Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) offers superior thermal conductivity and electrical performance compared to FR4, making it ideal for high-frequency and high-current applications. FR4 is a widely used glass-reinforced epoxy laminate known for its mechanical strength and cost-effectiveness but has lower thermal and electrical properties than CCL. Choosing between Copper Clad Laminate and FR4 depends on balancing performance requirements with budget constraints in PCB manufacturing.
Table of Comparison
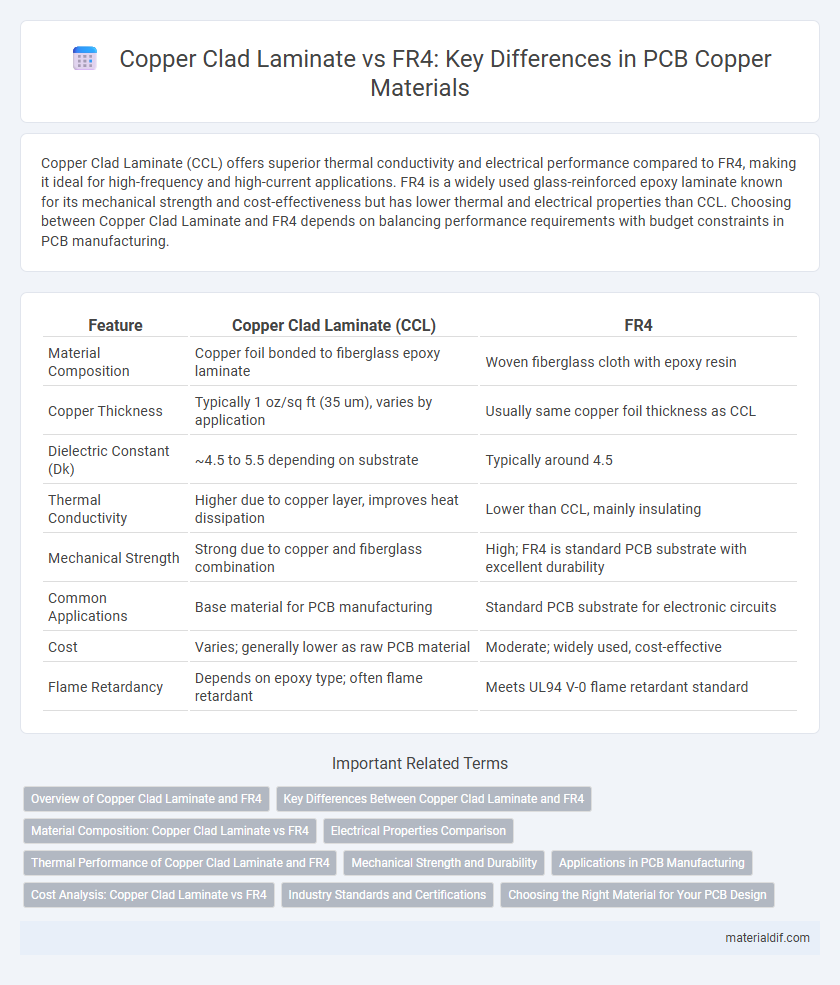
| Feature | Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) | FR4 |
|---|---|---|
| Material Composition | Copper foil bonded to fiberglass epoxy laminate | Woven fiberglass cloth with epoxy resin |
| Copper Thickness | Typically 1 oz/sq ft (35 um), varies by application | Usually same copper foil thickness as CCL |
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | ~4.5 to 5.5 depending on substrate | Typically around 4.5 |
| Thermal Conductivity | Higher due to copper layer, improves heat dissipation | Lower than CCL, mainly insulating |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong due to copper and fiberglass combination | High; FR4 is standard PCB substrate with excellent durability |
| Common Applications | Base material for PCB manufacturing | Standard PCB substrate for electronic circuits |
| Cost | Varies; generally lower as raw PCB material | Moderate; widely used, cost-effective |
| Flame Retardancy | Depends on epoxy type; often flame retardant | Meets UL94 V-0 flame retardant standard |
Overview of Copper Clad Laminate and FR4
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) is a foundational material used in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, consisting of a thin copper foil bonded to a non-conductive substrate, providing excellent electrical conductivity and mechanical strength. FR4, a specific type of CCL, is composed of woven fiberglass cloth with an epoxy resin binder, known for its high flame resistance and dimensional stability under heat. The main distinction lies in FR4's enhanced thermal and mechanical properties, making it the most widely used material for PCBs in consumer electronics and industrial applications.
Key Differences Between Copper Clad Laminate and FR4
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) serves as the foundational material combining copper foil with fiberglass epoxy resin, while FR4 refers specifically to a grade of CCL known for its flame-retardant properties and high mechanical strength. Key differences include their composition, where FR4 incorporates flame-resistant additives meeting UL94 V-0 standards, enhancing safety and durability in electronic applications. Electrical insulation, thermal resistance, and dimensional stability also distinguish FR4, making it the preferred choice in printed circuit boards requiring high-performance criteria.
Material Composition: Copper Clad Laminate vs FR4
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) consists of a thin layer of copper foil laminated onto a non-conductive substrate, typically fiberglass or paper-based epoxy resin. FR4, a common grade of CCL, is composed of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with a flame-resistant epoxy resin, providing enhanced mechanical strength and thermal stability. The key difference lies in FR4's flame-retardant properties and consistent dielectric performance, making it the standard material for multilayer printed circuit boards (PCBs).
Electrical Properties Comparison
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) exhibits superior electrical conductivity compared to FR4 due to its high-purity copper layer, enabling efficient signal transmission and reduced resistance. FR4, a composite material composed of woven glass fabric and epoxy resin, offers excellent dielectric properties with a typical dielectric constant (Dk) around 4.5, making it suitable for moderate-frequency PCB applications. While CCL emphasizes conductivity and current-carrying capacity, FR4 balances electrical insulation with mechanical strength, essential for multilayer circuit boards requiring controlled impedance.
Thermal Performance of Copper Clad Laminate and FR4
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) offers superior thermal conductivity compared to FR4, with typical values ranging from 0.3 to 1.0 W/mK for CCL versus 0.25 W/mK for FR4. The enhanced heat dissipation in Copper Clad Laminates improves reliability in high-power and high-frequency applications by reducing thermal stress. While FR4 remains popular for standard PCB substrates, CCL is preferred in thermal management scenarios due to its better heat transfer capabilities.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) exhibits superior mechanical strength compared to standard FR4 due to its enhanced copper foil bonding and resin matrix, which improves resistance to bending and impacts. FR4, while widely used, has moderate durability under mechanical stress and can degrade faster in harsh environments. The enhanced durability of CCL makes it preferable for high-performance printed circuit boards that require long-lasting structural integrity.
Applications in PCB Manufacturing
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) and FR4 are essential materials in PCB manufacturing, with Copper Clad Laminate serving as the base substrate combining copper foil with insulating material, while FR4 is a widely used flame-retardant epoxy resin composite substrate. Copper Clad Laminates excel in high-frequency applications, flexible circuits, and multilayer PCBs due to their excellent copper adhesion and thermal conductivity. FR4 is preferred for standard rigid PCB applications, offering cost-effective mechanical strength and reliable electrical insulation across diverse electronic devices.
Cost Analysis: Copper Clad Laminate vs FR4
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) generally offers a lower upfront cost compared to FR4, making it a more economical choice for high-volume printed circuit board (PCB) production. While FR4 provides enhanced mechanical strength and thermal resistance, its higher material and processing costs contribute to an increased overall expense. Evaluating total cost requires considering factors such as copper thickness, dielectric properties, and manufacturing complexity inherent to each substrate.
Industry Standards and Certifications
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) and FR4 are both essential materials in PCB manufacturing, with FR4 being the most widely used due to its compliance with industry standards such as IPC-4101 and UL 94 V-0 flame retardancy certification. CCL serves as the base material in FR4 laminates, primarily composed of woven fiberglass cloth impregnated with epoxy resin, ensuring mechanical strength and flame resistance per IPC and UL certifications. The rigorous adherence to these standards guarantees that PCBs made from FR4 and CCL meet performance, safety, and reliability requirements for electronic applications across multiple industries.
Choosing the Right Material for Your PCB Design
Copper Clad Laminate (CCL) and FR4 are essential materials in PCB manufacturing, with CCL providing the conductive copper layer and FR4 offering robust mechanical strength and excellent thermal resistance. Selecting the right material depends on factors such as electrical performance, temperature tolerance, and the complexity of the PCB design. High-frequency applications often benefit from specialized CCLs with low dielectric loss, while FR4 remains a versatile choice for cost-effective, durable circuit boards.
Copper Clad Laminate vs FR4 Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com