Graphite powder offers a finer texture ideal for lubricating delicate pet grooming tools, while graphite granules provide a coarser consistency suitable for air purification or odor control in pet environments. The powder form enhances smooth application and penetrates small crevices, whereas granules are favored for slow release and longer-lasting effects. Choosing between the two depends on the specific pet care need, balancing ease of use against durability and application method.
Table of Comparison
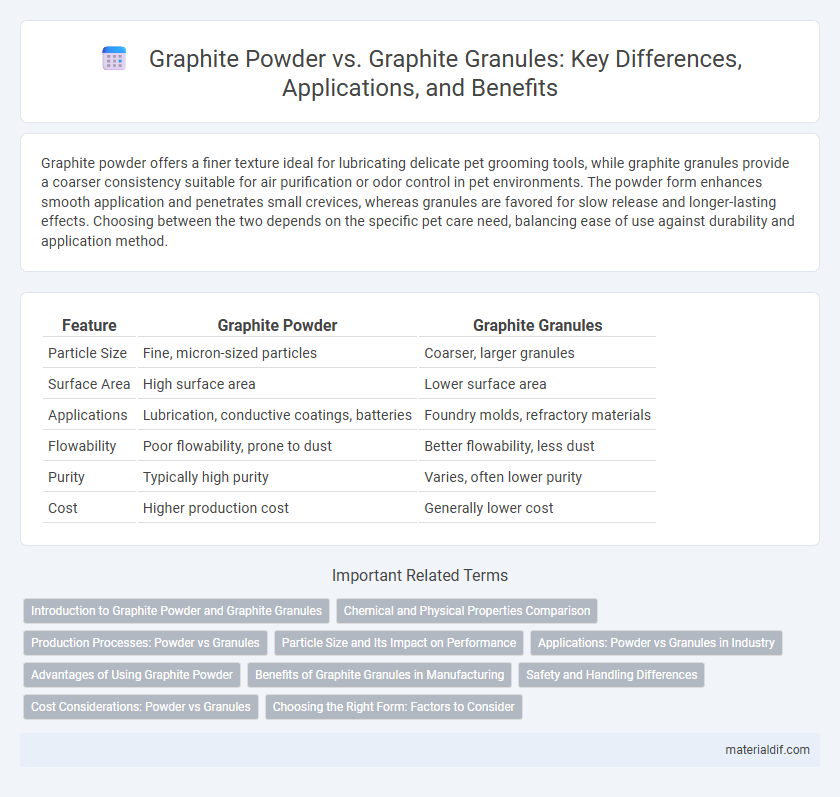
| Feature | Graphite Powder | Graphite Granules |
|---|---|---|
| Particle Size | Fine, micron-sized particles | Coarser, larger granules |
| Surface Area | High surface area | Lower surface area |
| Applications | Lubrication, conductive coatings, batteries | Foundry molds, refractory materials |
| Flowability | Poor flowability, prone to dust | Better flowability, less dust |
| Purity | Typically high purity | Varies, often lower purity |
| Cost | Higher production cost | Generally lower cost |
Introduction to Graphite Powder and Graphite Granules
Graphite powder consists of fine, micron-sized particles known for its high surface area and excellent lubricity, making it suitable for applications requiring uniform coverage and enhanced conductivity. Graphite granules are larger, coarser particles often utilized in industrial processes that demand bulk handling, improved flow characteristics, and stronger thermal resistance. Understanding the physical form differences between graphite powder and granules is essential for selecting the appropriate material in manufacturing, lubrication, or refractory applications.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Graphite powder exhibits finer particle size, higher surface area, and enhanced reactivity compared to graphite granules, which consist of larger, more crystalline particles with lower surface area. Chemically, both forms maintain high purity carbon with excellent thermal stability and electrical conductivity, but powder's increased surface area accelerates chemical reactions and oxidation rates. Physically, graphite granules offer greater mechanical strength and reduced dust generation, making them preferable for applications requiring structural integrity and controlled handling.
Production Processes: Powder vs Granules
Graphite powder is produced by finely grinding natural or synthetic graphite, resulting in particles typically smaller than 75 microns, which enhances its surface area and reactivity for applications like lubricants and batteries. In contrast, graphite granules are formed by agglomerating finer graphite particles into larger granules through processes such as pelletizing or extrusion, providing improved flowability and reduced dust during handling. The choice between powder and granules depends on end-use requirements, where powders offer superior performance in coatings and composites, while granules suit metallurgical and foundry uses due to ease of dosing and reduced airborne particles.
Particle Size and Its Impact on Performance
Graphite powder features finer particle sizes than graphite granules, enhancing its surface area and improving conductivity and lubrication in high-precision applications. The smaller particles in graphite powder provide better dispersion and uniform coating, leading to superior performance in batteries, electrodes, and lubricants. Conversely, graphite granules, with larger particle size, offer advantages in thermal management and structural stability in applications requiring slower reaction rates and controlled reactivity.
Applications: Powder vs Granules in Industry
Graphite powder offers superior surface area and reactivity, making it ideal for applications like lubrication, refractory coatings, and batteries where fine dispersion is critical. Graphite granules provide improved flowability and reduced dust, preferred in metallurgy for casting, brake linings, and conductive composites. Industries select graphite powder or granules based on specific requirements of particle size, thermal conductivity, and electrical performance.
Advantages of Using Graphite Powder
Graphite powder offers superior surface area and finer particle size, enabling enhanced lubrication and conductivity compared to graphite granules. Its uniform consistency improves blending in industrial applications such as batteries, paints, and conductive coatings. The increased contact points in powder form provide better thermal stability and electrical performance in high-precision devices.
Benefits of Graphite Granules in Manufacturing
Graphite granules offer superior flowability and consistent particle size, enhancing precision in manufacturing processes such as molding and casting. Their larger, uniform structure improves thermal conductivity and reduces dust generation, leading to a safer and more efficient working environment. These benefits make graphite granules ideal for applications requiring uniform heat distribution and improved material handling.
Safety and Handling Differences
Graphite powder poses a higher inhalation risk due to its fine particle size, requiring the use of respiratory protection and controlled ventilation during handling, whereas graphite granules have reduced airborne dust generation, making them safer for general handling. Powder form is more prone to static buildup and combustion under specific conditions, so grounding and fire prevention measures are critical, while granules exhibit lower flammability risks. Proper personal protective equipment (PPE) and dust control practices are essential when working with graphite powder to minimize exposure, compared to the relatively straightforward handling procedures for granules.
Cost Considerations: Powder vs Granules
Graphite powder generally costs less than graphite granules due to its simpler manufacturing process and higher availability, making it a budget-friendly option for large-scale industrial applications. Granules, requiring more precise processing to maintain size uniformity and particle integrity, tend to be more expensive but offer better flow properties and reduced dust generation. Cost considerations should balance budget constraints with the performance requirements, as powder suits applications emphasizing affordability while granules justify higher costs with enhanced handling and material consistency.
Choosing the Right Form: Factors to Consider
Choosing the right form between graphite powder and graphite granules depends on application-specific factors such as surface area, particle size, and flow properties. Graphite powder offers higher surface area and is ideal for lubrication and conductive coatings, while granules provide better flowability and are preferred in metallurgy and battery electrodes. Consider the required dispersion, processing methods, and end-use performance to determine the optimal graphite form for your needs.
Graphite Powder vs Graphite Granules Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com