Copper mesh offers higher flexibility and better conformity to irregular surfaces, making it ideal for electromagnetic shielding in complex shapes. Copper grid provides enhanced structural strength and uniform conductivity, suitable for grounding and large-scale electrical applications. Both materials deliver excellent corrosion resistance and electrical performance, but the choice depends on the specific requirements of durability and adaptability.
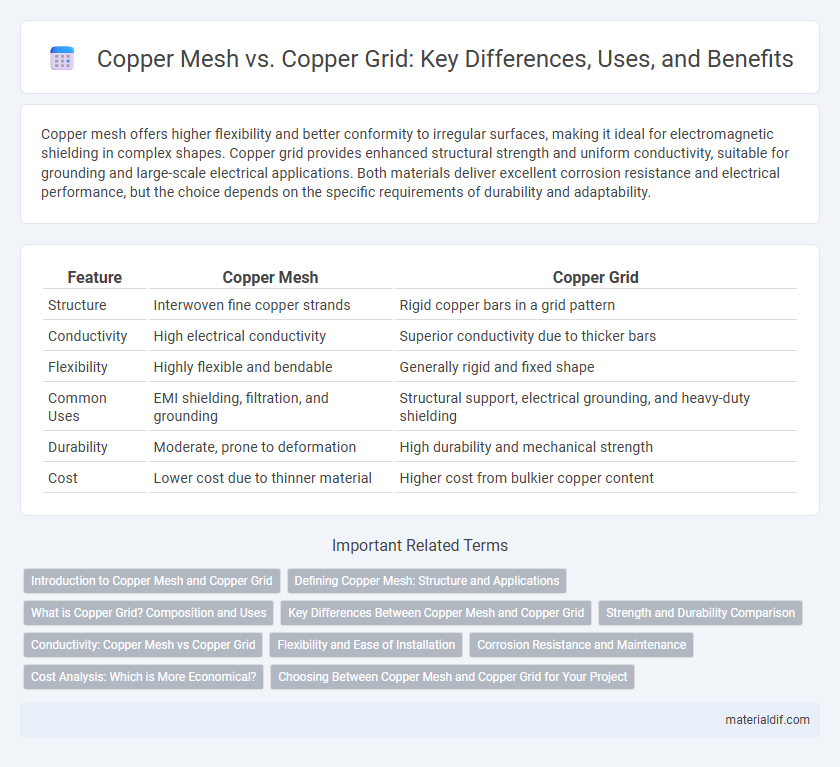
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Copper Mesh | Copper Grid |
|---|---|---|
| Structure | Interwoven fine copper strands | Rigid copper bars in a grid pattern |
| Conductivity | High electrical conductivity | Superior conductivity due to thicker bars |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible and bendable | Generally rigid and fixed shape |
| Common Uses | EMI shielding, filtration, and grounding | Structural support, electrical grounding, and heavy-duty shielding |
| Durability | Moderate, prone to deformation | High durability and mechanical strength |
| Cost | Lower cost due to thinner material | Higher cost from bulkier copper content |
Introduction to Copper Mesh and Copper Grid
Copper mesh features interwoven strands forming a flexible, porous material ideal for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and filtration applications. Copper grid consists of rigid, uniformly spaced bars providing structural support and enhanced conductivity for grounding systems and electronic enclosures. Both materials leverage copper's excellent electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and thermal properties for diverse industrial uses.
Defining Copper Mesh: Structure and Applications
Copper mesh consists of interwoven or welded strands forming a flexible, breathable fabric with varied aperture sizes, ideal for electromagnetic shielding, insect screens, and filtration systems. Its structure allows excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance, making it suitable for grounding in electrical installations and reinforcement in composite materials. Copper mesh is preferred in applications requiring adaptability and fine particle control compared to rigid copper grids.
What is Copper Grid? Composition and Uses
Copper grid consists of a network of intersecting copper wires or strips forming a structured pattern, typically composed of pure copper or copper alloys for enhanced conductivity and durability. It is widely used in electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, grounding systems, and as an electrode material in electrochemical applications due to its excellent electrical and thermal conductivity. Copper grids provide a stable and efficient conductive pathway, making them ideal for use in electronics, battery manufacturing, and industrial filtration systems.
Key Differences Between Copper Mesh and Copper Grid
Copper mesh consists of fine woven strands creating a flexible, lightweight structure ideal for electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding, while copper grid features rigid, thicker bars arranged in a crisscross pattern providing enhanced mechanical strength and higher current-carrying capacity. Copper mesh offers superior surface area contact for static dissipation and filtration applications, whereas copper grid is preferred in grounding and large-scale electrical distribution due to its robustness and conductivity. The choice between copper mesh and copper grid depends on specific requirements for flexibility, conductivity, strength, and surface interaction in industrial or electronic environments.
Strength and Durability Comparison
Copper mesh offers superior flexibility and tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring easy shaping and resilience under stress. Copper grids, with their rigid and uniform structure, provide enhanced durability and stability in heavy-duty environments. Overall, copper grids excel in load-bearing scenarios, while copper mesh provides better resistance to deformation and tearing.
Conductivity: Copper Mesh vs Copper Grid
Copper mesh offers superior conductivity compared to copper grid due to its finer wire strands, which create a denser network that facilitates more efficient electron flow. The high surface area of copper mesh enables enhanced electrical contact and reduced resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring maximum conductivity. Conversely, copper grids, with their thicker and more widely spaced wires, provide lower conductivity but greater mechanical stability in electrical systems.
Flexibility and Ease of Installation
Copper mesh offers superior flexibility compared to copper grid, allowing it to conform easily to irregular surfaces and complex shapes, making it ideal for applications requiring adaptability. The pliable nature of copper mesh simplifies installation processes, reducing time and labor costs in projects such as electromagnetic shielding or grounding. Conversely, copper grids are more rigid and better suited for structural applications where stability and precise alignment are critical.
Corrosion Resistance and Maintenance
Copper mesh offers high corrosion resistance due to its fine weaving, which allows for better airflow and moisture evaporation, reducing oxidation risks. Copper grid, while sturdy, may trap moisture in larger gaps, leading to faster corrosion without regular maintenance. Both require periodic cleaning, but copper mesh typically demands less upkeep to maintain longevity in corrosive environments.
Cost Analysis: Which is More Economical?
Copper mesh generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to copper grid due to simpler manufacturing and reduced material usage. Copper grid, while initially more expensive, provides enhanced durability and electrical conductivity that can reduce long-term maintenance and replacement expenses. Evaluating total cost of ownership reveals copper mesh as economical for budget-conscious projects, whereas copper grid suits applications demanding higher performance and longevity.
Choosing Between Copper Mesh and Copper Grid for Your Project
Choosing between copper mesh and copper grid depends on the specific requirements of your project, such as electrical conductivity, flexibility, and surface area. Copper mesh offers superior flexibility and airflow, making it ideal for electromagnetic shielding and filtration applications, while copper grid provides higher structural strength and uniform current distribution, suitable for grounding and cathodic protection systems. Consider factors like mechanical durability, conductivity needs, and environmental exposure to determine the optimal choice for enhanced performance and longevity.
Copper Mesh vs Copper Grid Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com