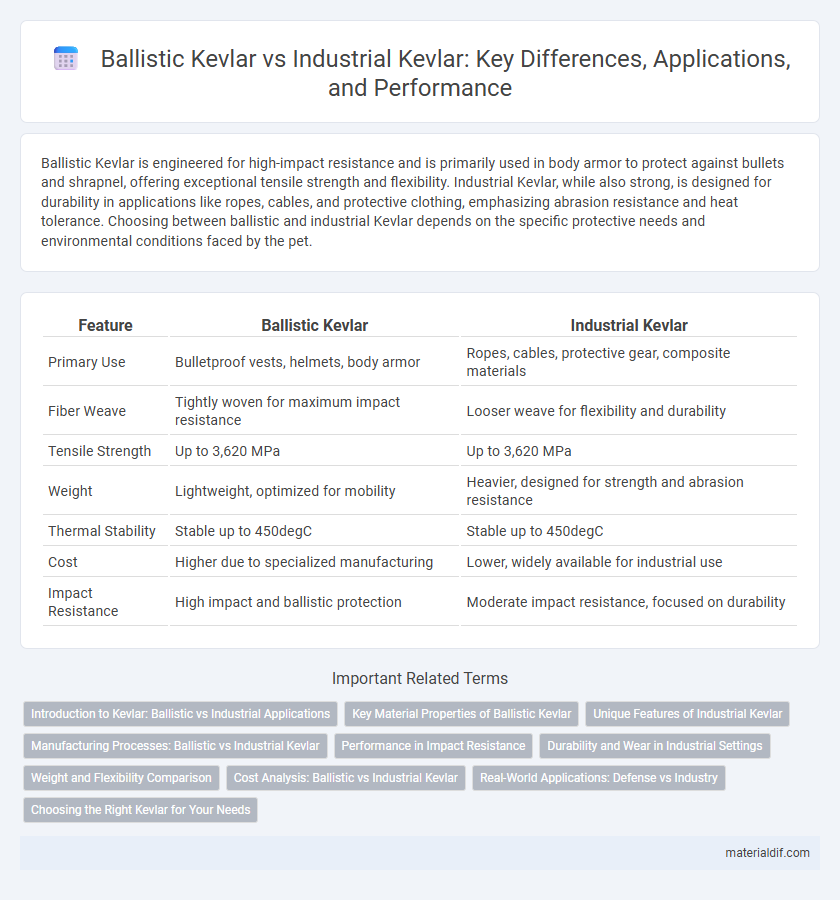
Ballistic Kevlar is engineered for high-impact resistance and is primarily used in body armor to protect against bullets and shrapnel, offering exceptional tensile strength and flexibility. Industrial Kevlar, while also strong, is designed for durability in applications like ropes, cables, and protective clothing, emphasizing abrasion resistance and heat tolerance. Choosing between ballistic and industrial Kevlar depends on the specific protective needs and environmental conditions faced by the pet.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ballistic Kevlar | Industrial Kevlar |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Bulletproof vests, helmets, body armor | Ropes, cables, protective gear, composite materials |
| Fiber Weave | Tightly woven for maximum impact resistance | Looser weave for flexibility and durability |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 3,620 MPa | Up to 3,620 MPa |
| Weight | Lightweight, optimized for mobility | Heavier, designed for strength and abrasion resistance |
| Thermal Stability | Stable up to 450degC | Stable up to 450degC |
| Cost | Higher due to specialized manufacturing | Lower, widely available for industrial use |
| Impact Resistance | High impact and ballistic protection | Moderate impact resistance, focused on durability |
Introduction to Kevlar: Ballistic vs Industrial Applications
Kevlar, a high-strength synthetic fiber developed by DuPont, serves distinct purposes in ballistic and industrial applications based on its weave, thickness, and treatment. Ballistic Kevlar is engineered for personal armor and protective gear, emphasizing impact resistance and energy absorption to safeguard against bullets and shrapnel. Industrial Kevlar finds extensive use in construction, automotive, and aerospace sectors, providing durability, cut resistance, and heat stability for ropes, protective gloves, and composite materials.
Key Material Properties of Ballistic Kevlar
Ballistic Kevlar is engineered for impact resistance, featuring high tensile strength and exceptional energy absorption to effectively stop bullets and shrapnel. Its tightly woven aramid fibers create a dense, lightweight material that maintains flexibility while providing superior durability under high-stress conditions. Designed specifically for body armor applications, Ballistic Kevlar exhibits enhanced resistance to penetration and abrasion compared to Industrial Kevlar, which prioritizes chemical resistance and thermal stability for manufacturing uses.
Unique Features of Industrial Kevlar
Industrial Kevlar is engineered for exceptional durability and resistance to chemical corrosion, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications like conveyor belts, hoses, and gaskets. Its unique fiber structure enhances tensile strength and thermal stability, outperforming Ballistic Kevlar in abrasion resistance and flexibility under harsh environmental conditions. Unlike Ballistic Kevlar, which prioritizes impact resistance, Industrial Kevlar excels in sustained mechanical stress and wear resistance for prolonged industrial use.
Manufacturing Processes: Ballistic vs Industrial Kevlar
Ballistic Kevlar is manufactured using a high-tensile fiber spinning process that aligns polymer chains tightly to maximize strength and impact resistance, essential for protective gear such as body armor. Industrial Kevlar, on the other hand, undergoes a production method tailored for durability and thermal stability, optimized for applications like ropes, cables, and automotive parts. The differing polymer orientation and heat treatment techniques in each manufacturing process result in distinct performance characteristics suited to ballistic protection or industrial durability.
Performance in Impact Resistance
Ballistic Kevlar provides superior impact resistance through its high tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities, making it ideal for body armor and ballistic protection. Industrial Kevlar, while also strong, is optimized for cut resistance and durability in applications like ropes, cables, and protective gloves. The distinct fiber weaves and resin matrices in ballistic Kevlar enhance its ability to dissipate kinetic energy from high-velocity impacts compared to the more abrasion-focused performance of industrial Kevlar.
Durability and Wear in Industrial Settings
Ballistic Kevlar is engineered for maximum impact resistance and energy absorption, making it highly durable in high-velocity environments such as bulletproof vests and military gear. Industrial Kevlar, while still strong, prioritizes abrasion resistance and tensile strength to withstand continuous wear, chemical exposure, and mechanical stress in construction, automotive, and manufacturing applications. The enhanced durability of Industrial Kevlar ensures longevity under harsh conditions, whereas Ballistic Kevlar excels in protecting against ballistic threats but may experience wear more quickly in abrasive industrial settings.
Weight and Flexibility Comparison
Ballistic Kevlar typically weighs more than industrial Kevlar due to its dense, tightly woven fibers designed to absorb high-impact energy, making it less flexible but highly durable for protective gear. Industrial Kevlar offers lighter weight and enhanced flexibility, optimized for applications requiring maneuverability such as ropes and cables. The trade-off between weight and flexibility highlights ballistic Kevlar's suitability for body armor, while industrial Kevlar serves well in dynamic environments needing strength without stiffness.
Cost Analysis: Ballistic vs Industrial Kevlar
Ballistic Kevlar typically incurs higher costs due to its complex manufacturing processes and stringent quality standards required for personal protective equipment and military applications. Industrial Kevlar, used primarily in automotive and aerospace components, offers a more cost-effective solution with slightly lower tensile strength and less rigid performance criteria. Cost analysis reveals that while ballistic Kevlar demands greater investment, its superior durability and energy absorption justify expenses in high-risk environments.
Real-World Applications: Defense vs Industry
Ballistic Kevlar is engineered for high-impact resistance and is predominantly used in defense applications such as bulletproof vests, helmets, and vehicle armor to provide critical protection in combat scenarios. Industrial Kevlar, while maintaining strength and durability, is tailored for applications like cut-resistant gloves, ropes, and conveyor belts, where abrasion resistance and flexibility are paramount. The distinct fiber weave and resin treatments in Ballistic Kevlar optimize energy absorption, whereas Industrial Kevlar balances tensile strength with durability for heavy-duty industrial use.
Choosing the Right Kevlar for Your Needs
Ballistic Kevlar features high tensile strength and superior impact resistance, making it ideal for body armor and ballistic applications. Industrial Kevlar emphasizes cut, heat, and abrasion resistance, suitable for gloves, ropes, and protective gear in manufacturing environments. Selecting the right Kevlar depends on whether protection from high-velocity projectiles or durability against industrial hazards is the primary requirement.
Ballistic Kevlar vs Industrial Kevlar Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com