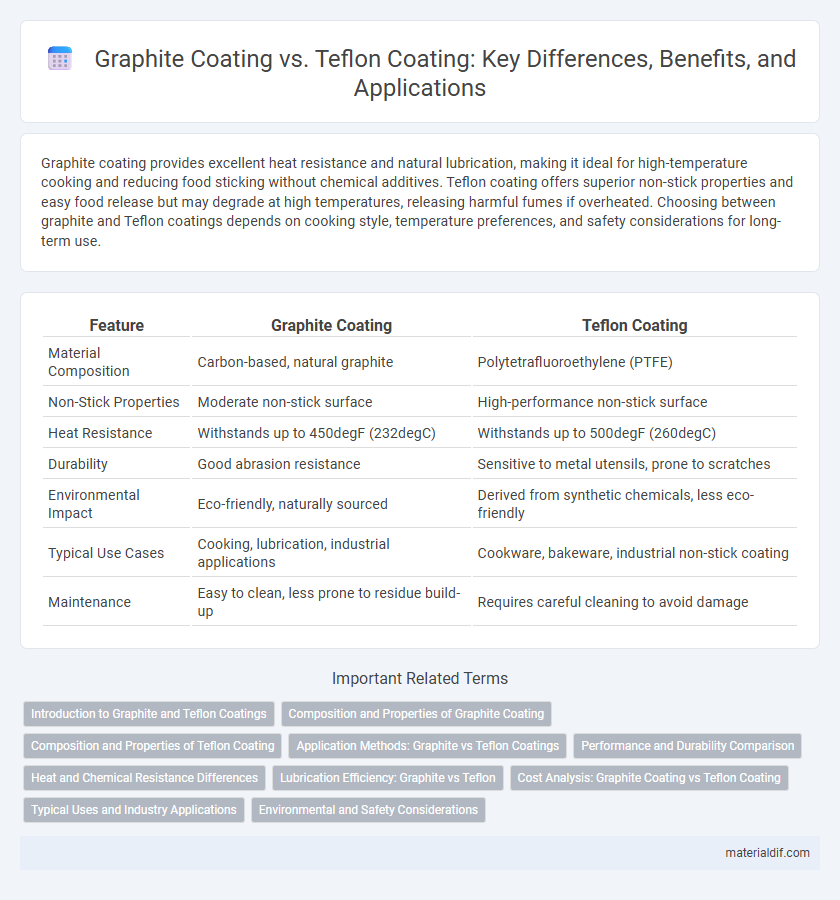
Graphite coating provides excellent heat resistance and natural lubrication, making it ideal for high-temperature cooking and reducing food sticking without chemical additives. Teflon coating offers superior non-stick properties and easy food release but may degrade at high temperatures, releasing harmful fumes if overheated. Choosing between graphite and Teflon coatings depends on cooking style, temperature preferences, and safety considerations for long-term use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphite Coating | Teflon Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Carbon-based, natural graphite | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) |
| Non-Stick Properties | Moderate non-stick surface | High-performance non-stick surface |
| Heat Resistance | Withstands up to 450degF (232degC) | Withstands up to 500degF (260degC) |
| Durability | Good abrasion resistance | Sensitive to metal utensils, prone to scratches |
| Environmental Impact | Eco-friendly, naturally sourced | Derived from synthetic chemicals, less eco-friendly |
| Typical Use Cases | Cooking, lubrication, industrial applications | Cookware, bakeware, industrial non-stick coating |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean, less prone to residue build-up | Requires careful cleaning to avoid damage |
Introduction to Graphite and Teflon Coatings
Graphite coating offers excellent lubrication and high-temperature resistance, making it ideal for industrial applications requiring reduced friction and wear. Teflon coating, known for its non-stick properties and chemical inertness, provides superior resistance to corrosion and easy release in cookware and machinery parts. Both coatings serve distinct purposes: graphite excels in dry lubrication and heat management, while Teflon is preferred for its non-reactivity and low surface energy.
Composition and Properties of Graphite Coating
Graphite coating consists primarily of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, providing excellent lubricity, high thermal conductivity, and resistance to corrosion and wear. Unlike Teflon coating, which is made from polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) and characterized by non-stick and chemical inertness, graphite coatings excel in high-temperature environments and electrical conductivity. The unique layered structure of graphite allows easy shear between layers, offering superior anti-friction properties ideal for industrial applications requiring durability and heat resistance.
Composition and Properties of Teflon Coating
Teflon coating consists primarily of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), a synthetic fluoropolymer renowned for its non-stick, chemical resistance, and high-temperature tolerance properties. Unlike graphite coatings, which rely on carbon layers for lubrication, Teflon offers superior low friction and hydrophobic characteristics due to its molecular structure. Its composition allows Teflon coatings to provide enhanced corrosion resistance and durability in harsh chemical environments.
Application Methods: Graphite vs Teflon Coatings
Graphite coatings are typically applied using spray, dip, or brush methods that allow even distribution of the dry lubricant on surfaces, enhancing wear resistance and thermal conductivity. Teflon coatings, often applied through powder coating, spraying, or dip coating, form a non-stick, chemically inert layer ideal for reducing friction in dynamic applications. The choice of application method affects the coating thickness, adhesion, and overall performance tailored to specific industrial needs.
Performance and Durability Comparison
Graphite coating offers superior heat resistance and excellent lubricity, making it ideal for high-temperature applications, whereas Teflon coating excels in low friction and non-stick properties but degrades faster under extreme heat. Graphite coatings typically exhibit greater durability and maintain performance efficiency over extended use, while Teflon coatings tend to wear out more quickly due to surface abrasion and chemical exposure. The choice between graphite and Teflon coatings depends on specific performance requirements, with graphite favored for heavy-duty operations and Teflon preferred for applications demanding smooth, non-stick surfaces.
Heat and Chemical Resistance Differences
Graphite coating offers exceptional heat resistance, typically withstanding temperatures up to 500degC, while Teflon coating endures up to around 260degC, making graphite more suitable for high-temperature applications. In terms of chemical resistance, Teflon provides superior resistance to a wide range of acids, bases, and solvents compared to graphite, which can degrade or oxidize under harsh chemical exposure. The choice between graphite and Teflon coatings depends on whether the priority is enduring extreme heat or resisting aggressive chemicals.
Lubrication Efficiency: Graphite vs Teflon
Graphite coating offers superior lubrication efficiency due to its layered structure, which reduces friction by allowing easy shear between layers, making it ideal for high-pressure and high-temperature applications. Teflon coating provides excellent low-friction properties with chemical resistance and non-stick characteristics, but its lubrication performance diminishes under heavy loads or abrasive conditions. Graphite outperforms Teflon in scenarios requiring durable, long-lasting lubrication, particularly in mechanical parts exposed to extreme environments.
Cost Analysis: Graphite Coating vs Teflon Coating
Graphite coating offers a more cost-effective solution compared to Teflon coating due to lower raw material expenses and simpler application processes, making it ideal for budget-conscious projects. Teflon coating, while pricier, provides superior non-stick properties and chemical resistance, which may justify the higher initial investment in industrial or high-performance uses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals graphite coating reduces upfront costs but may require more frequent maintenance, whereas Teflon coating ensures longer durability and lower lifecycle expenses.
Typical Uses and Industry Applications
Graphite coating is widely used in industries such as metallurgy, automotive, and aerospace for its excellent lubricity, high-temperature resistance, and chemical inertness, making it ideal for molds, bearings, and seals. Teflon coating dominates applications requiring low friction, non-stick properties, and chemical resistance, commonly found in cookware, electrical insulation, and food processing equipment. Both coatings serve distinct purposes, with graphite excelling in wear resistance and thermal stability, while Teflon is preferred for its non-reactive, easy-release surface characteristics.
Environmental and Safety Considerations
Graphite coating is made from natural carbon materials that are non-toxic, biodegradable, and environmentally friendly, reducing health risks during application and disposal. Teflon coating, composed of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), can release harmful fumes when overheated, posing safety hazards and environmental concerns due to its persistence and bioaccumulation potential. Choosing graphite over Teflon supports sustainable practices by minimizing chemical exposure and facilitating safer waste management.
Graphite Coating vs Teflon Coating Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com