Copper tubing offers superior flexibility and ease of installation for plumbing and HVAC systems, making it ideal for transporting fluids and gases in various residential and industrial applications. In contrast, copper sheets provide excellent durability and conductivity, commonly used in roofing, electrical projects, and artistic designs where flat, malleable material is essential. Choosing between copper tubing and copper sheets depends on the specific requirements for shape, application, and mechanical strength.
Table of Comparison
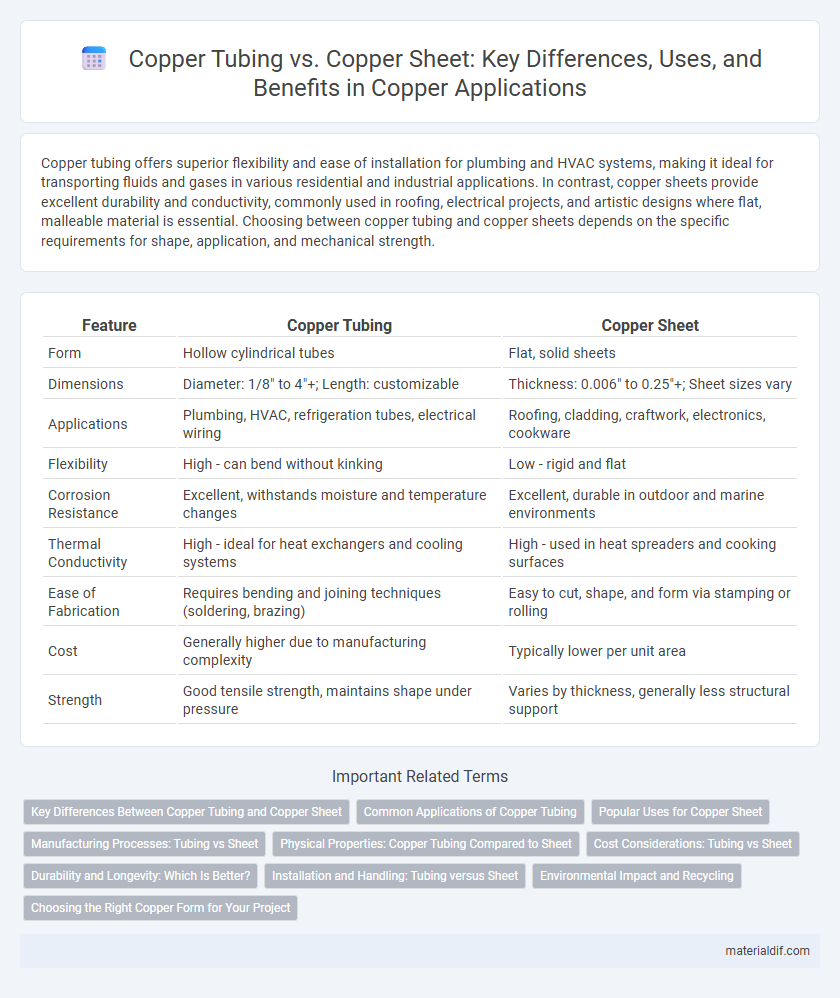
| Feature | Copper Tubing | Copper Sheet |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Hollow cylindrical tubes | Flat, solid sheets |
| Dimensions | Diameter: 1/8" to 4"+; Length: customizable | Thickness: 0.006" to 0.25"+; Sheet sizes vary |
| Applications | Plumbing, HVAC, refrigeration tubes, electrical wiring | Roofing, cladding, craftwork, electronics, cookware |
| Flexibility | High - can bend without kinking | Low - rigid and flat |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, withstands moisture and temperature changes | Excellent, durable in outdoor and marine environments |
| Thermal Conductivity | High - ideal for heat exchangers and cooling systems | High - used in heat spreaders and cooking surfaces |
| Ease of Fabrication | Requires bending and joining techniques (soldering, brazing) | Easy to cut, shape, and form via stamping or rolling |
| Cost | Generally higher due to manufacturing complexity | Typically lower per unit area |
| Strength | Good tensile strength, maintains shape under pressure | Varies by thickness, generally less structural support |
Key Differences Between Copper Tubing and Copper Sheet
Copper tubing features a hollow, cylindrical shape designed for fluid or gas transportation, while copper sheet is flat and solid, ideal for roofing, flashing, and crafting applications. The tubing's round cross-section provides structural integrity and flexibility for plumbing, HVAC, and refrigeration systems, whereas copper sheets offer uniform thickness and surface area suited for electrical components and decorative uses. Material thickness and fabrication methods differ significantly, with tubing requiring extrusion or seamless drawing processes, contrasting with the rolling and annealing used for copper sheets.
Common Applications of Copper Tubing
Copper tubing is widely used in plumbing, HVAC systems, and refrigeration due to its excellent thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance. Its flexibility and durability make it ideal for water supply lines, gas lines, and medical gas systems in hospitals. Copper tubing is also essential in heat exchangers and air conditioning units where efficient heat transfer is critical.
Popular Uses for Copper Sheet
Copper sheet is widely used in roofing, flashing, and decorative architectural features due to its durability and corrosion resistance. It also finds applications in electrical components and heat exchangers because of its excellent thermal and electrical conductivity. In contrast to copper tubing, which is primarily used for plumbing and HVAC systems, copper sheets provide versatile flat surfaces ideal for fabrication and metalworking projects.
Manufacturing Processes: Tubing vs Sheet
Copper tubing is manufactured primarily through extrusion and drawing processes, which involve pulling heated copper billets through dies to create seamless, cylindrical shapes with precise dimensions. In contrast, copper sheets are produced by rolling large copper slabs into thin, flat layers using hot and cold rolling techniques, ensuring uniform thickness and smooth surfaces. Both processes require controlled annealing to enhance ductility, but tubing demands tighter tolerances for diameter and wall thickness compared to sheet production.
Physical Properties: Copper Tubing Compared to Sheet
Copper tubing exhibits greater flexibility and tensile strength compared to copper sheets, making it ideal for plumbing and HVAC applications requiring durability and corrosion resistance. Copper sheets, by contrast, offer superior malleability and surface area, suited for fabrication, roofing, and artistic uses. The distinct physical properties result from their differing thicknesses and manufacturing processes, influencing their thermal conductivity and mechanical resilience.
Cost Considerations: Tubing vs Sheet
Copper tubing generally costs more than copper sheet due to its complex manufacturing process, which involves extrusion and drawing to achieve precise dimensions and durability. Copper sheet is typically less expensive because it requires simpler rolling and cutting processes, making it more accessible for large surface applications. When budgeting for projects, consider that tubing's higher material and fabrication costs may be offset by its suitability for plumbing and HVAC systems, while sheets offer cost-effective solutions for roofing and decorative uses.
Durability and Longevity: Which Is Better?
Copper tubing offers superior durability due to its seamless, cylindrical structure, which resists pressure and corrosion more effectively than copper sheets. Copper sheets, while versatile and easier to fabricate, are more prone to dents and surface damage, reducing their longevity in high-stress applications. For long-term use in plumbing and industrial settings, copper tubing generally outlasts copper sheets by maintaining structural integrity under variable conditions.
Installation and Handling: Tubing versus Sheet
Copper tubing offers easier installation due to its flexibility and pre-formed shape, allowing seamless bending around obstacles without specialized tools, which reduces labor time and complexity. Copper sheets require precise cutting, shaping, and sealing, demanding skilled labor and additional equipment to ensure tight seams and secure fittings. Handling copper tubing is generally safer and more convenient on-site, while copper sheets require careful handling to avoid kinks and sharp edges that can complicate installation.
Environmental Impact and Recycling
Copper tubing offers superior recyclability compared to copper sheets due to its higher purity and minimal manufacturing waste, enabling efficient closed-loop recycling processes. The environmental impact of copper tubing is reduced by its longevity and corrosion resistance, which decreases the frequency of replacement and resource consumption. Copper sheets, while also recyclable, often involve more complex processing and trimming waste, leading to slightly higher environmental footprints during production and recycling phases.
Choosing the Right Copper Form for Your Project
Choosing the right copper form for your project depends on its specific requirements, such as flexibility, strength, and ease of installation. Copper tubing is ideal for plumbing and HVAC systems due to its durability and ability to withstand high pressure, while copper sheets are preferable for roofing, flashing, and decorative purposes because of their flat, malleable surfaces. Understanding the thermal conductivity, corrosion resistance, and thickness needed will ensure optimal performance in your application.
Copper Tubing vs Copper Sheet Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com