Copper wire offers superior flexibility and ease of installation, making it ideal for electrical wiring and intricate circuits. Copper rods provide greater mechanical strength and durability, commonly used in construction and manufacturing applications. Selecting between copper wire and copper rod depends on the specific requirements for conductivity, strength, and application environment.
Table of Comparison
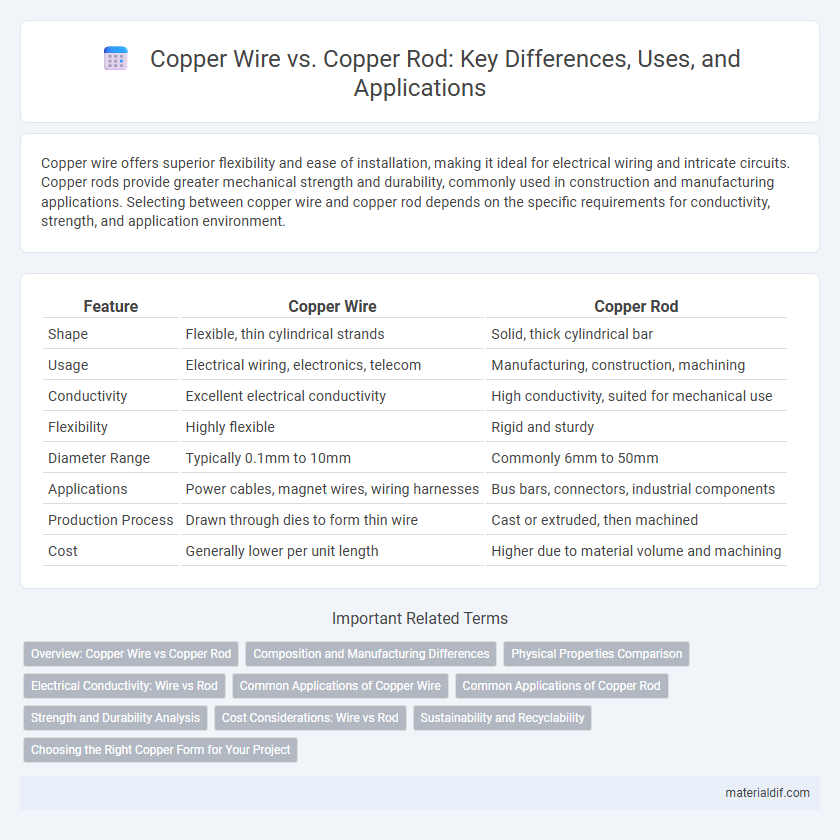
| Feature | Copper Wire | Copper Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Flexible, thin cylindrical strands | Solid, thick cylindrical bar |
| Usage | Electrical wiring, electronics, telecom | Manufacturing, construction, machining |
| Conductivity | Excellent electrical conductivity | High conductivity, suited for mechanical use |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible | Rigid and sturdy |
| Diameter Range | Typically 0.1mm to 10mm | Commonly 6mm to 50mm |
| Applications | Power cables, magnet wires, wiring harnesses | Bus bars, connectors, industrial components |
| Production Process | Drawn through dies to form thin wire | Cast or extruded, then machined |
| Cost | Generally lower per unit length | Higher due to material volume and machining |
Overview: Copper Wire vs Copper Rod
Copper wire consists of thin strands of copper used primarily for electrical conductivity and flexible applications, featuring high tensile strength and excellent corrosion resistance. Copper rods are solid, cylindrical bars commonly utilized in construction, manufacturing, and machining processes due to their durability and structural integrity. Both copper wire and copper rod offer copper's inherent properties such as conductivity and malleability, but differ in form and typical industrial usage.
Composition and Manufacturing Differences
Copper wire is typically composed of highly pure copper with minimal alloying elements to enhance electrical conductivity, whereas copper rods may contain small amounts of alloying metals to improve mechanical strength. The manufacturing process for copper wire involves drawing the copper through progressively smaller dies to achieve thin, flexible strands, while copper rods are produced by continuous casting or extrusion into thicker, rigid bars. These differences result in copper wire being ideal for electrical and electronic applications, whereas copper rods suit structural and industrial uses.
Physical Properties Comparison
Copper wire exhibits high flexibility and excellent electrical conductivity, making it ideal for intricate electrical applications, while copper rod is characterized by a solid, rigid structure with enhanced mechanical strength suitable for heavy-duty construction and manufacturing purposes. The tensile strength of copper rods typically ranges between 210 to 370 MPa, substantially higher than that of copper wires, which usually fall around 200 MPa due to their thinner gauge and flexibility. Thermal conductivity remains consistent in both forms, approximately 390 W/m*K, but the physical form directly influences their use in electrical wiring versus structural components.
Electrical Conductivity: Wire vs Rod
Copper wire exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to copper rod due to its smaller diameter and greater surface area, which allow for more efficient current flow and reduced resistance. The manufacturing process of copper wire involves drawing metal through dies, enhancing grain structure alignment and further improving conductivity. Copper rod, while still highly conductive, is typically utilized in applications requiring bulk current carrying capacity where mechanical strength is prioritized over maximized conductivity.
Common Applications of Copper Wire
Copper wire is widely used in electrical wiring, telecommunications, and power generation due to its excellent conductivity and flexibility. It is essential in residential and commercial building wiring, automotive electrical systems, and electronic devices. Copper wire's ability to transmit signals with minimal loss makes it ideal for use in data cables and networking infrastructure.
Common Applications of Copper Rod
Copper rods are extensively used in electrical wiring, grounding systems, and manufacturing of electrical busbars due to their excellent conductivity and mechanical strength. They are commonly applied in construction for plumbing, roofing, and industrial machinery components where durability and corrosion resistance are critical. Copper rods also serve as raw material for producing wire rods, fasteners, and automotive parts, making them essential in diverse industrial applications.
Strength and Durability Analysis
Copper wire offers enhanced flexibility but has lower tensile strength compared to copper rods, which exhibit superior mechanical strength and rigidity. The denser grain structure in copper rods contributes to increased durability and resistance to deformation under stress. Applications requiring robust structural support prioritize copper rods for their high strength-to-weight ratio and longevity.
Cost Considerations: Wire vs Rod
Copper wire generally costs more than copper rod due to the extensive manufacturing processes involved, including drawing and annealing to achieve desired flexibility and diameter. Copper rods have lower production costs as they are less processed, primarily used as raw material for fabrication or further machining. When budget constraints exist, choosing copper rod over wire can result in significant savings, especially in large-scale industrial applications where form factor is secondary.
Sustainability and Recyclability
Copper wire and copper rod both offer exceptional sustainability and recyclability, with copper's inherent ability to be recycled infinitely without loss of quality. Copper wire, commonly used in electrical applications, benefits from high recycling rates that reduce energy consumption by up to 85% compared to primary production. Copper rods, often utilized in manufacturing and construction, also contribute significantly to circular economies due to their durable, recyclable nature and widespread acceptance in metal recycling streams.
Choosing the Right Copper Form for Your Project
Copper wire offers superior flexibility and conductivity, making it ideal for electrical wiring and intricate installation projects. Copper rods provide greater strength and durability, suited for heavy-duty applications like manufacturing and construction. Selecting the appropriate copper form depends on the specific requirements for flexibility, strength, and ease of manipulation in your project.
Copper Wire vs Copper Rod Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com