Natural graphite, extracted directly from mining operations, offers high purity and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for industrial applications. Recycled graphite, sourced from spent batteries and electronic waste, provides an eco-friendly alternative by reducing mining impacts and conserving resources. Both types serve critical roles in sustainable graphite supply chains, balancing performance with environmental responsibility.
Table of Comparison
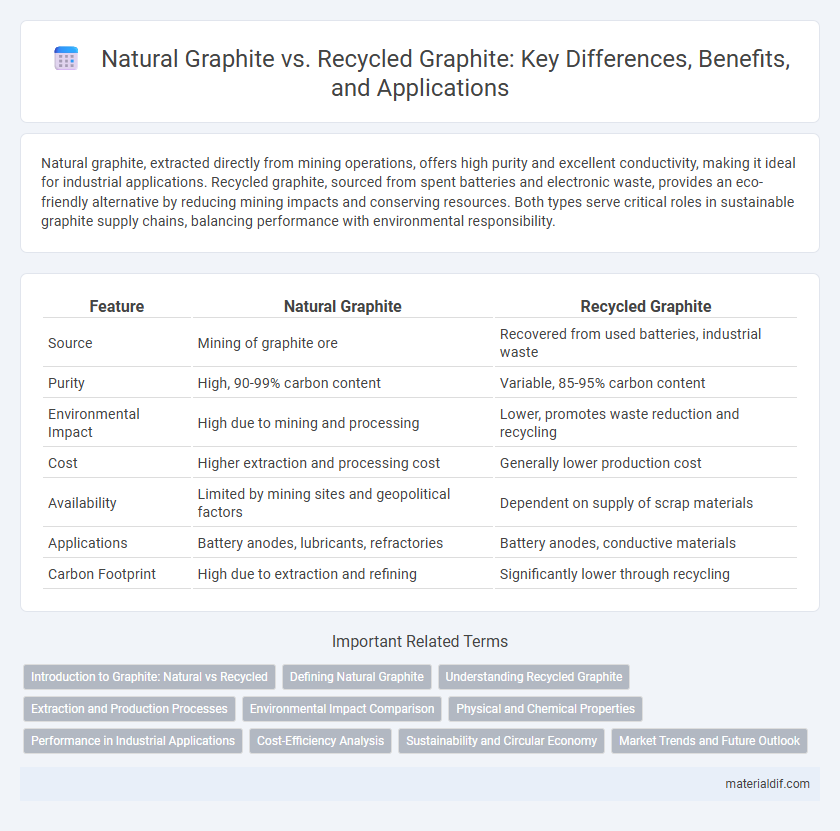
| Feature | Natural Graphite | Recycled Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Mining of graphite ore | Recovered from used batteries, industrial waste |
| Purity | High, 90-99% carbon content | Variable, 85-95% carbon content |
| Environmental Impact | High due to mining and processing | Lower, promotes waste reduction and recycling |
| Cost | Higher extraction and processing cost | Generally lower production cost |
| Availability | Limited by mining sites and geopolitical factors | Dependent on supply of scrap materials |
| Applications | Battery anodes, lubricants, refractories | Battery anodes, conductive materials |
| Carbon Footprint | High due to extraction and refining | Significantly lower through recycling |
Introduction to Graphite: Natural vs Recycled
Natural graphite, sourced through mining, offers high purity and excellent conductivity, making it ideal for batteries and industrial applications. Recycled graphite, derived from spent batteries and industrial waste, supports sustainability by reducing environmental impact and conserving natural resources. Both forms play crucial roles in advancing energy storage technologies and promoting circular economy practices.
Defining Natural Graphite
Natural graphite is a crystalline form of carbon extracted directly from graphite ore through mining processes. It exhibits three main types: flake, vein, and amorphous graphite, each with distinct purity and particle size characteristics. Its high purity and excellent thermal and electrical conductivity make it essential for applications in batteries, lubricants, and refractory materials.
Understanding Recycled Graphite
Recycled graphite is derived from processing spent lithium-ion batteries and industrial scrap, offering a sustainable alternative to natural graphite by reducing reliance on mining. It provides comparable electrochemical performance, making it a valuable material for battery anodes and other applications. The recycling process helps conserve natural resources, lowers carbon emissions, and supports circular economy goals in the graphite supply chain.
Extraction and Production Processes
Natural graphite extraction involves mining from open-pit or underground mines, followed by crushing, milling, and flotation to separate graphite flakes from the ore. Recycled graphite is obtained by reclaiming graphite from spent lithium-ion batteries and industrial waste through chemical and thermal treatment processes, reducing environmental impact and raw material dependency. The production of natural graphite requires significant energy-intensive beneficiation, whereas recycled graphite production emphasizes material recovery and purification efficiency.
Environmental Impact Comparison
Natural graphite mining involves significant land disturbance, water consumption, and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to habitat disruption and pollution. Recycled graphite, sourced from spent batteries and industrial waste, reduces the need for raw material extraction, lowers energy usage, and minimizes environmental pollution. Utilizing recycled graphite supports circular economy principles by decreasing carbon footprint and resource depletion compared to natural graphite extraction.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Natural graphite exhibits a layered crystalline structure with high purity levels, typically containing 90-99% carbon, which provides excellent electrical conductivity and lubricity. Recycled graphite often has variable purity, ranging from 70-95% carbon, and may include impurities or altered particle sizes affecting its performance in electrochemical applications. The physical properties such as density and hardness can differ significantly, with natural graphite displaying more consistent morphology and chemical stability, whereas recycled graphite's properties depend on the source material and processing methods.
Performance in Industrial Applications
Natural graphite exhibits superior electrical conductivity and thermal stability, making it ideal for high-performance industrial applications such as battery anodes and lubricants. Recycled graphite offers comparable mechanical properties and cost-effectiveness but may contain impurities that affect consistency and long-term performance. Industrial sectors prioritize natural graphite where reliability and efficiency are critical, while recycled graphite finds use in applications with less stringent performance requirements.
Cost-Efficiency Analysis
Natural graphite offers lower raw material costs but involves higher environmental and processing expenses, impacting overall cost-efficiency. Recycled graphite reduces expenses related to extraction and waste management, providing a more sustainable and often cheaper alternative in long-term usage. Cost-efficiency analysis must consider lifecycle costs, including energy consumption, yield, and material purity for both natural and recycled graphite sources.
Sustainability and Circular Economy
Natural graphite, sourced from mining, involves significant environmental impacts such as habitat disruption and high energy consumption, challenging its sustainability. Recycled graphite, recovered from spent batteries and industrial waste, reduces reliance on virgin materials and minimizes carbon emissions, supporting circular economy principles. Emphasizing recycled graphite fosters resource efficiency, waste reduction, and long-term material reuse critical for sustainable energy storage technologies.
Market Trends and Future Outlook
Natural graphite dominates the market due to its superior conductivity and purity, driving steady demand in electric vehicle batteries and industrial applications. Recycled graphite is gaining traction as sustainability initiatives and raw material shortages push manufacturers toward circular economy solutions. Market forecasts predict accelerated growth for recycled graphite, supported by technological advancements in purification processes and increasing regulatory pressure to reduce environmental impact.
Natural Graphite vs Recycled Graphite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com