Expandable graphite offers superior fire resistance due to its ability to expand and form an insulating layer when exposed to heat, making it ideal for fireproofing applications. Non-expandable graphite, while possessing excellent conductivity and lubrication properties, lacks this thermal expansion characteristic and is primarily used in electrical and mechanical industries. Choosing between the two depends on specific requirements such as thermal protection versus conductivity and mechanical performance.
Table of Comparison
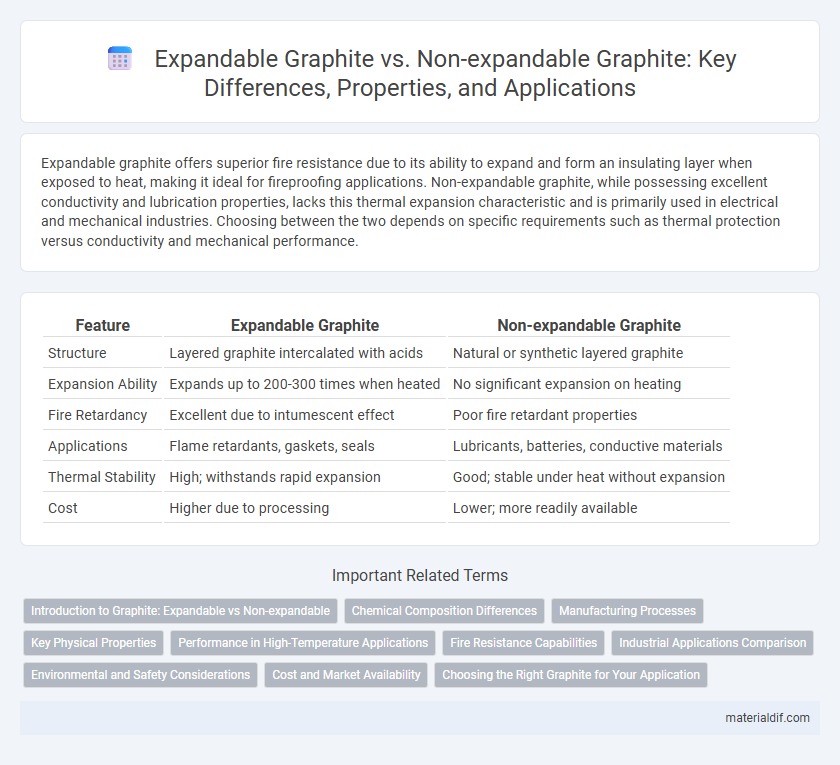
| Feature | Expandable Graphite | Non-expandable Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Layered graphite intercalated with acids | Natural or synthetic layered graphite |
| Expansion Ability | Expands up to 200-300 times when heated | No significant expansion on heating |
| Fire Retardancy | Excellent due to intumescent effect | Poor fire retardant properties |
| Applications | Flame retardants, gaskets, seals | Lubricants, batteries, conductive materials |
| Thermal Stability | High; withstands rapid expansion | Good; stable under heat without expansion |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Lower; more readily available |
Introduction to Graphite: Expandable vs Non-expandable
Expandable graphite consists of graphite flakes treated with acid compounds, enabling them to expand significantly when heated, which enhances its applications in fireproofing and insulation. Non-expandable graphite, composed of natural or synthetic graphite flakes without chemical treatment, remains stable under heat and is primarily used in lubricants, batteries, and conductive materials. Understanding these distinct properties helps industries select the appropriate graphite type based on thermal expansion requirements and functional performance.
Chemical Composition Differences
Expandable graphite contains intercalated compounds such as sulfuric acid or nitric acid, which decompose upon heating to produce gas that expands the graphite structure. Non-expandable graphite consists primarily of pure carbon with a layered crystalline structure, lacking these intercalated chemical species. This fundamental chemical composition difference results in expandable graphite's ability to exfoliate and increase in volume under heat, unlike non-expandable graphite.
Manufacturing Processes
Expandable graphite is produced by intercalating natural flake graphite with acids and oxidizing agents, followed by rapid heating to induce expansion. Non-expandable graphite undergoes mechanical milling or purification without chemical treatment, preserving its original layered structure. The manufacturing processes distinctly affect the material's properties, with expandable graphite offering enhanced thermal insulation and flame retardancy due to its unique expanded morphology.
Key Physical Properties
Expandable graphite exhibits a layered structure that allows it to increase in volume when heated, resulting in enhanced thermal insulation and fire-resistant properties. Non-expandable graphite maintains a stable, dense configuration that offers superior electrical conductivity and mechanical strength without significant dimensional change. The key physical differences include thermal expansion capacity, density, and surface area, directly influencing their respective applications in fire retardants and conductive materials.
Performance in High-Temperature Applications
Expandable graphite exhibits superior performance in high-temperature applications due to its ability to exfoliate and form an insulating char layer that enhances thermal stability and flame retardancy. Non-expandable graphite lacks this expansion capability, resulting in lower effectiveness in temperature resistance and thermal insulation. Consequently, expandable graphite is preferred in industries such as fireproof coatings and thermal management where enhanced high-temperature durability is critical.
Fire Resistance Capabilities
Expandable graphite exhibits superior fire resistance capabilities compared to non-expandable graphite due to its ability to rapidly expand when exposed to high temperatures, forming an insulating char layer that protects underlying materials from heat and flame. Non-expandable graphite lacks this expansion property, providing limited thermal barrier protection and lower fire retardancy. The expansion ratio of expandable graphite, which can reach up to 300 times its original volume, is a critical factor in enhancing its effectiveness in fire-resistant applications.
Industrial Applications Comparison
Expandable graphite exhibits superior thermal stability and excellent fire retardant properties, making it ideal for use in flameproof coatings, gaskets, and battery electrodes in the industrial sector. Non-expandable graphite offers high electrical conductivity and lubrication benefits, commonly applied in electrodes, brushes, and seals where expansion is not required. Industrial applications requiring heat resistance and volume expansion favor expandable graphite, while those demanding consistent structural integrity and electrical performance rely on non-expandable graphite.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Expandable graphite offers significant environmental benefits due to its ability to act as a flame retardant without releasing toxic gases, reducing the need for harmful chemical additives. Non-expandable graphite, while stable and inert, lacks this fire-resistant property, potentially increasing reliance on synthetic flame retardants that pose greater environmental and safety risks. The choice between these two forms impacts not only fire safety but also the overall ecological footprint of industrial and commercial applications.
Cost and Market Availability
Expandable graphite generally commands a higher price due to its specialized production process and enhanced flame retardant properties, limiting its widespread market availability compared to non-expandable graphite. Non-expandable graphite is more abundant and cost-effective, making it the preferred choice in industries requiring bulk graphite materials for applications like lubricants and batteries. The market demand for expandable graphite remains niche, heavily influenced by safety standards in construction and electronics, whereas non-expandable graphite benefits from broader industrial adoption and easier sourcing.
Choosing the Right Graphite for Your Application
Expandable graphite offers superior thermal stability and conductivity, making it ideal for fire-resistant materials and thermal management applications. Non-expandable graphite, with its consistent structure and natural form, suits uses requiring electrical conductivity and lubrication without expansion properties. Selecting the appropriate graphite depends on the specific application requirements, such as expansion behavior, thermal performance, and mechanical strength.
Expandable Graphite vs Non-expandable Graphite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com