Copper offers superior durability and thermal conductivity compared to plastic, making it ideal for plumbing and electrical applications. Unlike plastic, copper resists corrosion and can withstand higher temperatures, ensuring long-lasting performance. Copper's natural antimicrobial properties also reduce the risk of bacterial growth, enhancing safety in water supply systems.
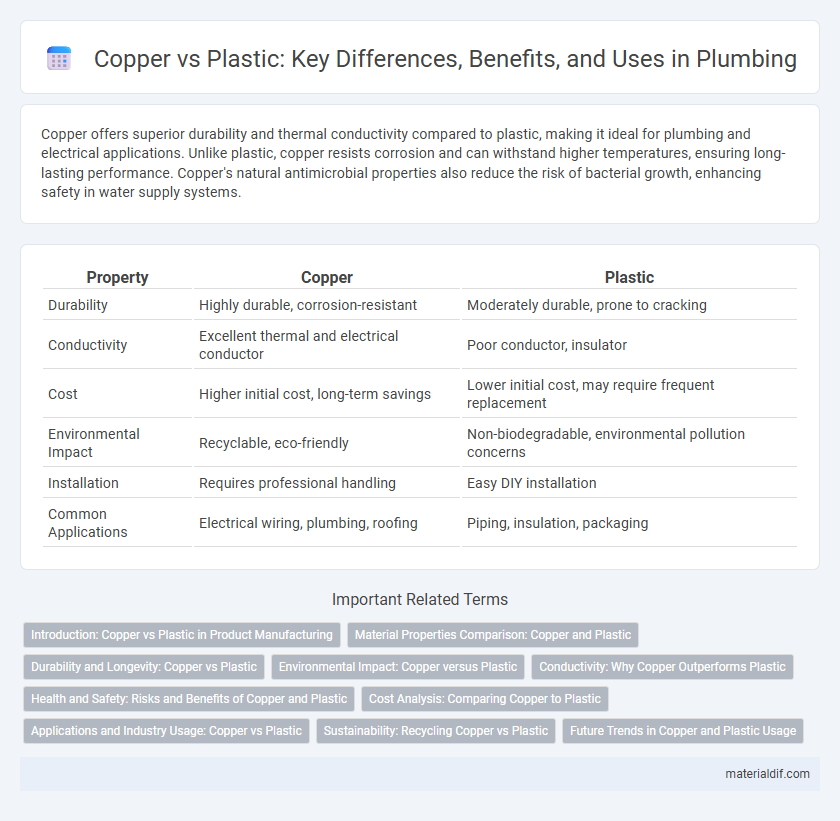
Table of Comparison
| Property | Copper | Plastic |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Highly durable, corrosion-resistant | Moderately durable, prone to cracking |
| Conductivity | Excellent thermal and electrical conductor | Poor conductor, insulator |
| Cost | Higher initial cost, long-term savings | Lower initial cost, may require frequent replacement |
| Environmental Impact | Recyclable, eco-friendly | Non-biodegradable, environmental pollution concerns |
| Installation | Requires professional handling | Easy DIY installation |
| Common Applications | Electrical wiring, plumbing, roofing | Piping, insulation, packaging |
Introduction: Copper vs Plastic in Product Manufacturing
Copper offers superior electrical conductivity and thermal resistance compared to plastic, making it a preferred material in product manufacturing where performance and durability are critical. Plastic, while lightweight and cost-effective, often lacks the strength and longevity required for high-demand applications, leading to faster wear and potential product failure. Manufacturers prioritize copper for applications involving heat dissipation, electrical wiring, and corrosion resistance, contrasting with plastic's common use in non-structural, insulating, or decorative components.
Material Properties Comparison: Copper and Plastic
Copper exhibits high thermal and electrical conductivity, superior tensile strength, and excellent corrosion resistance compared to plastic, which typically has lower durability and conductivity but offers lighter weight and greater flexibility. The density of copper (8.96 g/cm3) contrasts with plastic's significantly lower density (0.9-1.4 g/cm3), impacting their respective applications in weight-sensitive environments. Copper's natural antimicrobial properties and recyclability further distinguish it from most plastics, which can degrade with UV exposure and often present recycling challenges.
Durability and Longevity: Copper vs Plastic
Copper exhibits superior durability and longevity compared to plastic due to its resistance to corrosion, high temperatures, and mechanical wear. While plastic materials may degrade under UV exposure and physical stress, copper maintains structural integrity for decades, often exceeding 50 years in plumbing and electrical applications. The inherent antimicrobial properties and recyclability of copper further enhance its lifespan and environmental sustainability over plastic alternatives.
Environmental Impact: Copper versus Plastic
Copper demonstrates a significantly lower environmental impact compared to plastic due to its high recyclability and durability, reducing waste and resource consumption over time. Unlike plastic, which often contributes to pollution and takes centuries to decompose, copper can be recycled repeatedly without loss of quality, conserving natural resources and energy. Moreover, copper's natural antimicrobial properties decrease the need for chemical treatments, further minimizing its ecological footprint relative to plastic alternatives.
Conductivity: Why Copper Outperforms Plastic
Copper exhibits superior electrical conductivity with a conductivity rating of approximately 5.96 x 10^7 S/m, making it an ideal material for efficient electrical wiring compared to plastic, which is an insulator with negligible conductivity. This high conductivity allows copper to transmit electrical current with minimal resistance and heat generation, enhancing energy efficiency and safety in electrical applications. Plastic, by contrast, serves primarily as an insulating material to prevent electrical flow and protect against electrical hazards rather than conducting electricity.
Health and Safety: Risks and Benefits of Copper and Plastic
Copper offers superior antimicrobial properties, reducing the risk of bacterial contamination compared to plastic, which can harbor harmful pathogens on its surface. Exposure to copper is generally safe and essential for human health in trace amounts, while plastic pipes may leach harmful chemicals such as phthalates and BPA, posing potential health risks. Copper's durability and resistance to biofilm formation enhance water safety, whereas plastic's susceptibility to cracking and chemical leaching can compromise water quality and public health.
Cost Analysis: Comparing Copper to Plastic
Copper's initial installation costs are higher than plastic pipes due to material expenses and labor-intensive installation processes. However, copper offers greater durability, corrosion resistance, and longevity, often resulting in lower maintenance and replacement costs over time. Plastic pipes present a cost-effective upfront option but may incur additional expenses related to repairs and shorter service life in demanding environments.
Applications and Industry Usage: Copper vs Plastic
Copper excels in electrical wiring, plumbing, and HVAC systems due to its superior conductivity, durability, and corrosion resistance, making it the preferred choice in construction and electronics industries. Plastic, lightweight and cost-effective, dominates in packaging, automotive parts, and consumer goods, favored for its flexibility and insulation properties. Industries select copper for critical applications requiring longevity and thermal efficiency, while plastic is favored for mass production and design versatility.
Sustainability: Recycling Copper vs Plastic
Copper offers superior sustainability compared to plastic due to its high recyclability rate, with approximately 90% of copper used today being recycled without any loss in quality. Recycling copper consumes up to 85% less energy than producing it from virgin ore, significantly reducing environmental impact. In contrast, plastic recycling is less efficient, often downcycled, and generates considerable microplastic pollution, making copper a more sustainable material choice.
Future Trends in Copper and Plastic Usage
Copper's superior electrical conductivity and recyclability position it as a key material in future sustainable technologies, including electric vehicles and renewable energy infrastructure. Plastic, favored for its lightweight and cost-effectiveness, faces increasing scrutiny due to environmental concerns and regulatory restrictions on single-use applications. Advancements in biodegradable plastics and copper recycling innovations will significantly influence the trajectory of both materials in emerging industrial sectors.
Copper vs Plastic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com