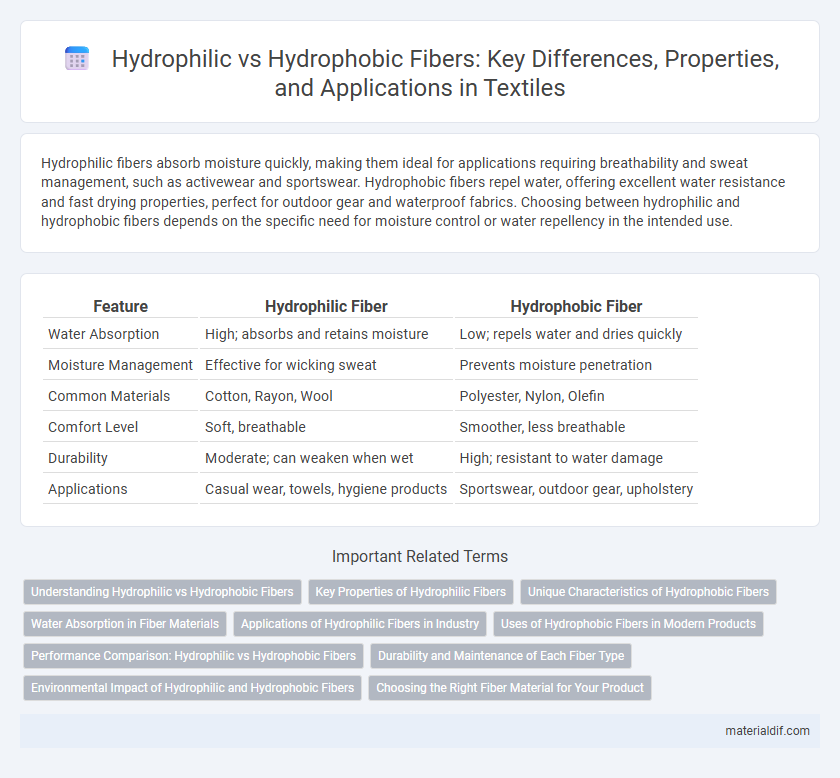
Hydrophilic fibers absorb moisture quickly, making them ideal for applications requiring breathability and sweat management, such as activewear and sportswear. Hydrophobic fibers repel water, offering excellent water resistance and fast drying properties, perfect for outdoor gear and waterproof fabrics. Choosing between hydrophilic and hydrophobic fibers depends on the specific need for moisture control or water repellency in the intended use.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Hydrophilic Fiber | Hydrophobic Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Water Absorption | High; absorbs and retains moisture | Low; repels water and dries quickly |
| Moisture Management | Effective for wicking sweat | Prevents moisture penetration |
| Common Materials | Cotton, Rayon, Wool | Polyester, Nylon, Olefin |
| Comfort Level | Soft, breathable | Smoother, less breathable |
| Durability | Moderate; can weaken when wet | High; resistant to water damage |
| Applications | Casual wear, towels, hygiene products | Sportswear, outdoor gear, upholstery |
Understanding Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic Fibers
Hydrophilic fibers absorb and retain moisture, making them ideal for applications requiring breathability and comfort, such as athletic wear and medical textiles. Hydrophobic fibers repel water, providing resistance to moisture and quick-drying properties, beneficial for outdoor and performance fabrics. Understanding the molecular structure differences helps in selecting fibers for specific environmental and functional requirements.
Key Properties of Hydrophilic Fibers
Hydrophilic fibers exhibit high moisture absorption and excellent wicking properties, making them ideal for applications requiring sweat management and breathability, such as activewear and medical textiles. These fibers, including cotton and rayon, readily attract and retain water molecules due to their polar chemical structure, which enhances comfort by maintaining skin dryness. The key properties of hydrophilic fibers also include biodegradability and softness, contributing to their sustainability and user-friendly tactile experience.
Unique Characteristics of Hydrophobic Fibers
Hydrophobic fibers, characterized by their low moisture absorption and high water resistance, excel in delivering quick-drying performance and maintaining structural integrity under wet conditions. These fibers, including polyester and polypropylene, repel water molecules, reducing microbial growth and enhancing durability for outdoor and activewear applications. Their non-absorbent nature also contributes to lightweight textiles that resist stains and maintain breathability during intense physical activities.
Water Absorption in Fiber Materials
Hydrophilic fibers, such as cotton and viscose, exhibit high water absorption due to their polar chemical structure that attracts and retains water molecules effectively. In contrast, hydrophobic fibers like polyester and polypropylene repel water, resulting in low moisture absorption and quick drying properties. The water absorption capacity significantly influences the performance and comfort of textile materials in applications ranging from clothing to medical textiles.
Applications of Hydrophilic Fibers in Industry
Hydrophilic fibers, characterized by their strong affinity for water, are extensively utilized in the medical industry for wound dressings and surgical sutures due to their excellent moisture absorption and breathability. In the textile sector, these fibers enhance comfort in activewear by effectively managing sweat and moisture. Their applications extend to filtration systems where hydrophilic fibers improve the efficiency of liquid filtration and separation processes.
Uses of Hydrophobic Fibers in Modern Products
Hydrophobic fibers repel water, making them ideal for use in outdoor apparel, sportswear, and waterproof gear where moisture resistance is essential. These fibers enhance product durability by preventing water absorption, thus maintaining lightweight and quick-drying properties. Modern applications also include medical textiles and filtration systems, leveraging their ability to resist liquid penetration and microbial growth.
Performance Comparison: Hydrophilic vs Hydrophobic Fibers
Hydrophilic fibers excel in moisture absorption and quick drying, making them ideal for activewear and medical textiles, whereas hydrophobic fibers repel water, enhancing durability and stain resistance in outdoor gear and upholstery. Hydrophilic fibers promote comfort by wicking sweat away from the skin, while hydrophobic fibers maintain thermal insulation by preventing water penetration. Performance comparison highlights hydrophilic fibers' effectiveness in moisture management versus hydrophobic fibers' superior water repellency and longevity.
Durability and Maintenance of Each Fiber Type
Hydrophilic fibers, such as cotton and rayon, absorb moisture easily, which can lead to faster wear and require more frequent washing to prevent bacterial growth and odor. Hydrophobic fibers, including polyester and nylon, repel water, enhancing durability by reducing fiber swelling and weakening caused by moisture exposure while offering easier maintenance and quicker drying times. Choosing hydrophobic fibers improves fabric longevity and reduces maintenance effort, especially in activewear and outdoor textiles.
Environmental Impact of Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Fibers
Hydrophilic fibers, such as cotton and rayon, absorb water and tend to biodegrade more rapidly in natural environments, resulting in a lower long-term environmental footprint. In contrast, hydrophobic fibers like polyester and nylon repel water, resist biodegradation, and contribute more significantly to microplastic pollution and persistent environmental contamination. Choosing hydrophilic fibers supports ecosystem health by reducing synthetic waste accumulation and enhancing biodegradability in soil and water systems.
Choosing the Right Fiber Material for Your Product
Hydrophilic fibers absorb moisture quickly, making them ideal for products requiring high moisture management, such as activewear and medical textiles. Hydrophobic fibers repel water, providing excellent drying properties and durability, suitable for outdoor gear and water-resistant apparel. Selecting the right fiber material depends on product function, moisture control needs, and end-user comfort requirements.
Hydrophilic Fiber vs Hydrophobic Fiber Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com