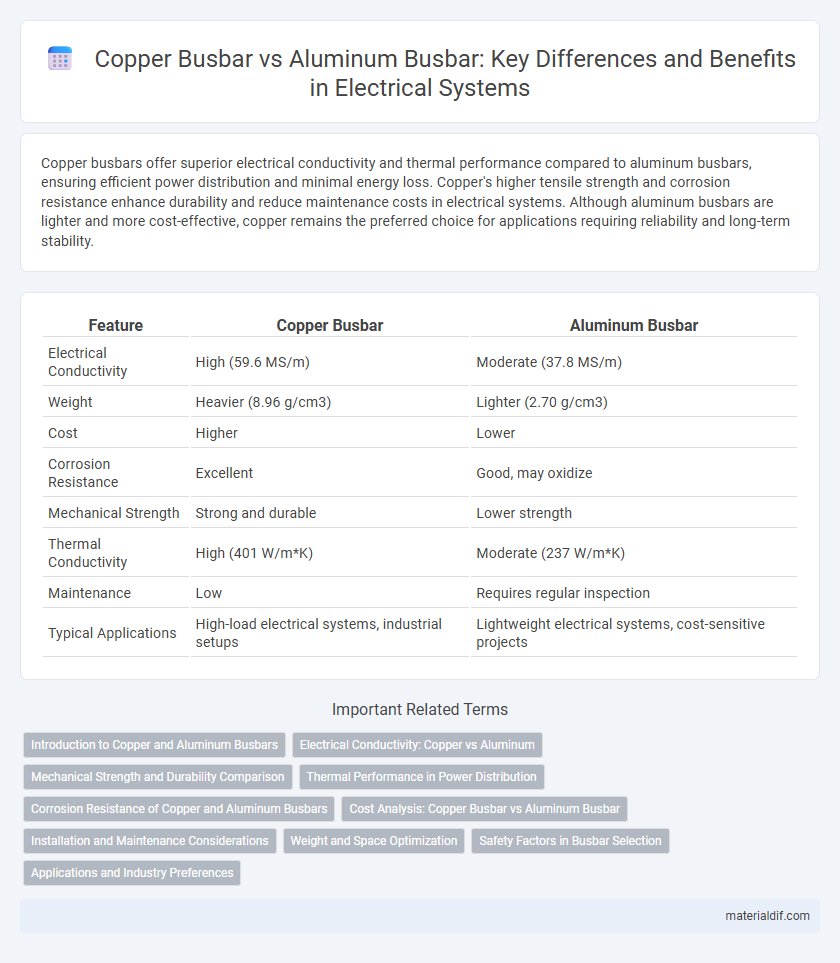
Copper busbars offer superior electrical conductivity and thermal performance compared to aluminum busbars, ensuring efficient power distribution and minimal energy loss. Copper's higher tensile strength and corrosion resistance enhance durability and reduce maintenance costs in electrical systems. Although aluminum busbars are lighter and more cost-effective, copper remains the preferred choice for applications requiring reliability and long-term stability.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Copper Busbar | Aluminum Busbar |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical Conductivity | High (59.6 MS/m) | Moderate (37.8 MS/m) |
| Weight | Heavier (8.96 g/cm3) | Lighter (2.70 g/cm3) |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good, may oxidize |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong and durable | Lower strength |
| Thermal Conductivity | High (401 W/m*K) | Moderate (237 W/m*K) |
| Maintenance | Low | Requires regular inspection |
| Typical Applications | High-load electrical systems, industrial setups | Lightweight electrical systems, cost-sensitive projects |
Introduction to Copper and Aluminum Busbars
Copper busbars offer superior electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and thermal performance compared to aluminum busbars, making them ideal for high-current applications. Aluminum busbars, while lighter and more cost-effective, have lower conductivity and require larger cross-sectional areas to match copper's performance. Both materials are widely used in electrical distribution systems, with choice dependent on application-specific factors such as weight constraints, budget, and environmental conditions.
Electrical Conductivity: Copper vs Aluminum
Copper busbars exhibit significantly higher electrical conductivity, approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, compared to aluminum busbars which typically measure around 3.5 x 10^7 S/m. This superior conductivity in copper reduces energy losses and improves efficiency in electrical systems. Despite aluminum's lighter weight, copper remains the preferred material where minimal resistance and optimal current carrying capacity are crucial.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Comparison
Copper busbars exhibit superior mechanical strength and durability compared to aluminum busbars, making them ideal for applications subject to high stress and vibration. Copper's higher tensile strength and resistance to deformation ensure better performance under mechanical loads and longer lifespan in demanding environments. In contrast, aluminum busbars, while lighter, are more prone to bending and corrosion, reducing their overall reliability and durability.
Thermal Performance in Power Distribution
Copper busbars exhibit superior thermal conductivity, approximately 400 W/m*K, compared to aluminum's 205 W/m*K, enabling more efficient heat dissipation in power distribution systems. This enhanced thermal performance reduces hotspots and enhances overall system reliability and longevity. Consequently, copper busbars maintain lower operating temperatures under high current loads, minimizing thermal expansion and associated mechanical stresses.
Corrosion Resistance of Copper and Aluminum Busbars
Copper busbars exhibit superior corrosion resistance compared to aluminum busbars due to copper's natural oxide layer, which forms a protective barrier against environmental elements and prevents further surface degradation. Aluminum busbars are more prone to oxidative corrosion and may require additional protective coatings or treatments to enhance their lifespan in corrosive environments. This inherent corrosion resistance of copper ensures better conductivity retention and reliability in electrical applications where exposure to moisture or chemicals is a concern.
Cost Analysis: Copper Busbar vs Aluminum Busbar
Copper busbars generally have a higher initial cost compared to aluminum busbars due to copper's superior conductivity and durability. Aluminum busbars offer a cost-effective solution with lower material and installation expenses, despite requiring larger cross-sections to achieve similar electrical performance. Long-term cost analysis should consider maintenance, lifespan, and conductivity losses, where copper often proves more economical over time.
Installation and Maintenance Considerations
Copper busbars offer superior conductivity and durability, simplifying installation by requiring smaller cross-sections and fewer supports compared to aluminum busbars. Maintenance of copper busbars is generally easier due to their resistance to corrosion and lower thermal expansion, reducing the risk of loosening connections and ensuring long-term reliability. Aluminum busbars demand more frequent inspections and anti-oxidation treatments to prevent degradation and maintain performance.
Weight and Space Optimization
Copper busbars offer superior conductivity with a higher density than aluminum, resulting in smaller cross-sectional areas for equivalent current ratings, which optimizes space in electrical panels. While aluminum busbars are lighter by approximately 40% than copper, copper's compact size reduces overall panel volume and enhances thermal performance. This space-saving advantage makes copper busbars ideal for applications requiring high current capacity within limited installation areas.
Safety Factors in Busbar Selection
Copper busbars provide superior electrical conductivity and higher thermal resistance than aluminum busbars, reducing the risk of overheating and electrical faults. Their greater mechanical strength enhances durability and resistance to deformation under high electrical loads, improving overall safety. Although aluminum busbars are lighter and cost-effective, the increased oxidation and lower conductivity can lead to higher operational risks, making copper the safer choice in critical electrical applications.
Applications and Industry Preferences
Copper busbars are widely preferred in heavy-duty electrical applications such as power distribution, switchgear, and industrial motor controls due to their superior electrical conductivity, mechanical strength, and corrosion resistance. Aluminum busbars find increasing use in cost-sensitive projects and applications like HVAC systems, renewable energy installations, and building electrical infrastructure where lightweight and cost efficiency are critical. Industries like manufacturing, automotive, and utilities often select copper busbars for reliability and performance, while construction and renewable energy sectors lean toward aluminum for economic advantages and ease of installation.
Copper Busbar vs Aluminum Busbar Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com