Kevlar weaving incorporates the high-strength synthetic fibers of Kevlar, providing superior durability and resistance to wear compared to plain weaving techniques. While plain weaving uses a simple over-and-under pattern that offers basic strength and flexibility, Kevlar weaving enhances tear resistance and impact protection, making it ideal for pet products requiring robust performance. This advanced weaving method ensures extended product lifespan and safety for pets in demanding environments.
Table of Comparison
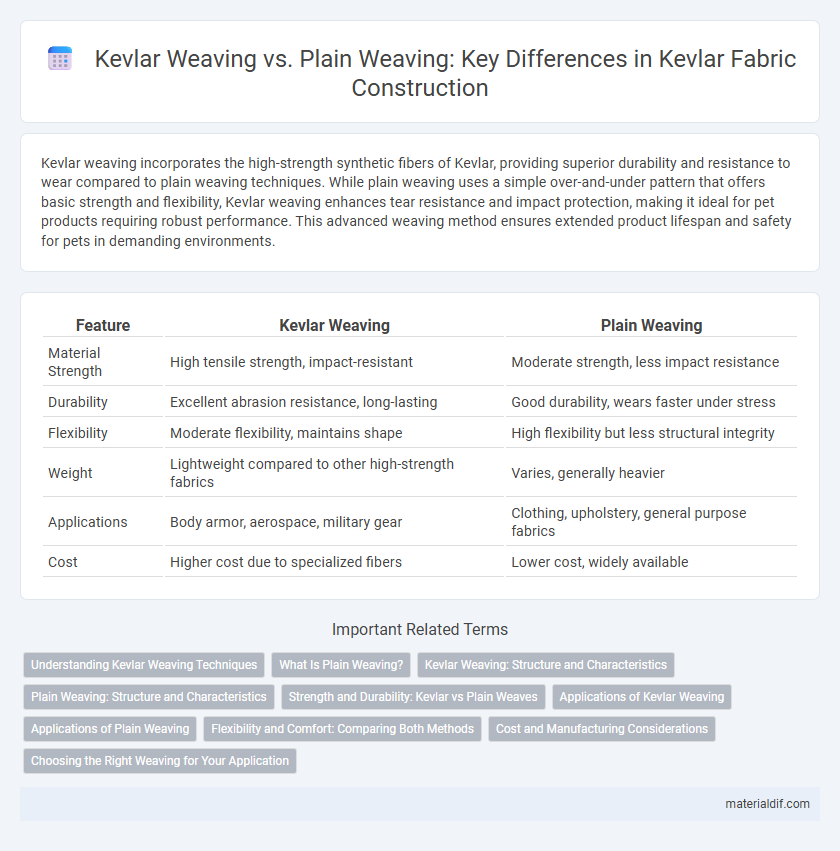
| Feature | Kevlar Weaving | Plain Weaving |
|---|---|---|
| Material Strength | High tensile strength, impact-resistant | Moderate strength, less impact resistance |
| Durability | Excellent abrasion resistance, long-lasting | Good durability, wears faster under stress |
| Flexibility | Moderate flexibility, maintains shape | High flexibility but less structural integrity |
| Weight | Lightweight compared to other high-strength fabrics | Varies, generally heavier |
| Applications | Body armor, aerospace, military gear | Clothing, upholstery, general purpose fabrics |
| Cost | Higher cost due to specialized fibers | Lower cost, widely available |
Understanding Kevlar Weaving Techniques
Kevlar weaving techniques involve interlacing aramid fibers in specific patterns to maximize strength and durability, outperforming plain weaving by enhancing impact resistance and flexibility. Kevlar's unique fiber structure, when woven using techniques like twill or satin weaves, improves tensile strength and shear resistance crucial for ballistic and protective applications. Unlike plain weaving, Kevlar weaving optimizes fiber alignment, resulting in superior performance in high-stress environments.
What Is Plain Weaving?
Plain weaving is the most basic textile weaving technique where warp and weft fibers cross over and under each other in a simple crisscross pattern, creating a strong, balanced fabric. Compared to Kevlar weaving, which often uses more complex patterns like twill to enhance flexibility and strength, plain weaving produces a denser and more rigid material. This weaving method is commonly used in traditional fabrics but offers less impact resistance and durability than specialized Kevlar weaves engineered for ballistic protection.
Kevlar Weaving: Structure and Characteristics
Kevlar weaving features interlaced aramid fibers arranged in a tight, uniform pattern that enhances tensile strength and resistance to impact compared to plain weaving. The unique cross-thread structure of Kevlar weaving provides superior durability and flexibility, making it ideal for ballistic and protective applications. Its high density and minimal fiber slippage contribute to exceptional abrasion resistance and long-lasting performance.
Plain Weaving: Structure and Characteristics
Plain weaving features a simple crisscross pattern where warp and weft threads alternate over and under each other, creating a balanced, tightly bonded fabric structure. This weaving style offers excellent dimensional stability, uniform strength distribution, and a smooth surface ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to abrasion. Plain weaving in Kevlar fabrics enhances impact resistance while maintaining flexibility, making it suitable for body armor, protective gear, and composite reinforcements.
Strength and Durability: Kevlar vs Plain Weaves
Kevlar weaving enhances strength and durability by utilizing tightly interlaced aramid fibers that resist impact, abrasion, and tensile stress far better than traditional plain weaves made from cotton or polyester. The unique molecular structure of Kevlar provides superior toughness, enabling Kevlar weaves to withstand extreme conditions and high-force applications, making them ideal for ballistic and protective gear. Compared to plain weaving, Kevlar's complex fiber alignment ensures prolonged material integrity and resistance to wear, significantly extending product lifespan in demanding environments.
Applications of Kevlar Weaving
Kevlar weaving enhances impact resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for protective gear such as body armor, helmets, and ballistic shields. Unlike plain weaving, Kevlar's specialized weave patterns distribute force more efficiently, offering superior durability for aerospace and automotive components. These applications leverage Kevlar weaving to optimize safety and performance in high-stress environments.
Applications of Plain Weaving
Plain weaving produces fabrics with a simple crisscross pattern, offering uniform strength and durability ideal for everyday textile applications. Unlike Kevlar weaving, which prioritizes high tensile strength and impact resistance for protective gear, plain weaving is commonly used in garments, upholstery, and lightweight industrial fabrics. Its versatility and ease of production make plain weaving suitable for applications requiring comfort and moderate durability rather than extreme protection.
Flexibility and Comfort: Comparing Both Methods
Kevlar weaving offers enhanced flexibility due to its tightly interlaced aramid fibers, allowing for better movement and comfort in protective gear compared to plain weaving. Plain weaving, characterized by its simple over-under pattern, tends to be stiffer and less conforming, which can reduce comfort during extended wear. The superior flexibility of Kevlar woven fabrics makes them ideal for applications requiring agility without compromising ballistic resistance.
Cost and Manufacturing Considerations
Kevlar weaving requires specialized looms and skilled labor, increasing manufacturing costs compared to plain weaving of conventional fibers like cotton. The high tensile strength and heat resistance of Kevlar necessitate precise tension control and slower weaving speeds, further elevating production expenses. Despite higher initial costs, Kevlar's durability and performance justify the investment in industries demanding advanced protective materials.
Choosing the Right Weaving for Your Application
Kevlar weaving enhances impact resistance and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications like ballistic protection and aerospace components, where durability is crucial. Plain weaving offers a tighter, more uniform fabric structure, providing better flexibility and abrasion resistance suitable for protective clothing and industrial uses. Selecting the right weaving depends on prioritizing either maximum strength and toughness with Kevlar weaving or improved flexibility and surface smoothness with plain weaving.
Kevlar weaving vs Plain weaving Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com