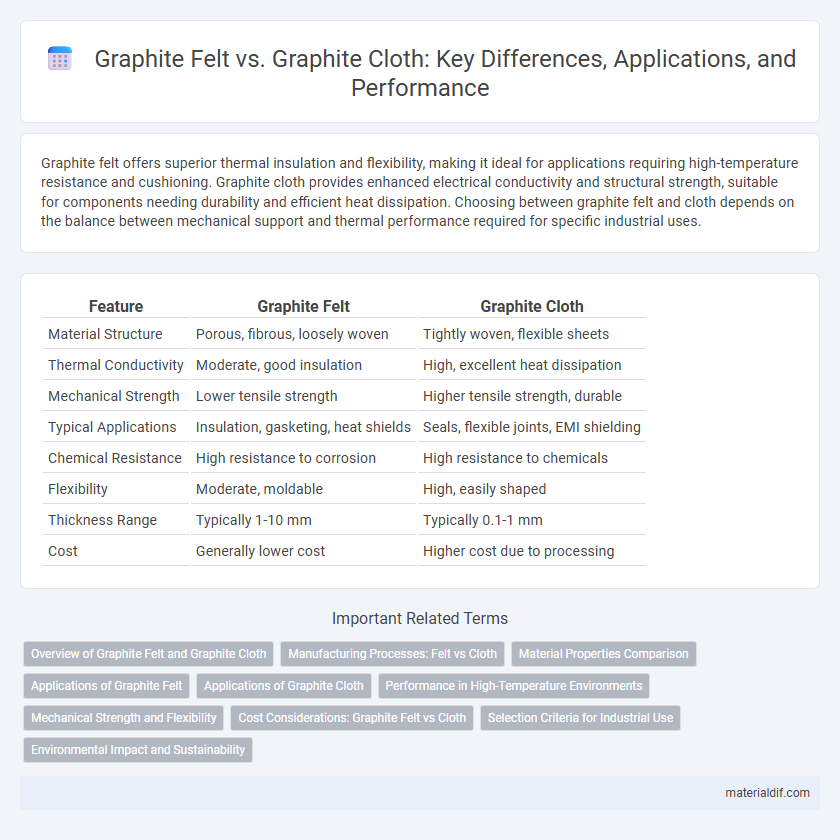
Graphite felt offers superior thermal insulation and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring high-temperature resistance and cushioning. Graphite cloth provides enhanced electrical conductivity and structural strength, suitable for components needing durability and efficient heat dissipation. Choosing between graphite felt and cloth depends on the balance between mechanical support and thermal performance required for specific industrial uses.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Graphite Felt | Graphite Cloth |
|---|---|---|
| Material Structure | Porous, fibrous, loosely woven | Tightly woven, flexible sheets |
| Thermal Conductivity | Moderate, good insulation | High, excellent heat dissipation |
| Mechanical Strength | Lower tensile strength | Higher tensile strength, durable |
| Typical Applications | Insulation, gasketing, heat shields | Seals, flexible joints, EMI shielding |
| Chemical Resistance | High resistance to corrosion | High resistance to chemicals |
| Flexibility | Moderate, moldable | High, easily shaped |
| Thickness Range | Typically 1-10 mm | Typically 0.1-1 mm |
| Cost | Generally lower cost | Higher cost due to processing |
Overview of Graphite Felt and Graphite Cloth
Graphite felt is a porous, flexible material made from carbon fibers, offering excellent thermal insulation and high-temperature resistance for applications such as furnace linings and thermal barriers. Graphite cloth consists of woven carbon fibers, providing superior mechanical strength, electrical conductivity, and chemical resistance, commonly used in aerospace and battery technologies. Both materials differ significantly in structure and properties, influencing their suitability for specific industrial uses.
Manufacturing Processes: Felt vs Cloth
Graphite felt is produced through a fiber entanglement process where graphite fibers are randomly oriented and bonded into a non-woven mat, resulting in a highly porous, flexible material ideal for insulation and filtration. Graphite cloth manufacturing involves weaving graphite fibers into a tight, uniform fabric, offering superior strength, electrical conductivity, and dimensional stability for applications requiring durability and precision. The distinct manufacturing techniques of felt and cloth directly influence their mechanical properties, porosity, and performance in high-temperature environments.
Material Properties Comparison
Graphite felt offers superior thermal insulation and flexibility due to its porous, fibrous structure, making it ideal for high-temperature sealing applications. Graphite cloth features a tighter weave with enhanced mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, suited for environments requiring durability and efficient heat dissipation. Both materials exhibit excellent chemical resistance and oxidation stability, but graphite cloth generally provides higher tensile strength and lower compressibility compared to graphite felt.
Applications of Graphite Felt
Graphite felt is highly valued in high-temperature applications such as thermal insulation, fuel cells, and industrial furnaces due to its superior heat resistance, flexibility, and porous structure, which enables excellent thermal shock absorption and gas permeability. Unlike graphite cloth, graphite felt provides enhanced cushioning and sealing capabilities, making it ideal for gasketing and filtration in chemical processing and aerospace industries. Its lightweight and compressibility also contribute to its effectiveness in battery electrodes and heat management systems, where durability and surface area are critical.
Applications of Graphite Cloth
Graphite cloth is widely used in aerospace and automotive industries for thermal insulation and electromagnetic shielding due to its high tensile strength and excellent thermal conductivity. Its flexible, lightweight structure makes it ideal for applications requiring durability and resistance to extreme temperatures, such as heat exchangers and battery thermal management systems. Unlike graphite felt, graphite cloth offers superior mechanical stability and dimensional consistency, making it preferred for precision components and structural reinforcement.
Performance in High-Temperature Environments
Graphite felt offers superior thermal insulation and flexibility, making it ideal for high-temperature environments requiring efficient heat resistance and shock absorption up to 3000degF (1650degC). Graphite cloth provides higher mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, suitable for applications demanding durability and thermal stability at elevated temperatures. Choosing between graphite felt and cloth depends on balancing insulation performance versus structural integrity in extreme heat conditions.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility
Graphite felt exhibits superior flexibility due to its fibrous structure, allowing it to conform to irregular shapes while maintaining mechanical integrity. Graphite cloth, composed of woven carbon fibers, offers enhanced mechanical strength and durability under high-stress conditions but with reduced flexibility compared to felt. The choice between graphite felt and cloth depends on application requirements balancing flexibility and tensile strength performance.
Cost Considerations: Graphite Felt vs Cloth
Graphite felt is generally more cost-effective than graphite cloth due to its lower manufacturing complexity and material density, making it suitable for large-scale insulation and filtration applications. Graphite cloth, while higher in price, offers superior mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, justifying its use in specialized high-performance environments. Budget allocation for projects should balance the initial cost savings of graphite felt against the long-term durability and efficiency benefits provided by graphite cloth.
Selection Criteria for Industrial Use
Graphite felt offers higher thermal insulation and flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring conformability and resistance to thermal shock in industrial settings. Graphite cloth provides superior mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, which suits applications demanding durability and efficient heat dissipation. Selection between graphite felt and graphite cloth depends on factors such as temperature range, mechanical stress, chemical exposure, and required electrical properties in the specific industrial process.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Graphite felt exhibits lower environmental impact than graphite cloth due to its production process, which typically consumes less energy and generates fewer emissions. Graphite cloth, while offering superior strength and flexibility, often involves more intensive manufacturing and resource use, leading to a higher carbon footprint. Sustainable applications favor graphite felt for energy-efficient industries aiming to minimize ecological damage and carbon emissions during production.
Graphite Felt vs Graphite Cloth Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com