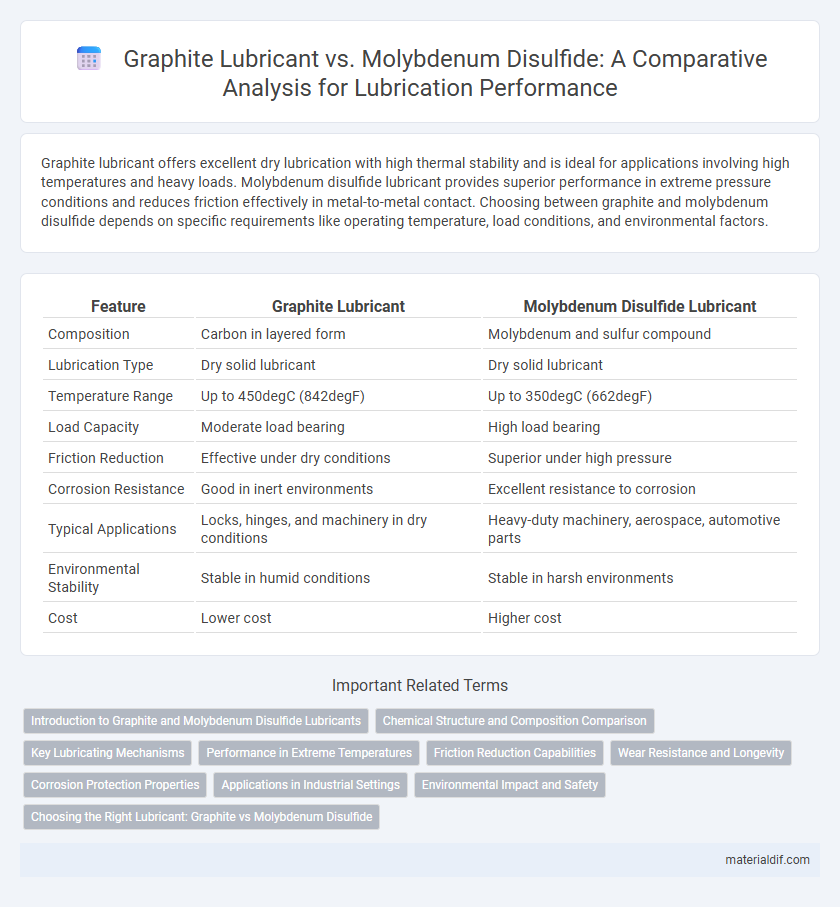
Graphite lubricant offers excellent dry lubrication with high thermal stability and is ideal for applications involving high temperatures and heavy loads. Molybdenum disulfide lubricant provides superior performance in extreme pressure conditions and reduces friction effectively in metal-to-metal contact. Choosing between graphite and molybdenum disulfide depends on specific requirements like operating temperature, load conditions, and environmental factors.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphite Lubricant | Molybdenum Disulfide Lubricant |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Carbon in layered form | Molybdenum and sulfur compound |
| Lubrication Type | Dry solid lubricant | Dry solid lubricant |
| Temperature Range | Up to 450degC (842degF) | Up to 350degC (662degF) |
| Load Capacity | Moderate load bearing | High load bearing |
| Friction Reduction | Effective under dry conditions | Superior under high pressure |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good in inert environments | Excellent resistance to corrosion |
| Typical Applications | Locks, hinges, and machinery in dry conditions | Heavy-duty machinery, aerospace, automotive parts |
| Environmental Stability | Stable in humid conditions | Stable in harsh environments |
| Cost | Lower cost | Higher cost |
Introduction to Graphite and Molybdenum Disulfide Lubricants
Graphite lubricant, composed of layered carbon atoms, offers exceptional thermal stability and excellent dry lubrication properties, reducing friction in high-temperature environments. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) lubricant features a unique laminar structure that provides superior load-carrying capacity and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for heavy-duty applications. Both lubricants function by creating a low-friction film, but graphite excels in oxidizing conditions while molybdenum disulfide performs better under extreme pressure and moisture exposure.
Chemical Structure and Composition Comparison
Graphite lubricant consists primarily of layers of carbon atoms arranged in a hexagonal lattice, creating a planar structure that facilitates easy shear between layers and excellent lubrication properties. In contrast, molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) lubricant features a layered structure composed of molybdenum atoms sandwiched between sulfur atoms, providing strong interlayer bonding and exceptional load-bearing capacity. The chemical composition of graphite is pure carbon (C), while molybdenum disulfide is a compound of molybdenum (Mo) and sulfur (S), influencing their respective friction-reducing mechanisms and thermal stability.
Key Lubricating Mechanisms
Graphite lubricant reduces friction primarily through its layered crystal structure, allowing easy shear between layers under pressure and heat. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) acts by forming a solid lubricating film with low shear strength, providing effective lubrication even in extreme conditions like high vacuum or heavy loads. Both materials excel in dry lubrication, but MoS2 tends to offer superior performance in high-pressure environments due to its stronger chemical stability and film formation.
Performance in Extreme Temperatures
Graphite lubricant offers excellent performance in extreme temperatures due to its ability to withstand heat up to 4500degF (2482degC) without breaking down, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. In contrast, molybdenum disulfide lubricant operates effectively up to approximately 750degF (400degC) but degrades beyond this, limiting its use in ultra-high-temperature environments. Both lubricants provide low friction and wear resistance, but graphite's exceptional thermal stability gives it a distinct advantage in extreme heat conditions.
Friction Reduction Capabilities
Graphite lubricant offers excellent friction reduction due to its layered crystal structure, which allows easy shear between layers, making it ideal for high-temperature applications. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) lubricant exhibits superior friction reduction in extreme pressure and vacuum environments thanks to its ability to maintain low friction under heavy loads. Both lubricants effectively minimize wear, but MoS2 outperforms graphite in maintaining consistent low friction under high-stress conditions.
Wear Resistance and Longevity
Graphite lubricant offers excellent wear resistance by forming a durable, self-lubricating film that reduces friction and extends component longevity under high temperature conditions. Molybdenum disulfide lubricant provides superior load-bearing capacity and wear protection, especially in extreme pressure environments, which significantly enhances equipment lifespan. Both lubricants improve wear resistance and longevity, but molybdenum disulfide excels in heavy-duty applications due to its greater hardness and stability.
Corrosion Protection Properties
Graphite lubricant offers excellent corrosion protection by forming a stable, dry film that resists moisture and chemical exposure, preventing rust and metal degradation. Molybdenum disulfide (MoS2) lubricant also provides corrosion resistance but primarily excels under high-pressure and high-temperature conditions, where its layered structure reduces friction and wear. For long-term corrosion protection in humid or chemically aggressive environments, graphite lubricant is more effective, whereas MoS2 is preferred for combined lubrication and moderate corrosion prevention in extreme mechanical conditions.
Applications in Industrial Settings
Graphite lubricant excels in high-temperature industrial applications such as foundries, steel mills, and automotive manufacturing due to its excellent thermal stability and dry lubrication properties. Molybdenum disulfide lubricant is preferred for heavy-duty machinery and high-pressure environments like mining equipment and hydraulic systems, offering superior load-carrying capacity and protection against wear. Both lubricants improve equipment lifespan and efficiency by reducing friction, but selection depends on specific operational conditions and performance requirements.
Environmental Impact and Safety
Graphite lubricant offers excellent environmental benefits due to its natural composition and biodegradability, posing minimal risks during disposal and use. Molybdenum disulfide lubricant, while effective in reducing friction, may contain trace heavy metals that raise environmental concerns and require careful handling to prevent soil and water contamination. Both lubricants necessitate safety measures, but graphite's non-toxic profile generally makes it safer for workers and ecosystems during application and degradation.
Choosing the Right Lubricant: Graphite vs Molybdenum Disulfide
Graphite lubricant excels in high-temperature environments and offers excellent conductivity, making it ideal for applications requiring dry lubrication and electrical conductivity. Molybdenum disulfide lubricant provides superior load-bearing capacity and wear resistance under extreme pressure, suited for heavy machinery and metal-on-metal contacts. Selecting the right lubricant depends on operational conditions such as temperature, load, and the need for conductivity or protection against friction and wear.
Graphite Lubricant vs Molybdenum Disulfide Lubricant Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com