Graphite felt offers superior thermal conductivity and excellent chemical resistance compared to glass wool, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation applications. Its lightweight and flexible structure enhances durability while providing efficient heat retention. Glass wool, while cost-effective and widely used, lacks the high-temperature stability and robustness that graphite felt delivers in demanding industrial settings.
Table of Comparison
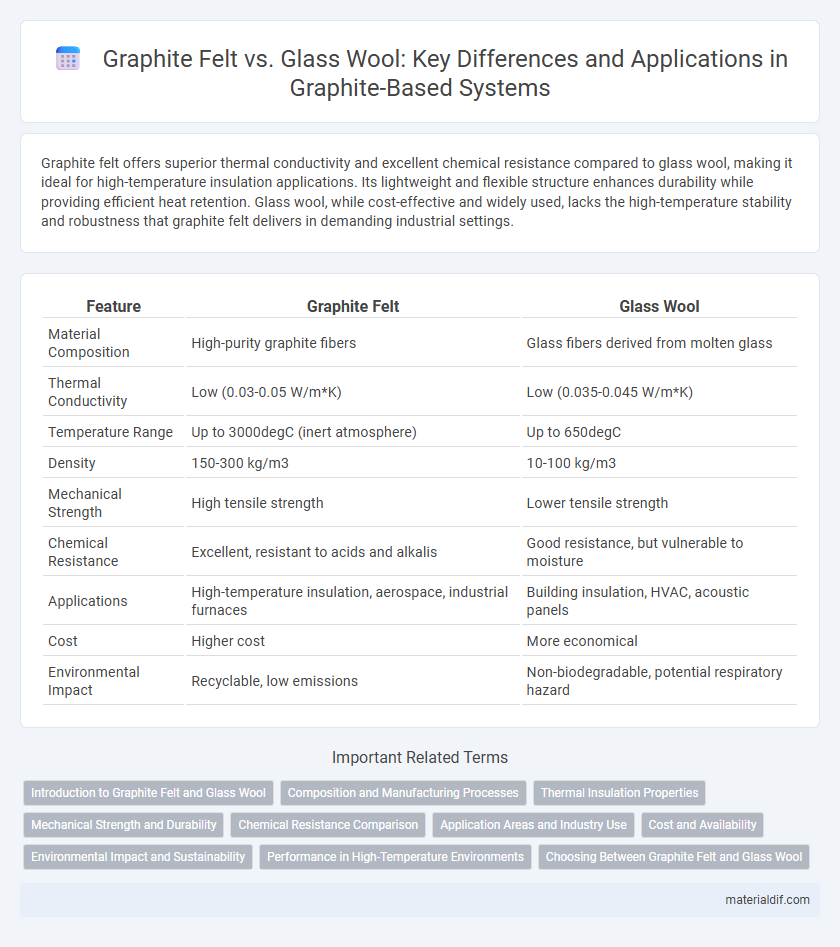
| Feature | Graphite Felt | Glass Wool |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | High-purity graphite fibers | Glass fibers derived from molten glass |
| Thermal Conductivity | Low (0.03-0.05 W/m*K) | Low (0.035-0.045 W/m*K) |
| Temperature Range | Up to 3000degC (inert atmosphere) | Up to 650degC |
| Density | 150-300 kg/m3 | 10-100 kg/m3 |
| Mechanical Strength | High tensile strength | Lower tensile strength |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent, resistant to acids and alkalis | Good resistance, but vulnerable to moisture |
| Applications | High-temperature insulation, aerospace, industrial furnaces | Building insulation, HVAC, acoustic panels |
| Cost | Higher cost | More economical |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, low emissions | Non-biodegradable, potential respiratory hazard |
Introduction to Graphite Felt and Glass Wool
Graphite felt is a high-temperature insulation material made from expanded graphite fibers, known for its excellent thermal conductivity and resistance to oxidation, widely used in industrial applications such as heat treatment and energy storage. Glass wool consists of fine glass fibers formed into a mat, offering superior thermal insulation, sound absorption, and fire resistance, commonly utilized in building insulation and HVAC systems. Both materials differ significantly in composition, thermal performance, and typical industrial applications, with graphite felt excelling in high-temperature environments and glass wool preferred for general insulation needs.
Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Graphite felt is composed primarily of flexible graphite fibers produced through high-temperature graphitization of carbon precursors, resulting in excellent thermal conductivity and chemical resistance. Glass wool consists of fine fibers of molten glass spun into a wool-like mat, offering high thermal insulation but lower thermal conductivity compared to graphite felt. Manufacturing graphite felt involves carbonizing and graphitizing fibrous precursors under controlled atmospheres, whereas glass wool is created by melting raw materials and fiberizing them using centrifugal or blowing techniques.
Thermal Insulation Properties
Graphite felt exhibits superior thermal insulation properties compared to glass wool, offering lower thermal conductivity and enhanced heat resistance up to 3000degC. The unique porous structure of graphite felt minimizes heat loss, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications. In contrast, glass wool insulation typically operates effectively only up to around 450degC and may degrade under extreme thermal conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Graphite felt exhibits superior mechanical strength and durability compared to glass wool, making it more resistant to compression and wear in high-temperature environments. Its robust fiber structure provides excellent tensile strength and dimensional stability under thermal cycling, whereas glass wool tends to degrade and lose integrity over time with prolonged heat exposure. This enhanced durability positions graphite felt as a preferred insulation material in industrial applications requiring long-lasting thermal performance.
Chemical Resistance Comparison
Graphite felt exhibits superior chemical resistance compared to glass wool, particularly against acidic and alkaline environments, making it ideal for harsh industrial applications. Its inert carbon structure withstands corrosion from strong chemicals, whereas glass wool fibers can degrade when exposed to aggressive substances over time. This durability ensures longer service life and reduced maintenance costs in chemical processing or high-temperature filtration systems.
Application Areas and Industry Use
Graphite felt exhibits superior thermal conductivity and chemical resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature insulation in aerospace, metallurgy, and petrochemical industries. Glass wool is widely applied in building insulation, HVAC systems, and soundproofing due to its cost-effectiveness and excellent acoustic properties. Industrial users prefer graphite felt for furnace insulation and thermal management, while glass wool dominates residential and commercial construction for energy efficiency and noise control.
Cost and Availability
Graphite felt offers superior thermal insulation at a higher initial cost compared to glass wool, which remains more affordable and widely available. The price of graphite felt fluctuates due to limited manufacturing sources, while glass wool benefits from mass production, ensuring consistent supply and lower market prices. Industries requiring long-term durability and high-temperature resistance often opt for graphite felt despite its higher cost because glass wool's availability cannot match the specialized performance needs.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphite felt exhibits superior sustainability compared to glass wool, as its manufacturing process consumes less energy and generates fewer emissions. Graphite felt is also more durable and recyclable, reducing landfill waste and environmental pollution over its lifecycle. Glass wool, typically made from silica sand and recycled glass, has higher embodied energy and lower thermal efficiency, leading to increased operational energy consumption and carbon footprint.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Graphite felt outperforms glass wool in high-temperature environments due to its superior thermal stability and resistance to oxidation at temperatures exceeding 1600degC. Its low thermal conductivity ensures excellent insulation, reducing heat loss in industrial applications such as furnaces and kilns. Glass wool, limited to around 450degC, degrades faster and loses insulating properties when exposed to extreme heat, making graphite felt a more durable choice for performance-critical settings.
Choosing Between Graphite Felt and Glass Wool
Graphite Felt offers superior thermal conductivity and higher temperature resistance compared to Glass Wool, making it ideal for industrial insulation applications requiring durability under extreme heat. Glass Wool provides excellent sound absorption and cost-effective thermal insulation suitable for residential and commercial building use. Choosing between Graphite Felt and Glass Wool depends on the specific requirements for temperature tolerance, thermal performance, and budget constraints in the intended application.
Graphite Felt vs Glass Wool Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com