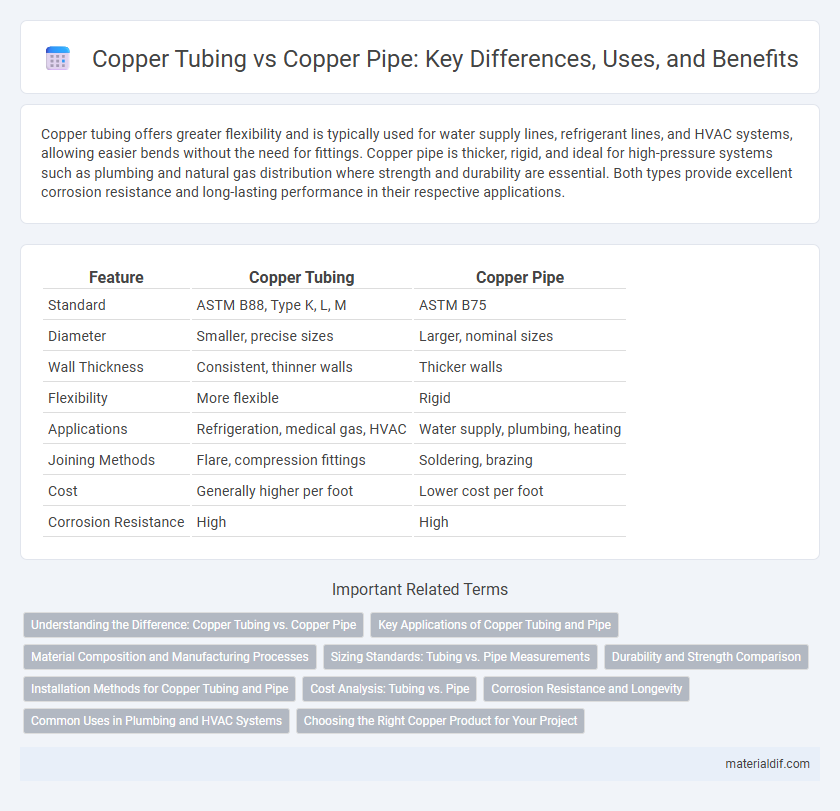
Copper tubing offers greater flexibility and is typically used for water supply lines, refrigerant lines, and HVAC systems, allowing easier bends without the need for fittings. Copper pipe is thicker, rigid, and ideal for high-pressure systems such as plumbing and natural gas distribution where strength and durability are essential. Both types provide excellent corrosion resistance and long-lasting performance in their respective applications.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Copper Tubing | Copper Pipe |
|---|---|---|
| Standard | ASTM B88, Type K, L, M | ASTM B75 |
| Diameter | Smaller, precise sizes | Larger, nominal sizes |
| Wall Thickness | Consistent, thinner walls | Thicker walls |
| Flexibility | More flexible | Rigid |
| Applications | Refrigeration, medical gas, HVAC | Water supply, plumbing, heating |
| Joining Methods | Flare, compression fittings | Soldering, brazing |
| Cost | Generally higher per foot | Lower cost per foot |
| Corrosion Resistance | High | High |
Understanding the Difference: Copper Tubing vs. Copper Pipe
Copper tubing and copper pipe differ primarily in manufacturing process and application; tubing is typically drawn through a die to achieve exact diameters with thinner walls, while pipe is usually manufactured through casting or extrusion with thicker walls for strength. Copper tubing offers precise dimensions, flexibility, and is commonly used in HVAC and refrigeration systems, whereas copper pipe, available in nominal sizes and schedules, is preferred for plumbing and water supply due to its durability. Understanding these distinctions is crucial for selecting the appropriate copper material based on system requirements and performance criteria.
Key Applications of Copper Tubing and Pipe
Copper tubing is predominantly used in HVAC systems, refrigeration, and plumbing applications requiring precise bending and flexibility, such as water supply lines and refrigerant lines. Copper pipe, with thicker walls and rigid structure, is mainly applied in industrial piping, gas distribution, and fire sprinkler systems where durability and pressure resistance are critical. Both copper tubing and pipe offer excellent corrosion resistance, thermal conductivity, and longevity, making them essential for residential, commercial, and industrial infrastructure.
Material Composition and Manufacturing Processes
Copper tubing typically uses more malleable copper alloys, such as soft copper, which allows for easier bending and shaping without joints. Copper pipe is generally made from harder copper alloys, providing greater rigidity and strength, suitable for structural and plumbing applications under higher pressure. Manufacturing processes for tubing involve extrusion and annealing to enhance flexibility, whereas copper pipes undergo casting or drawing followed by tempering to achieve durability and pressure resistance.
Sizing Standards: Tubing vs. Pipe Measurements
Copper tubing uses nominal sizes based on outside diameter (OD), which ensures consistent fit with fittings regardless of wall thickness variations. Copper pipe employs nominal sizes referring approximately to inside diameter (ID), causing size discrepancies when compared to tubing with the same nominal designation. This fundamental difference in sizing standards affects the selection process for plumbing or HVAC systems, ensuring proper compatibility and flow characteristics depending on the application.
Durability and Strength Comparison
Copper tubing offers greater flexibility and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for applications requiring bending without compromising durability. Copper pipe, with a thicker wall and rigid structure, provides superior strength and pressure handling capabilities for high-demand plumbing and industrial systems. Both materials maintain excellent longevity, but pipe is preferred where mechanical strength and durability under high pressure are crucial.
Installation Methods for Copper Tubing and Pipe
Copper tubing uses flexible coil lengths and requires specialized fittings like compression or flare fittings for installation, allowing easier bends without jointing. Copper pipe installations rely on rigid straight sections connected through soldering, brazing, or mechanical fittings, making them suitable for structural support in plumbing systems. Professional installation ensures leak-proof connections and adherence to building codes for both tubing and pipe applications.
Cost Analysis: Tubing vs. Pipe
Copper tubing generally costs more upfront than copper pipe due to its thinner walls and precise manufacturing process, which enhances flexibility and corrosion resistance. However, the overall installation expenses for copper tubing tend to be lower because its ease of bending reduces the need for fittings and labor time, offsetting the higher material cost. Copper pipe, while less expensive initially, often incurs elevated labor and fitting costs, making copper tubing a more cost-effective choice in complex plumbing projects.
Corrosion Resistance and Longevity
Copper tubing and copper pipe both offer excellent corrosion resistance due to their copper composition, but copper tubing typically exhibits superior corrosion resistance because of its seamless construction, reducing potential entry points for moisture and contaminants. This seamless design contributes to enhanced longevity, often resulting in service life exceeding 50 years in plumbing systems. In contrast, copper pipe, which can be either seamless or welded, may have welded joints that are more susceptible to corrosion and failure over time, impacting overall durability.
Common Uses in Plumbing and HVAC Systems
Copper tubing is primarily used in HVAC systems for refrigerant lines and residential water supply lines due to its flexibility and ease of installation. Copper pipe, with thicker walls and rigid form, is preferred for plumbing applications involving high pressure water distribution and gas lines. Both materials offer excellent corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity, making them ideal for efficient heat exchange and long-lasting plumbing infrastructure.
Choosing the Right Copper Product for Your Project
Copper tubing offers flexibility and easier installation for residential plumbing and refrigeration, while copper pipe provides greater strength and durability ideal for water supply and gas lines. Selecting the right copper product depends on the application's pressure requirements, diameter specifications, and local building codes to ensure safety and longevity. Understanding the differences in wall thickness, measured as K, L, or M types, helps optimize performance and cost-effectiveness for your project.
Copper Tubing vs Copper Pipe Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com