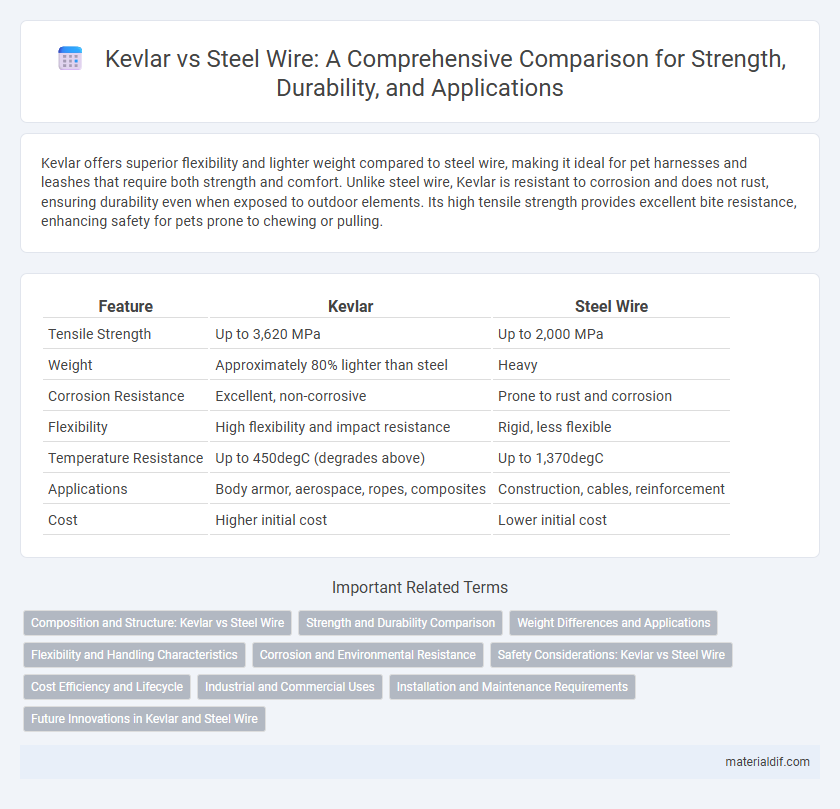
Kevlar offers superior flexibility and lighter weight compared to steel wire, making it ideal for pet harnesses and leashes that require both strength and comfort. Unlike steel wire, Kevlar is resistant to corrosion and does not rust, ensuring durability even when exposed to outdoor elements. Its high tensile strength provides excellent bite resistance, enhancing safety for pets prone to chewing or pulling.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Kevlar | Steel Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3,620 MPa | Up to 2,000 MPa |
| Weight | Approximately 80% lighter than steel | Heavy |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, non-corrosive | Prone to rust and corrosion |
| Flexibility | High flexibility and impact resistance | Rigid, less flexible |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 450degC (degrades above) | Up to 1,370degC |
| Applications | Body armor, aerospace, ropes, composites | Construction, cables, reinforcement |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
Composition and Structure: Kevlar vs Steel Wire
Kevlar is a synthetic aramid fiber composed of long chains of poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide, exhibiting a molecular structure characterized by high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional tensile strength. Steel wire consists primarily of iron and carbon alloys with a crystalline lattice structure that provides rigidity and durability but at a significantly higher density. The polymeric molecular chains in Kevlar align parallel to each other, creating strong hydrogen bonds that contribute to its flexibility and impact resistance, whereas steel wire's metallic bonding results in superior hardness and load-bearing capacity under compression.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Kevlar exhibits a tensile strength of approximately 3,620 MPa, surpassing steel wire's typical range of 1,200 to 2,000 MPa, making it significantly stronger for weight-sensitive applications. Its exceptional durability stems from high resistance to fatigue, corrosion, and heat up to 450degC, whereas steel wire is prone to rust and weakening under prolonged environmental exposure. Kevlar's lightweight composite nature allows it to maintain strength without compromising flexibility, outperforming steel wire in long-term structural integrity and impact resistance.
Weight Differences and Applications
Kevlar exhibits a significantly lower density compared to steel wire, weighing approximately one-fifth as much while maintaining comparable tensile strength. This weight advantage makes Kevlar ideal for applications requiring lightweight yet strong materials, such as aerospace components, personal body armor, and high-performance sporting goods. Steel wire remains preferred in construction and heavy-duty applications where its higher rigidity and cost-effectiveness are critical despite its greater weight.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Kevlar exhibits superior flexibility compared to steel wire, allowing for easier bending and shaping without compromising strength. This high tensile fiber adapts better to dynamic loads and repetitive motion, enhancing its handling characteristics in applications such as protective gear and flexible cables. Steel wire, although stronger in absolute terms, is stiffer and more prone to fatigue under continuous bending, making Kevlar a preferred choice where lightweight flexibility is crucial.
Corrosion and Environmental Resistance
Kevlar exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to steel wire due to its synthetic polymer composition, which is inherently impervious to rust and chemical degradation. Unlike steel wire, Kevlar maintains structural integrity in harsh environmental conditions, including exposure to moisture, saltwater, and chemicals, making it ideal for marine, automotive, and aerospace applications. This enhanced environmental resistance results in longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in corrosive settings.
Safety Considerations: Kevlar vs Steel Wire
Kevlar offers superior safety compared to steel wire due to its high tensile strength combined with lightweight flexibility, reducing the risk of injury from wire snapping or recoil. Unlike steel wire, Kevlar is non-conductive and corrosion-resistant, minimizing electrical hazards and degradation-related failures in critical applications. These properties make Kevlar a safer alternative in environments where mechanical stress and exposure to elements pose significant risks.
Cost Efficiency and Lifecycle
Kevlar offers superior cost efficiency compared to steel wire due to its lighter weight and reduced handling expenses, which lower transportation and installation costs. Its extended lifecycle results from excellent corrosion resistance and fatigue durability, minimizing maintenance and replacement frequency. Steel wire, while strong, often incurs higher overall lifecycle costs due to susceptibility to rust and shorter service life.
Industrial and Commercial Uses
Kevlar offers superior strength-to-weight ratio compared to steel wire, making it ideal for industrial applications such as protective gear, conveyor belts, and ropes that require lightweight durability. Its resistance to corrosion and fatigue enhances performance in commercial uses like automotive belts and suspension cables, where steel wire's susceptibility to rust limits longevity. The adaptability of Kevlar in industries demanding high tensile strength and flexibility surpasses steel wire, reducing maintenance costs and improving safety standards.
Installation and Maintenance Requirements
Kevlar requires less installation effort than steel wire due to its lightweight and flexible nature, enabling easier handling and faster setup. Unlike steel wire, Kevlar does not rust or corrode, significantly reducing long-term maintenance needs and costs. Steel wire demands regular inspection and potential replacement due to corrosion and fatigue, whereas Kevlar maintains durability with minimal upkeep in harsh environments.
Future Innovations in Kevlar and Steel Wire
Future innovations in Kevlar focus on enhancing its tensile strength and heat resistance through nanotechnology and advanced polymer blending, aiming to outperform steel wire in lightweight ballistic protection and flexible structural applications. Research into steel wire emphasizes improving corrosion resistance and fatigue durability using novel alloy compositions and surface treatments, targeting infrastructure and automotive sectors. Emerging hybrid composites combining Kevlar fibers with steel wire seek to leverage the strengths of both materials for next-generation aerospace and defense solutions.
Kevlar vs Steel Wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com