Copper coils provide superior flexibility and are ideal for applications requiring precise winding and electromagnetic efficiency, while copper strips offer enhanced structural strength and conductivity in flat, rigid configurations. The choice between copper coil and strip depends on the mechanical demands and electrical performance needed in industries such as electronics, HVAC, and manufacturing. Copper coils excel in transformers and inductors, whereas copper strips are commonly used in bus bars and electrical connectors.
Table of Comparison
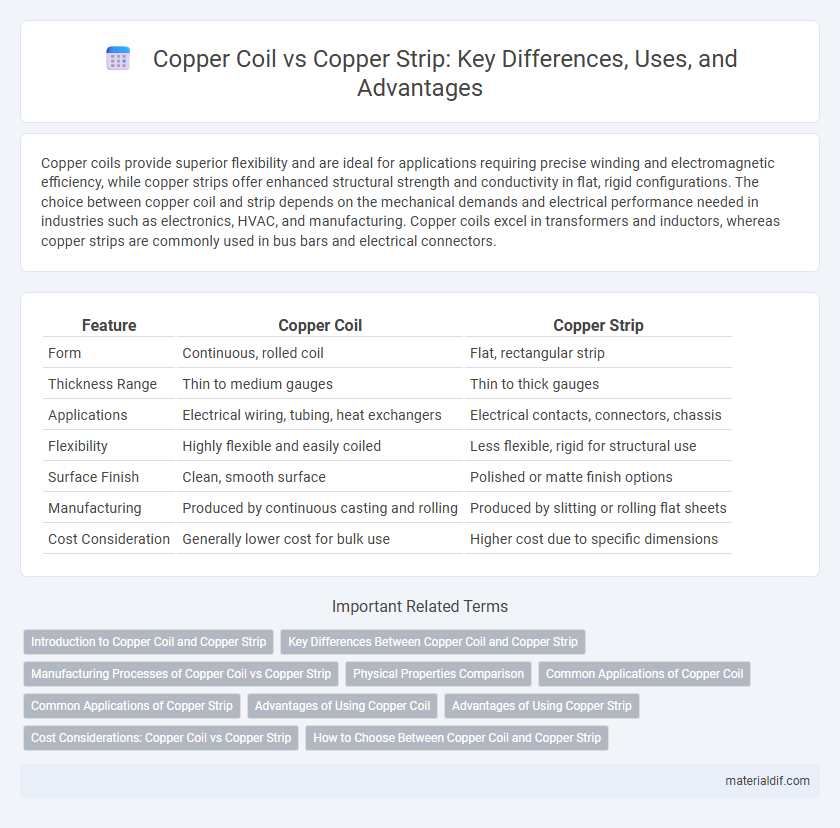
| Feature | Copper Coil | Copper Strip |
|---|---|---|
| Form | Continuous, rolled coil | Flat, rectangular strip |
| Thickness Range | Thin to medium gauges | Thin to thick gauges |
| Applications | Electrical wiring, tubing, heat exchangers | Electrical contacts, connectors, chassis |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and easily coiled | Less flexible, rigid for structural use |
| Surface Finish | Clean, smooth surface | Polished or matte finish options |
| Manufacturing | Produced by continuous casting and rolling | Produced by slitting or rolling flat sheets |
| Cost Consideration | Generally lower cost for bulk use | Higher cost due to specific dimensions |
Introduction to Copper Coil and Copper Strip
Copper coil consists of continuous, flexible copper wire wound into a spiral or roll, widely used in electrical wiring, heat exchangers, and refrigeration systems due to its excellent conductivity and thermal properties. Copper strip refers to flat, rectangular pieces of copper, typically employed in electrical connectors, busbars, and manufacturing applications that require high strength and precise dimensions. Both copper coil and copper strip offer superior corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, but their forms cater to different industrial uses and fabrication needs.
Key Differences Between Copper Coil and Copper Strip
Copper coils are typically used in applications requiring flexibility and continuous lengths, such as electrical wiring, HVAC systems, and transformers, whereas copper strips are flat, rigid, and commonly used in construction, electrical contacts, and circuits. The key difference lies in their shape and form factor: coils are rolled copper wires or tubing, offering ease of transport and installation in curved or circular paths, while strips provide flat, solid surfaces ideal for grounding and structural components. Material thickness and width also vary, with strips generally thicker and wider than the thinner gauge copper found in coils.
Manufacturing Processes of Copper Coil vs Copper Strip
Copper coils are manufactured through continuous casting and rolling processes that shape copper into long, cylindrical tubes ideal for electrical wiring and heat exchangers. Copper strips undergo hot rolling, cold rolling, and annealing to produce flat, thin sheets suited for electrical contacts, connectors, and industrial applications. The key manufacturing difference lies in the shaping technique: coils form tubular structures via extrusion or seamless drawing, while strips are created by flattening and precise thickness control through rolling mills.
Physical Properties Comparison
Copper coils exhibit excellent flexibility and high tensile strength, making them ideal for applications requiring winding and shaping. Copper strips have superior flatness and consistent thickness, offering enhanced conductivity and durability in surface applications. Both forms maintain excellent thermal and electrical conductivity, but the choice depends on the mechanical requirements of the specific application.
Common Applications of Copper Coil
Copper coil is widely used in HVAC systems, refrigeration units, and electrical windings due to its excellent thermal conductivity and flexibility. Its ability to withstand corrosion and high temperatures makes it ideal for heat exchangers, air conditioners, and transformers. Unlike copper strip, which is primarily used in electrical contacts and structural components, copper coil excels in applications requiring continuous continuous tubing or wire.
Common Applications of Copper Strip
Copper strip finds widespread use in electrical connectors, transformers, and PCB grounding due to its excellent conductivity and flexibility. It is essential in manufacturing busbars, lead frames, and shielding components in electronic devices, ensuring reliable current distribution and electromagnetic interference protection. The material's durability and corrosion resistance make copper strip ideal for battery tabs and heat exchangers across various industrial applications.
Advantages of Using Copper Coil
Copper coil offers superior flexibility and ease of installation compared to copper strip, making it ideal for applications requiring continuous lengths or complex shapes. Its enhanced thermal conductivity and corrosion resistance ensure efficient heat transfer and long-term durability in HVAC and electrical systems. The coil form also reduces waste and simplifies inventory management, resulting in cost-effective usage for manufacturing and construction projects.
Advantages of Using Copper Strip
Copper strips offer superior flexibility and easier fabrication compared to copper coils, making them ideal for intricate electrical and mechanical applications. Their uniform thickness and precise dimensions ensure consistent conductivity and enhanced durability in electronic components and circuit boards. The flat, rigid form of copper strips provides improved surface contact and heat dissipation, essential for efficient energy transfer and thermal management.
Cost Considerations: Copper Coil vs Copper Strip
Copper coil generally offers cost advantages due to its ability to be produced and transported in bulk, reducing handling and storage expenses compared to copper strip. Copper strip, while often more expensive per unit length, provides precise dimensions and is ideal for applications requiring specific thickness and width tolerances, impacting overall project costs. Evaluating the total cost of ownership includes material price, fabrication requirements, and waste minimization when choosing between copper coil and copper strip.
How to Choose Between Copper Coil and Copper Strip
Selecting between copper coil and copper strip depends on the specific application requirements such as flexibility, thickness, and surface area coverage. Copper coils offer superior flexibility and are ideal for winding and continuous feeding processes, while copper strips provide precision and stiffness suitable for structural components and electrical connections. Evaluating factors like conductivity, mechanical strength, and fabrication methods ensures the appropriate copper form is chosen for optimal performance and cost-efficiency.
Copper Coil vs Copper Strip Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com