Copper wire offers excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for wiring in electrical circuits and telecommunications. Copper foil, thinner and flat, is used primarily in printed circuit boards and electromagnetic shielding due to its easy layering and adhesive properties. Both forms capitalize on copper's conductivity but serve different purposes based on their shape and application requirements.
Table of Comparison
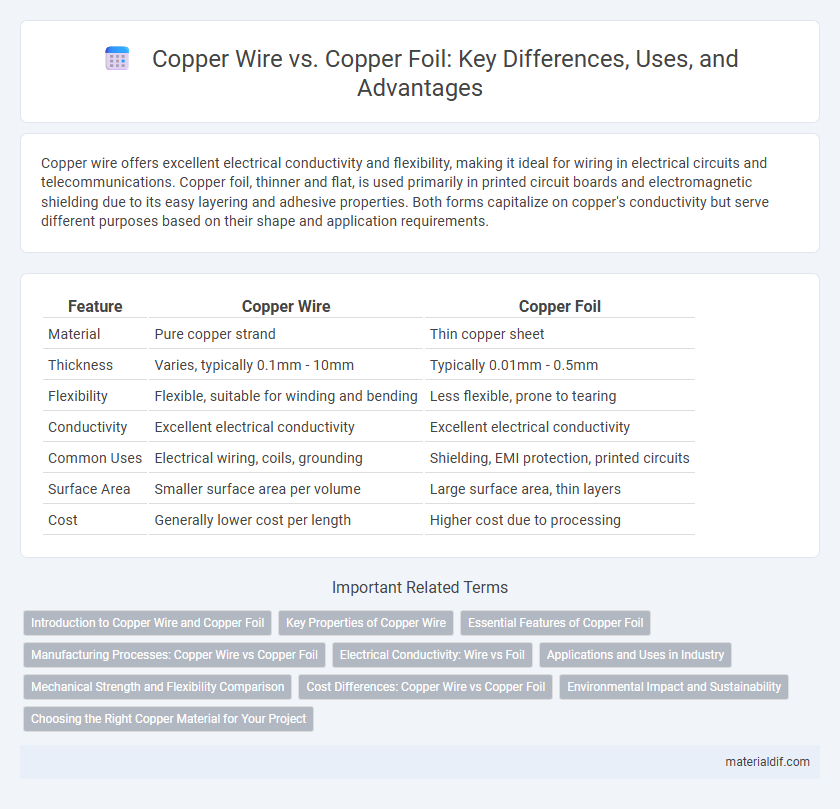
| Feature | Copper Wire | Copper Foil |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Pure copper strand | Thin copper sheet |
| Thickness | Varies, typically 0.1mm - 10mm | Typically 0.01mm - 0.5mm |
| Flexibility | Flexible, suitable for winding and bending | Less flexible, prone to tearing |
| Conductivity | Excellent electrical conductivity | Excellent electrical conductivity |
| Common Uses | Electrical wiring, coils, grounding | Shielding, EMI protection, printed circuits |
| Surface Area | Smaller surface area per volume | Large surface area, thin layers |
| Cost | Generally lower cost per length | Higher cost due to processing |
Introduction to Copper Wire and Copper Foil
Copper wire consists of cylindrical strands of highly conductive copper used extensively in electrical wiring, telecommunications, and electronics due to its excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility. Copper foil, on the other hand, is a thin sheet of copper primarily utilized in printed circuit boards (PCBs), electromagnetic shielding, and flexible electronics, valued for its uniform thickness and adhesive properties. Understanding the distinct physical forms and applications of copper wire and copper foil is essential for optimizing performance in electrical and electronic components.
Key Properties of Copper Wire
Copper wire exhibits superior electrical conductivity and tensile strength, making it essential for efficient power transmission and durable electrical connections. Its flexibility allows easy manipulation for winding coils and intricate circuitry, while high thermal conductivity supports effective heat dissipation in electronic components. The oxidation resistance of copper wire ensures long-lasting performance in both indoor and outdoor electrical applications.
Essential Features of Copper Foil
Copper foil offers superior flexibility and a thinner profile compared to copper wire, making it ideal for applications requiring lightweight and compact conductive materials. Its excellent electrical conductivity and high corrosion resistance ensure reliable performance in printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electromagnetic shielding. Unlike copper wire, copper foil can be precisely layered and patterned, optimizing space and enhancing thermal management in electronic devices.
Manufacturing Processes: Copper Wire vs Copper Foil
Copper wire manufacturing involves drawing molten copper through dies to create long, flexible strands used in electrical wiring and electronics. Copper foil production utilizes continuous casting and rolling processes to produce thin, flat sheets essential for lithium-ion batteries and printed circuit boards. Each method optimizes copper's electrical conductivity and mechanical properties for specific industrial applications.
Electrical Conductivity: Wire vs Foil
Copper wire exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to copper foil due to its thicker cross-sectional area, which reduces resistance and allows higher current flow. Copper foil, while thinner and more flexible, has increased surface resistance, making it less efficient for high-current applications but ideal for space-constrained electronics and flexible circuits. The conductivity of copper wire typically ranges around 5.8 x 10^7 S/m, whereas copper foil's conductivity can be slightly lower depending on thickness and processing.
Applications and Uses in Industry
Copper wire is widely used in electrical wiring, telecommunications, and power transmission due to its excellent conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for circuits and electrical connections. Copper foil finds extensive application in electronics manufacturing, particularly in printed circuit boards (PCBs) and electromagnetic shielding, where its thin, malleable properties provide efficient conductive layers. Industries rely on copper wire for durable, high-current applications, while copper foil serves in precision electronics and battery components, highlighting their distinct yet complementary roles.
Mechanical Strength and Flexibility Comparison
Copper wire offers superior mechanical strength due to its cylindrical shape and solid core, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and high tensile resistance. Copper foil, being thinner and flat, provides greater flexibility and conformability for intricate circuit designs and compact electronic components. Both materials balance conductivity with physical properties, but wire excels in strength while foil prioritizes flexibility.
Cost Differences: Copper Wire vs Copper Foil
Copper wire typically costs more than copper foil due to its manufacturing complexity and higher purity requirements for electrical conductivity. Copper foil, being thinner and produced through rolling processes, generally incurs lower material and production expenses. Pricing variations also depend on gauge thickness, with thinner copper foil offering more cost-effective solutions for applications like electronics and shielding compared to bulkier copper wire.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper wire offers greater durability and recyclability compared to copper foil, reducing environmental waste through multiple reuse cycles. Copper foil production involves energy-intensive processes that generate higher emissions, making copper wire a more sustainable choice for eco-conscious applications. The higher recyclability rate and longer lifespan of copper wire significantly lower its overall carbon footprint in electronic manufacturing.
Choosing the Right Copper Material for Your Project
Copper wire offers superior flexibility and conductivity, making it ideal for electrical wiring and circuits requiring dynamic movement or intricate connections. Copper foil provides a thin, uniform surface suitable for shielding, grounding, and lightweight structural applications where precise layering and adhesion are crucial. Selecting the right copper material depends on project requirements such as electrical performance, mechanical flexibility, and fabrication constraints.
Copper Wire vs Copper Foil Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com