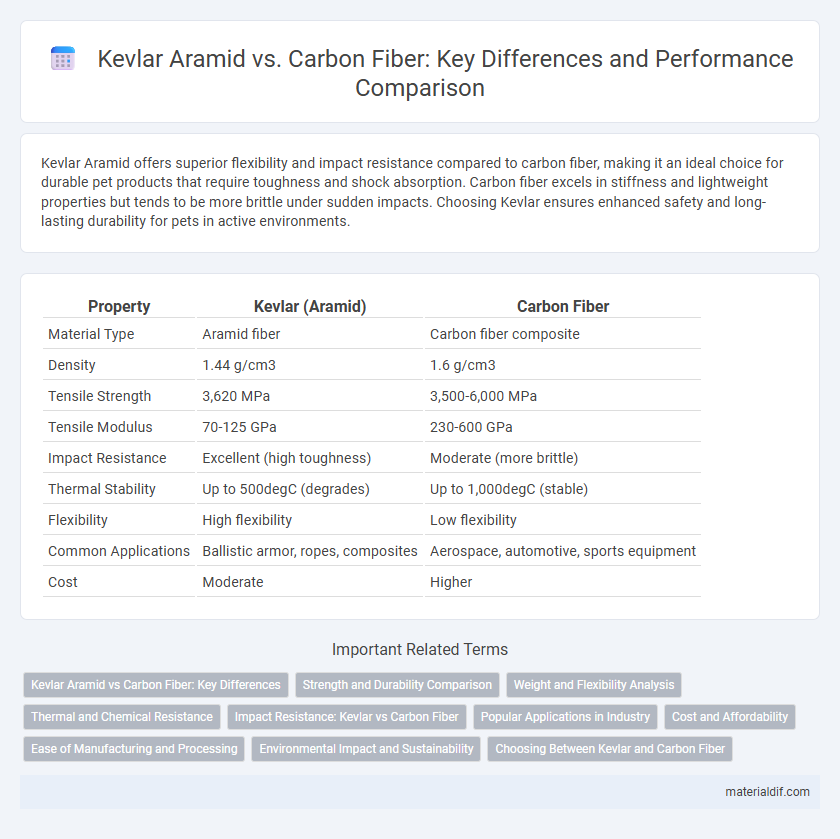
Kevlar Aramid offers superior flexibility and impact resistance compared to carbon fiber, making it an ideal choice for durable pet products that require toughness and shock absorption. Carbon fiber excels in stiffness and lightweight properties but tends to be more brittle under sudden impacts. Choosing Kevlar ensures enhanced safety and long-lasting durability for pets in active environments.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Kevlar (Aramid) | Carbon Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Material Type | Aramid fiber | Carbon fiber composite |
| Density | 1.44 g/cm3 | 1.6 g/cm3 |
| Tensile Strength | 3,620 MPa | 3,500-6,000 MPa |
| Tensile Modulus | 70-125 GPa | 230-600 GPa |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent (high toughness) | Moderate (more brittle) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC (degrades) | Up to 1,000degC (stable) |
| Flexibility | High flexibility | Low flexibility |
| Common Applications | Ballistic armor, ropes, composites | Aerospace, automotive, sports equipment |
| Cost | Moderate | Higher |
Kevlar Aramid vs Carbon Fiber: Key Differences
Kevlar aramid and carbon fiber differ primarily in composition, with Kevlar made from poly-paraphenylene terephthalamide and carbon fiber composed of thin strands of carbon atoms bonded in a crystalline formation. Kevlar excels in impact resistance and flexibility, making it ideal for bulletproof vests and protective gear, while carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and tensile strength, preferred in aerospace and automotive structural components. Weight efficiency is notable in both materials, but Kevlar tends to absorb energy better, whereas carbon fiber provides higher rigidity and fatigue resistance.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Kevlar aramid fibers exhibit exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, making them highly durable for applications requiring flexibility and toughness. Carbon fiber outperforms Kevlar in stiffness and compressive strength but is more brittle, leading to potential fractures under high-impact stress. The strength-to-weight ratio of Kevlar is superior in dynamic loads, while carbon fiber excels in static load-bearing scenarios.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Kevlar Aramid fibers exhibit a lower density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3 compared to carbon fiber's density ranging from 1.6 to 1.8 g/cm3, resulting in lighter applications where weight savings are critical. Kevlar offers superior flexibility and impact resistance due to its molecular structure, making it ideal for products requiring toughness and adaptability. In contrast, carbon fiber provides higher stiffness and tensile strength but less flexibility, which influences its use in rigid, lightweight components.
Thermal and Chemical Resistance
Kevlar aramid fibers exhibit superior thermal stability with a decomposition temperature around 500degC, outperforming carbon fiber's typical threshold near 400degC, making Kevlar ideal for high-temperature applications. Chemically, Kevlar resists many solvents, acids, and alkalis, maintaining structural integrity where carbon fiber composites often degrade or require protective coatings. This enhanced thermal and chemical resistance positions Kevlar as a preferable choice in environments with extreme thermal exposure and aggressive chemical agents.
Impact Resistance: Kevlar vs Carbon Fiber
Kevlar aramid fibers exhibit superior impact resistance compared to carbon fiber, absorbing and dispersing energy more effectively during sudden impacts. Carbon fiber offers higher stiffness and tensile strength but tends to be more brittle, resulting in lower tolerance to sharp, high-impact forces. Kevlar's unique molecular structure enhances its toughness and flexibility, making it the preferred choice for applications demanding exceptional impact protection.
Popular Applications in Industry
Kevlar aramid fibers are extensively used in body armor, aerospace components, and automotive parts due to their high tensile strength and impact resistance. Carbon fiber dominates in aerospace, automotive racing, and sports equipment for its superior stiffness-to-weight ratio and fatigue resistance. Both materials are pivotal in industries requiring lightweight durability, with Kevlar favored for flexibility and ballistic protection, while carbon fiber is preferred for structural rigidity and high-performance applications.
Cost and Affordability
Kevlar aramid fibers generally offer lower costs compared to carbon fiber, making them more affordable for applications requiring impact resistance and flexibility. Carbon fiber tends to be more expensive due to its higher manufacturing complexity, but it delivers superior stiffness and strength-to-weight ratios. Choosing Kevlar can reduce material expenses while maintaining durability in protective gear and composite structures.
Ease of Manufacturing and Processing
Kevlar aramid fibers offer superior ease of manufacturing and processing compared to carbon fiber due to their flexible filament structure, allowing for simpler weaving and molding techniques. Unlike carbon fiber, Kevlar does not require high-temperature curing, reducing production complexity and energy consumption. This facilitates faster prototyping and cost-effective fabrication in various applications such as protective gear and composite materials.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Kevlar aramid fibers exhibit a lower environmental impact compared to carbon fiber due to their energy-efficient production process and higher recyclability potential. Carbon fiber manufacturing consumes significantly more energy and generates higher greenhouse gas emissions, posing challenges to sustainability. Kevlar's biodegradability and reduced ecological footprint make it preferable for applications prioritizing environmental responsibility.
Choosing Between Kevlar and Carbon Fiber
When choosing between Kevlar aramid and carbon fiber, consider the specific application's requirements for strength, weight, and impact resistance. Kevlar excels in impact absorption and flexibility, making it ideal for protective gear and bulletproof vests, while carbon fiber offers superior stiffness and tensile strength, preferred in aerospace and automotive components. Evaluating the balance between durability and weight is crucial for optimizing performance in high-stress environments.
Kevlar Aramid vs Carbon Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com