Copper sheets are thinner and more flexible than copper plates, making them ideal for applications requiring easy bending and shaping, such as roofing and decorative crafts. Copper plates are thicker, providing greater strength and durability, which suits heavy-duty industrial uses like electrical busbars and structural components. Choosing between copper sheet and plate depends on the specific requirements for thickness, strength, and formability in a project.
Table of Comparison
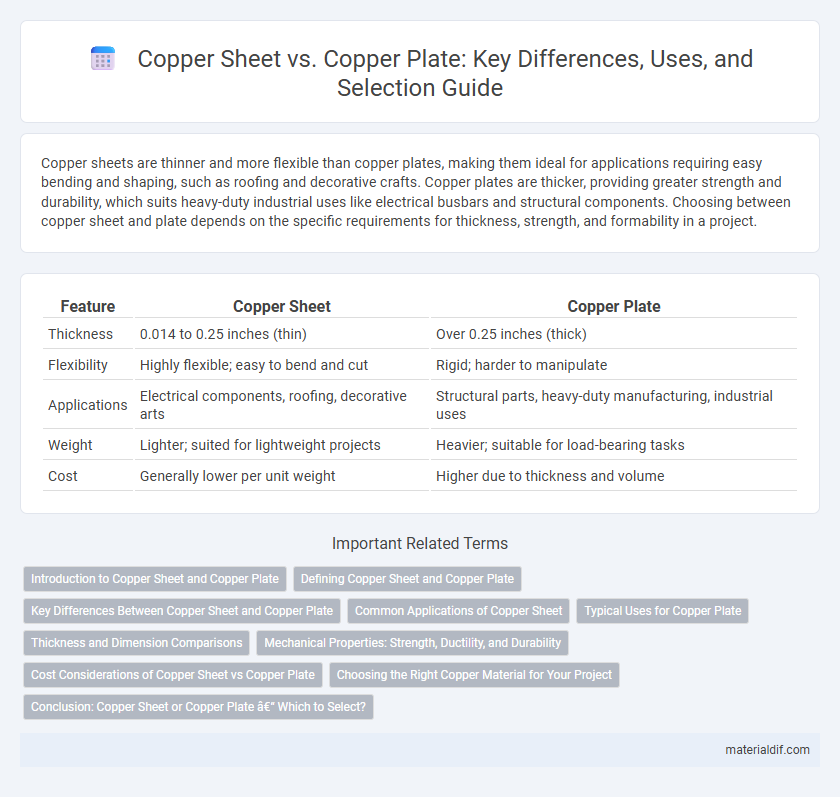
| Feature | Copper Sheet | Copper Plate |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | 0.014 to 0.25 inches (thin) | Over 0.25 inches (thick) |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible; easy to bend and cut | Rigid; harder to manipulate |
| Applications | Electrical components, roofing, decorative arts | Structural parts, heavy-duty manufacturing, industrial uses |
| Weight | Lighter; suited for lightweight projects | Heavier; suitable for load-bearing tasks |
| Cost | Generally lower per unit weight | Higher due to thickness and volume |
Introduction to Copper Sheet and Copper Plate
Copper sheets and copper plates differ primarily in thickness and application, with sheets typically measuring less than 6mm and plates exceeding that thickness. Copper sheets offer excellent flexibility, making them ideal for roofing, cladding, and decorative projects, while copper plates provide superior structural strength for heavy-duty industrial use. Both materials share high thermal and electrical conductivity, corrosion resistance, and excellent malleability, essential for electronics, plumbing, and manufacturing industries.
Defining Copper Sheet and Copper Plate
Copper sheet refers to thin, flat pieces of copper typically less than 6mm in thickness, commonly used in electrical applications, roofing, and decorative arts due to its malleability and conductivity. Copper plate is thicker, usually exceeding 6mm, offering greater strength and durability for structural components, industrial machinery, and heavy-duty fabrication. Both forms maintain copper's superior corrosion resistance and excellent thermal and electrical properties, with their distinctions mainly in thickness and intended use cases.
Key Differences Between Copper Sheet and Copper Plate
Copper sheets and copper plates primarily differ in thickness, with sheets being thinner and more flexible, typically under 6mm, while plates are thicker, often over 6mm, providing greater strength and rigidity. Sheets are ideal for applications requiring malleability, such as roofing and decorative projects, whereas plates are used in structural or heavy-duty environments like machinery bases and industrial equipment. The manufacturing process also varies, with sheets usually produced through rolling and plates often forged or cold-rolled for enhanced durability.
Common Applications of Copper Sheet
Copper sheets are widely used in roofing, flashing, and cladding due to their excellent corrosion resistance and malleability, offering a durable solution for architectural applications. Electroplating industries utilize copper sheets for their conductive properties, ensuring efficient material performance in electrical components. Additionally, copper sheets serve in crafting decorative items, HVAC systems, and electrical circuitry, benefiting from their thermal conductivity and ease of fabrication.
Typical Uses for Copper Plate
Copper plate is primarily used in applications requiring thicker, stronger metal such as industrial manufacturing, electrical components, and architectural features. Its superior thickness compared to copper sheet makes it ideal for heavy-duty fabrication, structural supports, and machining parts. Typical uses include electrical bus bars, heavy-duty roofing, and custom metalwork where durability and mechanical strength are essential.
Thickness and Dimension Comparisons
Copper sheets typically range in thickness from 0.006 inches to 0.125 inches, making them thinner and more flexible than copper plates, which generally start at 0.25 inches and can extend to several inches thick. Dimensionally, copper sheets are available in larger surface area formats, often measured in feet for width and length, whereas copper plates are produced in smaller, thicker slabs with more limited surface dimensions. The choice between copper sheet and plate hinges on the specific thickness and size needs of applications such as electrical grounding, roofing, or industrial fabrication.
Mechanical Properties: Strength, Ductility, and Durability
Copper sheets typically offer higher ductility, allowing for easy bending and forming, while copper plates provide greater strength and durability due to their increased thickness. The mechanical properties of copper plates make them ideal for heavy-duty applications requiring enhanced structural integrity, whereas copper sheets excel in tasks needing flexibility and moderate strength. Both materials maintain excellent corrosion resistance and electrical conductivity, inherent to copper, but their mechanical performance varies primarily by thickness and intended use.
Cost Considerations of Copper Sheet vs Copper Plate
Copper sheets generally cost less per unit area than copper plates due to their thinner gauge and lower material volume. Copper plates, being thicker and heavier, require more raw copper and incur higher manufacturing expenses, resulting in increased prices. Budgeting effectively for projects involving copper materials necessitates evaluating thickness requirements against cost differences between sheets and plates.
Choosing the Right Copper Material for Your Project
Copper sheets offer thin, flexible options ideal for applications requiring easy bending and detailed metalwork, while copper plates provide thicker, sturdier material suited for structural support and heavy-duty projects. Consider the specific thickness, durability requirements, and fabrication methods to determine whether a copper sheet or plate best matches the mechanical strength and aesthetic needs of your project. Industrial standards often classify sheets as materials under 6mm and plates as those 6mm or thicker, guiding precise selection for electrical, architectural, or manufacturing purposes.
Conclusion: Copper Sheet or Copper Plate – Which to Select?
Copper sheets are thinner and more flexible, making them ideal for applications requiring easy bending and shaping, such as roofing or craft projects. Copper plates are thicker and stronger, suited for heavy-duty industrial uses where durability and structural integrity are essential, like machinery parts or heavy electrical components. Selecting between copper sheet and plate depends on the specific thickness and strength requirements, with sheets preferred for lightweight tasks and plates for robust, high-stress applications.
Copper Sheet vs Copper Plate Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com