Refractory graphite is characterized by its high thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, making it ideal for use in extreme temperature environments such as furnace linings and aerospace components. Lubricating graphite, on the other hand, excels in reducing friction due to its layered structure, commonly used in machinery and automotive applications to enhance performance and durability. Understanding the distinct properties of refractory and lubricating graphite is essential for selecting the appropriate type for industrial and mechanical purposes.
Table of Comparison
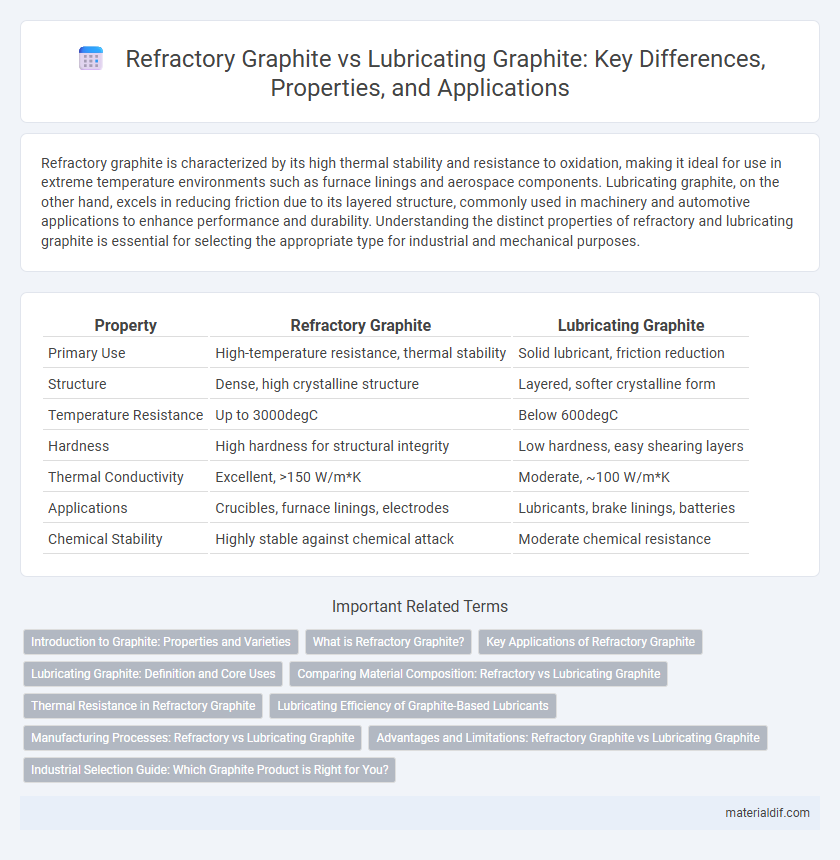
| Property | Refractory Graphite | Lubricating Graphite |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | High-temperature resistance, thermal stability | Solid lubricant, friction reduction |
| Structure | Dense, high crystalline structure | Layered, softer crystalline form |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 3000degC | Below 600degC |
| Hardness | High hardness for structural integrity | Low hardness, easy shearing layers |
| Thermal Conductivity | Excellent, >150 W/m*K | Moderate, ~100 W/m*K |
| Applications | Crucibles, furnace linings, electrodes | Lubricants, brake linings, batteries |
| Chemical Stability | Highly stable against chemical attack | Moderate chemical resistance |
Introduction to Graphite: Properties and Varieties
Refractory graphite exhibits exceptional thermal stability and high melting points, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace linings and crucibles. Lubricating graphite offers excellent lubricity due to its layered crystal structure, reducing friction in mechanical systems and improving wear resistance. These distinct properties arise from variations in purity, crystallinity, and particle size between refractory and lubricating graphite grades.
What is Refractory Graphite?
Refractory graphite is a high-purity form of graphite known for its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to oxidation, making it essential in high-temperature industrial applications such as metallurgy and aerospace. This type of graphite maintains structural integrity at temperatures above 3000degC, unlike lubricating graphite, which primarily functions as a solid lubricant. Its unique crystalline structure offers superior mechanical strength and thermal conductivity, enabling critical performance in refractory linings, electrodes, and heat exchangers.
Key Applications of Refractory Graphite
Refractory graphite exhibits exceptional thermal resistance and structural stability at high temperatures, making it ideal for applications in electric arc furnace linings, rocket nozzles, and high-temperature crucibles used in metal casting. Its ability to maintain mechanical integrity in extreme environments supports its use in heat exchangers and nuclear reactors where durability and heat resistance are critical. Unlike lubricating graphite, refractory graphite's primary role centers on structural applications requiring sustained performance under intense thermal and mechanical stress.
Lubricating Graphite: Definition and Core Uses
Lubricating graphite, characterized by its layered crystal structure, excels in reducing friction and wear in mechanical systems by acting as a dry lubricant under extreme temperatures and pressures. Primarily utilized in automotive brake linings, industrial machinery, and electrical contacts, lubricating graphite provides enhanced thermal stability and conductivity while maintaining excellent lubrication properties. Its ability to maintain performance in harsh environments makes it essential for applications requiring reliable, efficient friction management.
Comparing Material Composition: Refractory vs Lubricating Graphite
Refractory graphite is characterized by high purity and a dense crystalline structure composed primarily of natural flake graphite with minimal impurities, which imparts exceptional heat resistance and mechanical strength suitable for high-temperature industrial applications. Lubricating graphite contains a higher proportion of fine, amorphous graphite particles mixed with additives that enhance its self-lubricating properties, reducing friction in mechanical systems. The key distinction lies in the material composition: refractory graphite emphasizes thermal stability and structural integrity, while lubricating graphite prioritizes particle size and morphology to optimize lubrication performance.
Thermal Resistance in Refractory Graphite
Refractory graphite exhibits exceptional thermal resistance, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace linings and aerospace components. Its crystalline structure provides superior stability and durability under extreme thermal stress compared to lubricating graphite, which primarily focuses on reducing friction rather than resisting heat. This enhanced thermal resistance ensures refractory graphite maintains structural integrity and performance in environments exceeding 3000degC.
Lubricating Efficiency of Graphite-Based Lubricants
Lubricating graphite exhibits exceptional lubricating efficiency due to its layered crystal structure, which allows easy shear between layers, reducing friction and wear in mechanical applications. Compared to refractory graphite, lubricating graphite contains higher purity carbon with fewer impurities, enhancing its performance in high-pressure and high-temperature lubrication environments. Graphite-based lubricants minimize metal-to-metal contact, improve energy efficiency, and extend the lifespan of moving parts in automotive, industrial, and aerospace machinery.
Manufacturing Processes: Refractory vs Lubricating Graphite
Refractory graphite is produced through high-temperature treatment of carbon-rich precursors, involving processes like graphitization at temperatures above 2500degC to enhance thermal stability and mechanical strength. Lubricating graphite manufacturing typically involves milling natural graphite to fine powders, followed by purification and surface treatments to improve lubricity and reduce impurities. The key distinction lies in refractory graphite's intensive heat treatment for structural integrity, whereas lubricating graphite focuses on particle size refinement and purity for optimal lubrication performance.
Advantages and Limitations: Refractory Graphite vs Lubricating Graphite
Refractory graphite offers exceptional thermal stability and mechanical strength, making it ideal for high-temperature industrial applications like furnace linings, whereas lubricating graphite excels in reducing friction and wear in mechanical systems due to its layered structure. The main limitation of refractory graphite lies in its lower lubricity, which restricts its use where friction reduction is critical, while lubricating graphite lacks the high-temperature resistance needed for extreme thermal environments. Selecting between refractory and lubricating graphite depends on balancing the need for thermal endurance against the requirement for effective lubrication in specific applications.
Industrial Selection Guide: Which Graphite Product is Right for You?
Refractory graphite is ideal for high-temperature industrial applications such as furnace linings and electrodes due to its exceptional thermal stability and resistance to chemical corrosion. Lubricating graphite excels in reducing friction and wear in mechanical systems, making it suitable for automotive parts, bearings, and seals. Selecting the right graphite product depends on the specific operational conditions, desired performance characteristics, and environmental factors in your industrial application.
Refractory Graphite vs Lubricating Graphite Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com