crystalline structure due to its extended planar polymer chains, enhancing its tensile modulus and thermal stability. The chemical composition differences influence the distinct mechanical properties, with Kevlar 49 favored in high-performance composite applications due to its superior stiffness and strength.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Kevlar 29 exhibits high tensile strength and excellent impact resistance, making it ideal for ballistic and protective applications. Kevlar 49 offers superior stiffness and tensile modulus, enhancing structural efficiency in composites and aerospace engineering. The mechanical property differences between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49 influence their selection based on flexibility versus rigidity requirements in advanced material design.
Applications of Kevlar 29
Kevlar 29 is primarily used in ballistic and ballistic-resistant applications such as body armor, helmets, and vehicle armor due to its excellent impact resistance and tensile strength. It is also widely employed in ropes, cables, and protective gloves where flexibility and durability under stress are critical. Kevlar 29's toughness and energy-absorbing capacity make it ideal for personal protective equipment in law enforcement and military sectors.
Applications of Kevlar 49
Kevlar 49 is primarily utilized in aerospace, military armor, and high-performance composites due to its superior tensile strength and modulus compared to Kevlar 29. Its enhanced rigidity and resistance to heat make it ideal for ballistic helmets, structural panels, and reinforced aircraft components. Kevlar 49's applications extend to sporting goods and automotive parts where stiffness and lightweight characteristics are critical.
Tensile Strength and Modulus Analysis
Kevlar 29 exhibits a tensile strength of approximately 3,620 MPa with a tensile modulus around 70 GPa, making it suitable for ballistic protection and light composite applications. Kevlar 49 offers a higher tensile modulus of about 112 GPa and a tensile strength near 3,760 MPa, which enhances stiffness and dimensional stability for aerospace and high-performance composite structures. This difference in mechanical properties positions Kevlar 49 as the preferred choice for applications requiring higher rigidity, while Kevlar 29 remains ideal for impact-resistant uses.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Kevlar 29 offers exceptional durability with high tensile strength, making it ideal for ballistic and protective applications, but it has moderate environmental resistance, particularly against moisture and UV exposure. Kevlar 49 provides superior environmental resistance, including enhanced moisture and chemical stability, while maintaining robust mechanical properties suitable for aerospace and structural composites. The choice between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49 hinges on the balance required between mechanical durability and exposure to harsh environmental conditions.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Kevlar 29 is lighter and offers greater flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring agility and comfort. Kevlar 49, while slightly heavier, provides enhanced stiffness and higher tensile strength for structural use. The weight difference between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49 directly impacts their flexibility, with Kevlar 29 being preferred for lightweight protective gear and Kevlar 49 favored in composite reinforcement.
Cost and Availability
Kevlar 29 is generally more affordable and widely available compared to Kevlar 49, making it a popular choice for applications requiring strong, lightweight materials at a lower cost. Kevlar 49, while offering higher tensile strength and modulus, typically commands a premium price and may have more limited availability due to specialized manufacturing. Manufacturers often select Kevlar 29 for cost-sensitive projects, while Kevlar 49 is reserved for high-performance needs despite its higher expense.
Choosing Between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49
Kevlar 29 offers exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making it ideal for ballistic protection and body armor applications, while Kevlar 49 provides higher modulus and greater stiffness suited for aerospace and industrial composite materials. Selecting between Kevlar 29 and Kevlar 49 depends primarily on application requirements--Kevlar 29 excels in flexibility and energy absorption, whereas Kevlar 49 delivers superior dimensional stability and structural reinforcement. Understanding the balance between mechanical properties and performance needs ensures optimal utilization of these specialized aramid fibers.
Kevlar 29 vs Kevlar 49 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com