Lump graphite features irregular, coarse particles formed from natural graphite veins, offering higher purity and excellent conductivity ideal for industrial applications. Flake graphite consists of thin, flat layers that can be easily separated, providing superior lubrication and flexibility for uses in batteries and lubricants. Both types vary in structure and performance, influencing their suitability across diverse sectors such as metallurgy and energy storage.
Table of Comparison
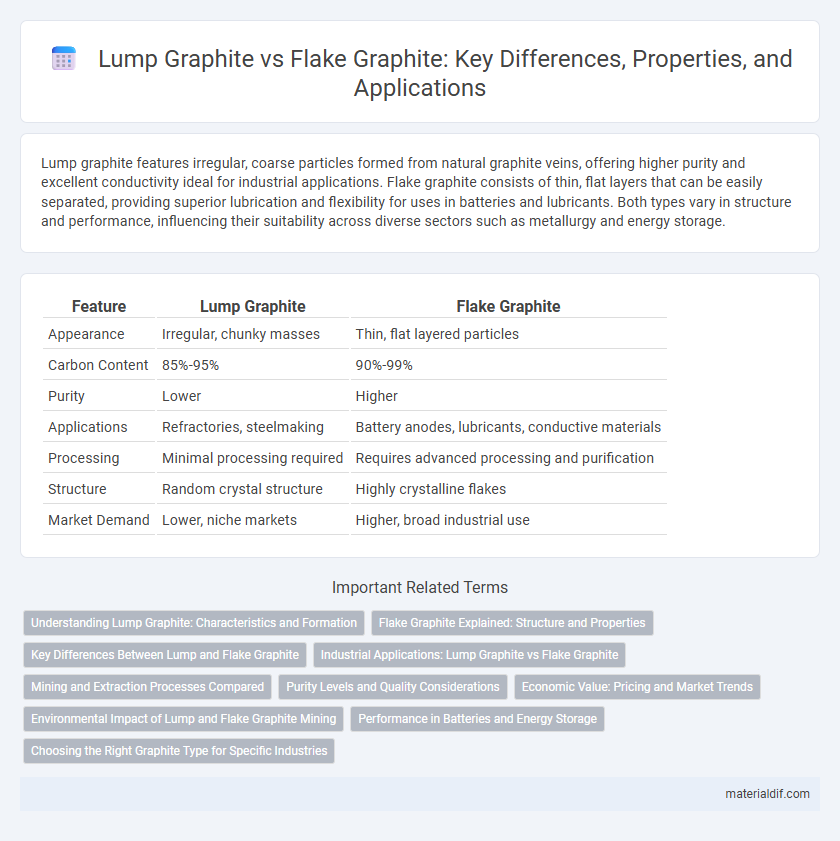
| Feature | Lump Graphite | Flake Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Appearance | Irregular, chunky masses | Thin, flat layered particles |
| Carbon Content | 85%-95% | 90%-99% |
| Purity | Lower | Higher |
| Applications | Refractories, steelmaking | Battery anodes, lubricants, conductive materials |
| Processing | Minimal processing required | Requires advanced processing and purification |
| Structure | Random crystal structure | Highly crystalline flakes |
| Market Demand | Lower, niche markets | Higher, broad industrial use |
Understanding Lump Graphite: Characteristics and Formation
Lump graphite is a naturally occurring form of graphite characterized by its coarse and chunky texture, resulting from the slow crystallization of carbon under high-temperature and high-pressure geological conditions. Unlike flake graphite, which forms thin, flat layers, lump graphite consists of irregular, tightly packed masses that exhibit high purity and excellent electrical conductivity. Its formation typically involves metamorphic processes in carbon-rich sedimentary rocks, leading to distinctive crystal structures beneficial for industrial applications such as refractory materials and lubricants.
Flake Graphite Explained: Structure and Properties
Flake graphite consists of thin, flat, plate-like particles with a hexagonal crystalline structure that provides excellent lubricity and high electrical conductivity. Its unique morphology allows for superior thermal stability, making it widely used in batteries, refractories, and conductive materials. The large surface area and high purity of flake graphite enhance its performance in applications requiring efficient heat dissipation and chemical resistance.
Key Differences Between Lump and Flake Graphite
Lump graphite consists of natural, irregularly shaped chunks formed by the heat and pressure of metamorphic processes, offering higher purity and superior conductivity compared to flake graphite. Flake graphite appears as thin, flat, layered plates, making it more suitable for applications requiring expansion and flexibility, such as lubricants and batteries. Key differences include morphology, purity levels, and crystalline structure, which influence their respective industrial uses and processing methods.
Industrial Applications: Lump Graphite vs Flake Graphite
Lump graphite is preferred in industrial applications requiring high thermal conductivity and wear resistance, such as in steelmaking and refractory linings, due to its dense, compact structure. Flake graphite, with its layered, flaky form, excels in applications like battery anodes, lubricants, and expandable graphite production because of its larger surface area and ease of exfoliation. Both types serve critical roles in manufacturing, but the choice depends on the specific thermal, mechanical, and chemical property requirements of the end-use.
Mining and Extraction Processes Compared
Lump graphite is typically extracted through open-pit or underground mining methods, followed by crushing and grading to separate pure carbon flakes, while flake graphite mining focuses on extracting large, flat flakes via similar techniques but often requires more intensive flotation and beneficiation processes to increase purity. Lump graphite generally demands less processing due to its natural crystalline form, resulting in lower extraction costs compared to flake graphite, which involves additional steps like grinding, screening, and chemical treatment to achieve high-quality output. Both graphite types rely on careful geological survey and resource estimation to optimize extraction efficiency and minimize environmental impact.
Purity Levels and Quality Considerations
Lump graphite and flake graphite differ significantly in purity levels and quality considerations, with lump graphite typically exhibiting higher purity due to its natural, crystalline structure and minimal processing requirements. Flake graphite, while abundant and versatile, often contains more impurities and requires extensive purification to achieve high-grade applications, especially in battery and refractory materials. The choice between lump and flake graphite hinges on the desired purity, with lump graphite favored for applications demanding exceptional quality and minimal contamination.
Economic Value: Pricing and Market Trends
Lump graphite typically commands higher prices than flake graphite due to its purity and suitability for specialized industrial applications such as refractory materials and battery anodes. Flake graphite dominates the market volume with broader uses in lubricants, conductive materials, and expandable graphite, influencing its pricing volatility based on demand fluctuations in multiple sectors. Market trends indicate increasing investment in flake graphite production driven by electric vehicle battery growth, while lump graphite retains premium status in niche markets requiring superior performance.
Environmental Impact of Lump and Flake Graphite Mining
Lump graphite mining typically involves surface or open-pit extraction methods that result in less environmental disturbance and lower energy consumption compared to flake graphite mining, which often requires deeper, more invasive operations like underground mining. Flake graphite extraction generates higher volumes of waste rock and tailings, increasing the potential for soil and water contamination due to the release of heavy metals and chemicals used in processing. Reclamation and management practices are critical to mitigating the ecological footprint of both lump and flake graphite mining, but flake graphite's larger scale and intensive processing generally lead to greater environmental challenges.
Performance in Batteries and Energy Storage
Lump graphite exhibits higher electrical conductivity and purity, making it ideal for enhancing battery performance and energy storage efficiency in lithium-ion cells. Flake graphite offers superior surface area and structural stability, which benefits electrode longevity and charge-discharge cycling in energy storage systems. Both forms impact battery capacity and lifecycle differently, with lump graphite optimizing power density and flake graphite improving durability.
Choosing the Right Graphite Type for Specific Industries
Lump graphite offers high purity and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for industries like refractory manufacturing and steel production where thermal resistance and structural integrity are critical. Flake graphite, characterized by its layered structure and high surface area, is preferred in battery production, lubricants, and conductive materials due to its adaptability and efficient electron flow. Selecting the appropriate graphite form depends on specific industrial requirements such as thermal stability, electrical conductivity, and mechanical strength.
Lump Graphite vs Flake Graphite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com