Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are known for their exceptional strength, high tensile properties, and resistance to abrasion, making them ideal for protective pet gear. Meta-aramid fibers, on the other hand, offer superior thermal stability and flame resistance but have lower tensile strength compared to para-aramids. Choosing between para-aramid and meta-aramid materials depends on whether durability or heat resistance is the priority for pet safety products.
Table of Comparison
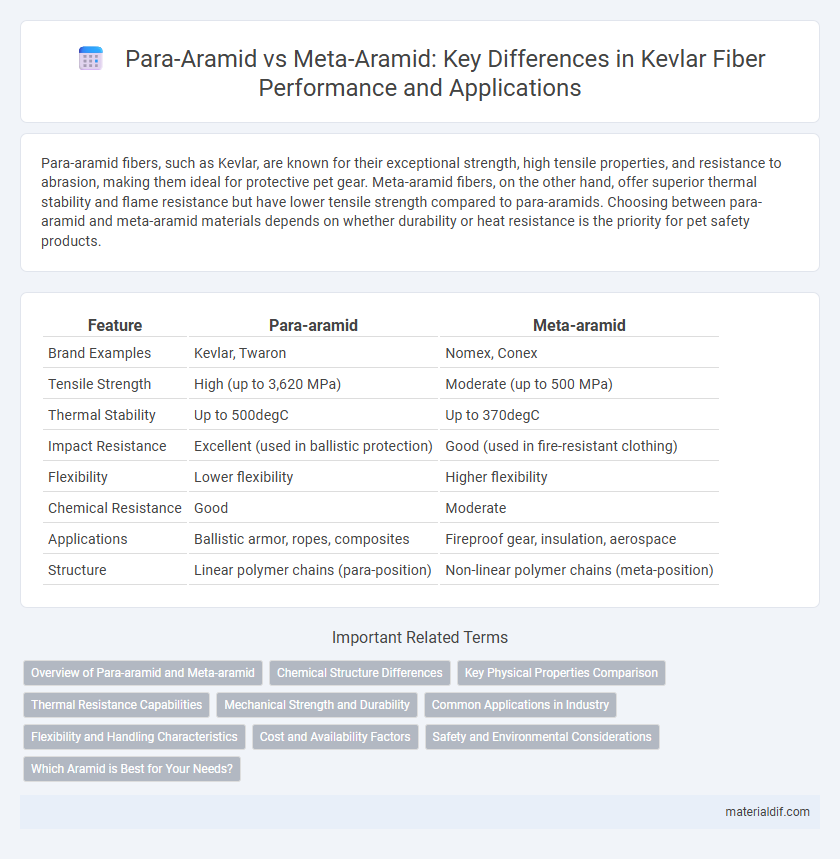
| Feature | Para-aramid | Meta-aramid |
|---|---|---|
| Brand Examples | Kevlar, Twaron | Nomex, Conex |
| Tensile Strength | High (up to 3,620 MPa) | Moderate (up to 500 MPa) |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC | Up to 370degC |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent (used in ballistic protection) | Good (used in fire-resistant clothing) |
| Flexibility | Lower flexibility | Higher flexibility |
| Chemical Resistance | Good | Moderate |
| Applications | Ballistic armor, ropes, composites | Fireproof gear, insulation, aerospace |
| Structure | Linear polymer chains (para-position) | Non-linear polymer chains (meta-position) |
Overview of Para-aramid and Meta-aramid
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, are known for their high tensile strength, excellent impact resistance, and thermal stability, making them ideal for ballistic and protective applications. Meta-aramid fibers like Nomex offer superior heat and flame resistance with good mechanical properties, often used in fire-resistant clothing and insulation. Both para-aramid and meta-aramid belong to the aramid family but differ in molecular structure, leading to distinct performance characteristics in strength and thermal protection.
Chemical Structure Differences
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, have rigid, linear polymer chains aligned parallel to the fiber axis, enhancing tensile strength and chemical resistance. Meta-aramid fibers feature molecules with a kinked, non-linear structure due to the meta-position of amide linkages, resulting in better thermal stability but lower strength compared to para-aramids. The distinct placement of amide groups in para-aramids creates strong inter-chain hydrogen bonding, while meta-aramids display less ordered packing due to their molecular geometry.
Key Physical Properties Comparison
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit high tensile strength and superior impact resistance, making them ideal for ballistic and protective applications, while meta-aramids like Nomex provide excellent thermal stability and flame resistance. Para-aramids have a higher modulus of elasticity, enabling greater stiffness and durability, whereas meta-aramids offer better flexibility and chemical resistance. The density of para-aramids typically ranges around 1.44 g/cm3, compared to meta-aramids at about 1.39 g/cm3, influencing their weight-to-strength ratio in different use cases.
Thermal Resistance Capabilities
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior thermal resistance capabilities compared to meta-aramid fibers, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures up to 400degC (752degF). Meta-aramids, like Nomex, generally withstand continuous exposure up to around 200-250degC (392-482degF) but offer better heat dissipation and flame resistance due to higher char yield. The para-aramid's tightly packed molecular structure provides enhanced tensile strength and heat resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature protective gear and industrial applications.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to meta-aramid fibers due to their highly oriented molecular structure that provides exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance. Meta-aramids offer greater thermal stability and chemical resistance but have lower tensile strength and less durability under mechanical stress. The choice between para-aramid and meta-aramid depends on applications requiring maximum strength and durability, favoring para-aramid for protective gear and composites.
Common Applications in Industry
Para-aramid fibers, known for their high strength and thermal resistance, are widely used in ballistic protection, aerospace components, and reinforced composites for automotive applications. Meta-aramid fibers excel in thermal stability and flame resistance, making them ideal for protective clothing, electrical insulation, and fire-resistant fabrics in the industrial sector. Both types of aramid fibers contribute to safety and durability across multiple industries, with para-aramid favoring mechanical performance and meta-aramid emphasizing heat and chemical resistance.
Flexibility and Handling Characteristics
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, exhibit superior flexibility and high tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring durable yet lightweight materials with excellent handling characteristics. Meta-aramid fibers, like Nomex, offer greater thermal stability and chemical resistance but provide less flexibility and a stiffer feel compared to para-aramids. These differences influence their use in protective gear, where para-aramids are preferred for impact resistance and comfort, while meta-aramids are selected for heat and flame resistance.
Cost and Availability Factors
Para-aramid fibers like Kevlar exhibit higher tensile strength and durability but typically come at a greater cost due to more complex manufacturing processes and limited production scales. Meta-aramids offer more affordable pricing and broader availability since their production techniques are less intensive and they serve a wider range of general-purpose applications. Cost-effectiveness and supply consistency make meta-aramids preferable for industries with budget constraints, whereas para-aramids are chosen for high-performance requirements despite their premium price.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer superior strength and impact resistance compared to meta-aramid fibers, making them ideal for high-performance safety applications like ballistic protection and industrial gloves. Meta-aramid fibers are valued for their excellent thermal stability and flame resistance, commonly used in firefighting gear and heat-resistant clothing where exposure to flames and heat is critical. Both types of aramid fibers are generally low in environmental impact during use; however, para-aramid's manufacturing involves more energy-intensive processes, while meta-aramid tends to be more chemically stable and easier to recycle, influencing overall safety and sustainability profiles.
Which Aramid is Best for Your Needs?
Para-aramid fibers, such as Kevlar, offer exceptional tensile strength and durability, making them ideal for ballistic protection and high-performance composite applications. Meta-aramid fibers, like Nomex, provide superior thermal and chemical resistance, suited for fire-resistant clothing and insulation. Choosing between para-aramid and meta-aramid depends on specific requirements for impact resistance or heat protection in your project.
Para-aramid vs Meta-aramid Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com