Electrolytic copper offers superior purity levels, making it ideal for high-performance electrical applications due to its excellent conductivity and minimal impurities. Recycled copper, while slightly lower in purity, provides an environmentally sustainable alternative by reducing the demand for new mining resources and lowering energy consumption during production. Choosing between electrolytic and recycled copper depends on balancing performance requirements with environmental impact considerations.
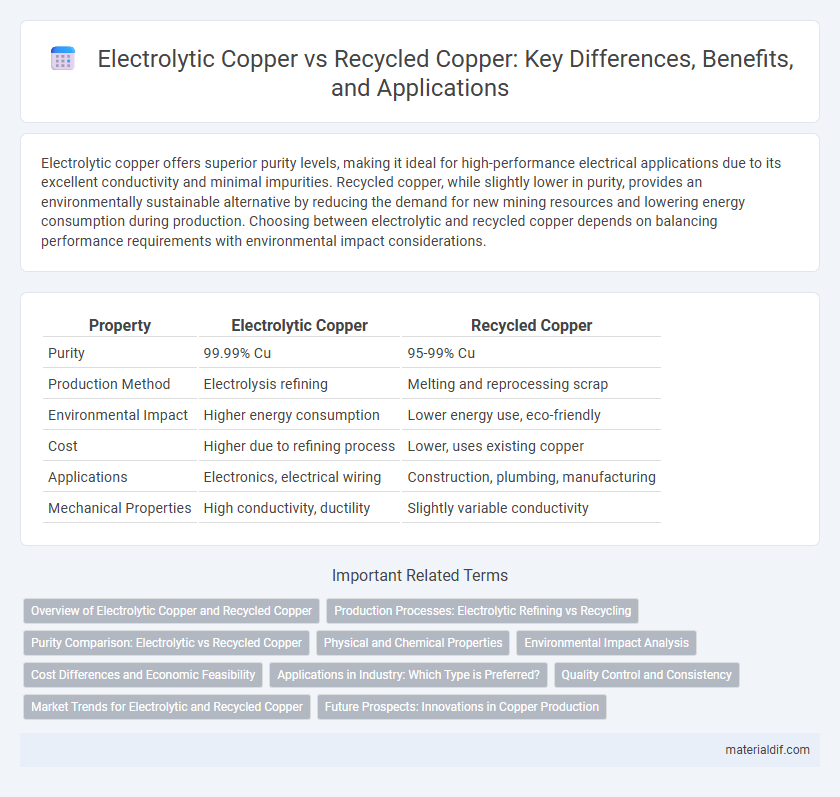
Table of Comparison
| Property | Electrolytic Copper | Recycled Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.99% Cu | 95-99% Cu |
| Production Method | Electrolysis refining | Melting and reprocessing scrap |
| Environmental Impact | Higher energy consumption | Lower energy use, eco-friendly |
| Cost | Higher due to refining process | Lower, uses existing copper |
| Applications | Electronics, electrical wiring | Construction, plumbing, manufacturing |
| Mechanical Properties | High conductivity, ductility | Slightly variable conductivity |
Overview of Electrolytic Copper and Recycled Copper
Electrolytic copper is produced through the electrorefining process, resulting in high-purity copper typically exceeding 99.99%, ideal for electrical and industrial applications requiring superior conductivity. Recycled copper is derived from scrap copper, melted and purified through various refining methods, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective alternative with slightly lower purity levels, generally around 99.5%. Both types maintain essential copper properties but differ in energy consumption, environmental impact, and production costs.
Production Processes: Electrolytic Refining vs Recycling
Electrolytic copper production involves the refining of impure copper anodes through an electrolytic cell, where pure copper is deposited on cathodes, resulting in high-purity copper exceeding 99.99%. Recycled copper is obtained by melting scrap copper and removing impurities through mechanical and chemical processes, which is less energy-intensive and supports circular economy goals. Electrolytic refining offers superior purity suitable for electronic and electrical applications, while recycled copper provides an eco-friendly alternative with slightly lower purity levels ideal for construction and manufacturing.
Purity Comparison: Electrolytic vs Recycled Copper
Electrolytic copper typically achieves purity levels of 99.99%, making it highly suitable for electrical and electronic applications requiring superior conductivity. Recycled copper, while environmentally beneficial and cost-effective, generally contains impurities that reduce its purity to around 95-99%, depending on the recycling process and source materials. The higher purity of electrolytic copper ensures better performance in critical industrial uses, whereas recycled copper is favored in less demanding applications.
Physical and Chemical Properties
Electrolytic copper exhibits higher purity levels, typically 99.99%, resulting in superior electrical conductivity and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to recycled copper, which may contain trace impurities affecting performance. Recycled copper often has variable alloy compositions due to mixed scrap sources, influencing its mechanical strength and melting point. Both forms maintain excellent ductility and thermal conductivity, but electrolytic copper's consistent chemical composition makes it preferable for high-precision electrical and industrial applications.
Environmental Impact Analysis
Electrolytic copper production consumes significant amounts of energy, mainly from non-renewable sources, resulting in higher greenhouse gas emissions compared to recycled copper. Recycled copper reduces mining waste, conserves natural resources, and lowers carbon footprint by up to 85% due to lower energy requirements in processing. The environmental impact analysis clearly favors recycled copper as a sustainable alternative, minimizing ecosystem disruption and resource depletion.
Cost Differences and Economic Feasibility
Electrolytic copper generally incurs higher production costs due to energy-intensive processes and stringent purity requirements, making it pricier than recycled copper, which benefits from lower processing expenses and reduced raw material extraction. Recycled copper offers significant economic feasibility by minimizing energy consumption and capitalizing on existing scrap materials, leading to cost savings and sustainability advantages. Market fluctuations in scrap availability and refining efficiency influence the cost-effectiveness of recycled copper compared to electrolytic copper, impacting supply chain decisions.
Applications in Industry: Which Type is Preferred?
Electrolytic copper is preferred in high-precision electrical and electronic applications due to its superior purity and conductivity, making it ideal for wiring, circuit boards, and semiconductor components. Recycled copper is widely used in construction, plumbing, and manufacturing of heavy machinery where cost efficiency and sustainability outweigh the need for ultra-high purity. Industrial sectors prioritize electrolytic copper for critical performance roles, while recycled copper satisfies broader industrial demands with environmental benefits.
Quality Control and Consistency
Electrolytic copper offers superior purity, typically exceeding 99.99%, due to rigorous quality control processes in electrolytic refining, resulting in consistent chemical composition and electrical conductivity. Recycled copper quality varies depending on the source material and the efficiency of the sorting and melting processes, making its consistency less predictable and often requiring further refinement to meet industrial standards. Quality control in electrolytic copper production is highly standardized, ensuring uniformity crucial for applications in electronics and high-performance wiring.
Market Trends for Electrolytic and Recycled Copper
Electrolytic copper maintains high purity levels, driving strong demand in electrical and electronics markets due to its superior conductivity and reliability. Recycled copper gains market traction as sustainability efforts and cost-efficiency become key drivers, with its share rising in building and automotive applications. Market trends indicate a growing preference for recycled copper in circular economies while electrolytic copper remains essential for high-performance industries.
Future Prospects: Innovations in Copper Production
Electrolytic copper offers high purity essential for advanced electronics, while recycled copper reduces environmental impact by conserving natural resources. Innovations in electrolytic refining improve energy efficiency, whereas advancements in recycling technologies enhance recovery rates and material quality. Future prospects emphasize integrating both methods to meet increasing demand sustainably and support circular economy models in the copper industry.
Electrolytic Copper vs Recycled Copper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com