Copper strips offer greater flexibility and are ideal for applications requiring precise bending and shaping, while copper bars provide higher structural strength and are suited for heavy-duty uses. Both forms exhibit excellent electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance, making them essential in electrical and construction industries. Selecting between copper strip and copper bar depends on the specific mechanical and electrical requirements of the project.
Table of Comparison
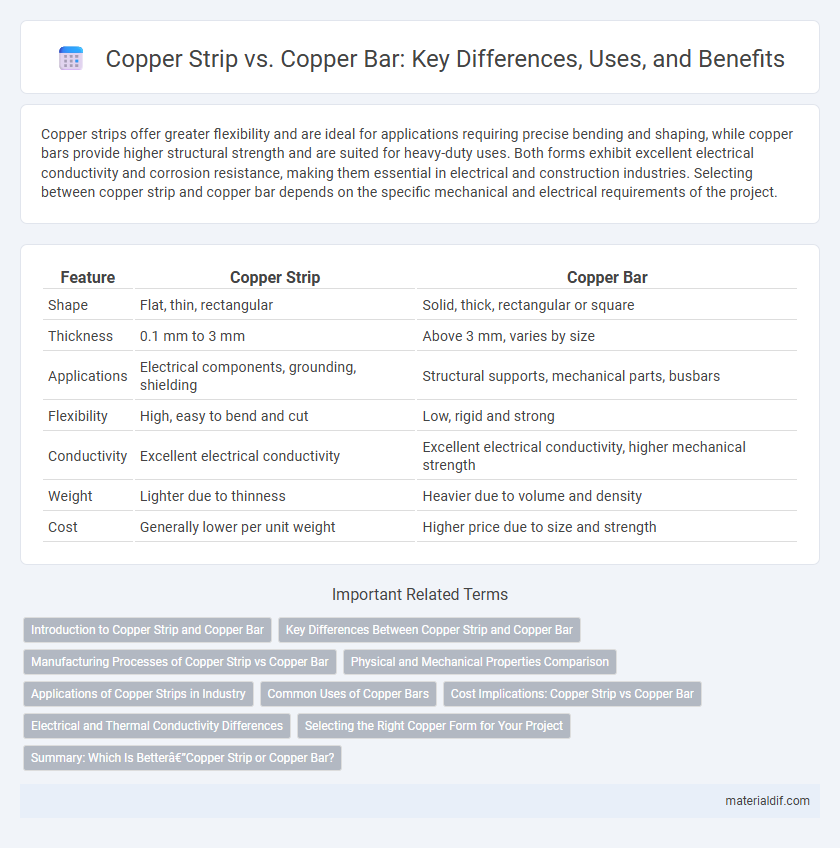
| Feature | Copper Strip | Copper Bar |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Flat, thin, rectangular | Solid, thick, rectangular or square |
| Thickness | 0.1 mm to 3 mm | Above 3 mm, varies by size |
| Applications | Electrical components, grounding, shielding | Structural supports, mechanical parts, busbars |
| Flexibility | High, easy to bend and cut | Low, rigid and strong |
| Conductivity | Excellent electrical conductivity | Excellent electrical conductivity, higher mechanical strength |
| Weight | Lighter due to thinness | Heavier due to volume and density |
| Cost | Generally lower per unit weight | Higher price due to size and strength |
Introduction to Copper Strip and Copper Bar
Copper strip and copper bar are essential forms of copper used across various industries, each with unique physical properties and applications. Copper strips are thin, flat pieces ideal for electrical connectors, circuit boards, and flexible components due to their excellent conductivity and malleability. Copper bars, thicker and more rigid, are commonly utilized in construction, electrical busbars, and heavy-duty manufacturing for their strength and durability.
Key Differences Between Copper Strip and Copper Bar
Copper strips are thin, flat pieces of copper metal primarily used for applications requiring flexibility and ease of bending, such as electrical grounding and connectors. Copper bars, on the other hand, are thicker, rectangular-shaped solid metal sections designed to provide structural support and superior electrical conductivity in heavy-duty industrial components. Key differences include their thickness, shape, mechanical strength, and typical usage environments, with strips favoring flexibility and bars excelling in load-bearing and high-current applications.
Manufacturing Processes of Copper Strip vs Copper Bar
Copper strip manufacturing involves hot rolling or cold rolling processes that reduce copper billets into thin, flat sheets with precise thickness and surface finish, ideal for electrical and industrial applications. Copper bars are typically produced through continuous casting or extrusion, resulting in solid rectangular or square cross-sections suited for structural and conductive uses. The manufacturing processes influence mechanical properties, with strips offering superior flexibility and bars providing enhanced strength and rigidity.
Physical and Mechanical Properties Comparison
Copper strips exhibit higher flexibility and better conductivity due to their thinner, flat geometry, making them ideal for applications requiring tight bends and efficient electrical paths. Copper bars offer superior mechanical strength and load-bearing capacity because of their thicker, more robust cross-section, which suits structural and heavy-duty electrical uses. Differences in thermal conductivity and tensile strength between copper strips and bars directly influence their selection in electrical, thermal, and mechanical engineering projects.
Applications of Copper Strips in Industry
Copper strips are widely used in the electronics industry for manufacturing connectors, circuit boards, and electromagnetic shielding due to their excellent conductivity and flexibility. They are also essential in the automotive sector for battery manufacturing and electrical wiring, where precise shaping and durability are critical. The versatility of copper strips enables their application in HVAC systems and electrical transformers, providing efficient heat dissipation and electrical performance.
Common Uses of Copper Bars
Copper bars are widely used in electrical applications, including busbars in power distribution systems due to their excellent conductivity and mechanical strength. They also serve in construction for grounding, structural supports, and heat exchangers, benefiting from copper's corrosion resistance and durability. In manufacturing, copper bars are essential for machining components in automotive and industrial machinery, offering precision and reliability.
Cost Implications: Copper Strip vs Copper Bar
Copper strip typically offers lower cost implications for manufacturing due to its reduced weight and ease of processing compared to copper bars. Copper bars, being thicker and bulkier, incur higher material costs and machining expenses, impacting overall project budgets. Economies of scale in copper strip production further enhance cost efficiency in large-scale applications.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Differences
Copper strips offer superior electrical conductivity compared to copper bars due to their increased surface area, which enhances current flow efficiency in applications such as circuit boards and electrical connectors. Thermal conductivity in copper strips is also higher relative to copper bars, allowing for better heat dissipation in components requiring rapid thermal management. Copper bars, while having lower conductivity values, provide greater mechanical strength and are preferred where structural support and durability are critical.
Selecting the Right Copper Form for Your Project
Copper strips offer flexibility and ease of bending, making them ideal for applications requiring precise shaping and electrical conductivity, such as circuit boards and grounding strips. Copper bars provide higher mechanical strength and durability, suitable for structural uses or heavy-duty electrical components where stability and load-bearing capacity are critical. Choosing between copper strip and bar depends on project requirements for flexibility, strength, and electrical performance to ensure optimal functionality.
Summary: Which Is Better—Copper Strip or Copper Bar?
Copper strips offer greater flexibility and are ideal for applications requiring bending and shaping, while copper bars provide superior strength and durability suited for structural and heavy-duty electrical uses. The choice depends on the specific requirements of conductivity, mechanical strength, and installation complexity within projects. Copper strips generally excel in electronics and circuitry, whereas copper bars are preferred in construction and industrial frameworks.
Copper Strip vs Copper Bar Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com