Copper tubing offers superior durability and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for plumbing and HVAC systems where fluid transport is essential. Copper wire, prized for its excellent electrical conductivity and flexibility, is commonly used in electrical wiring and cable applications. Both forms leverage copper's thermal and conductive properties but serve distinct purposes based on their physical structure and functional requirements.
Table of Comparison
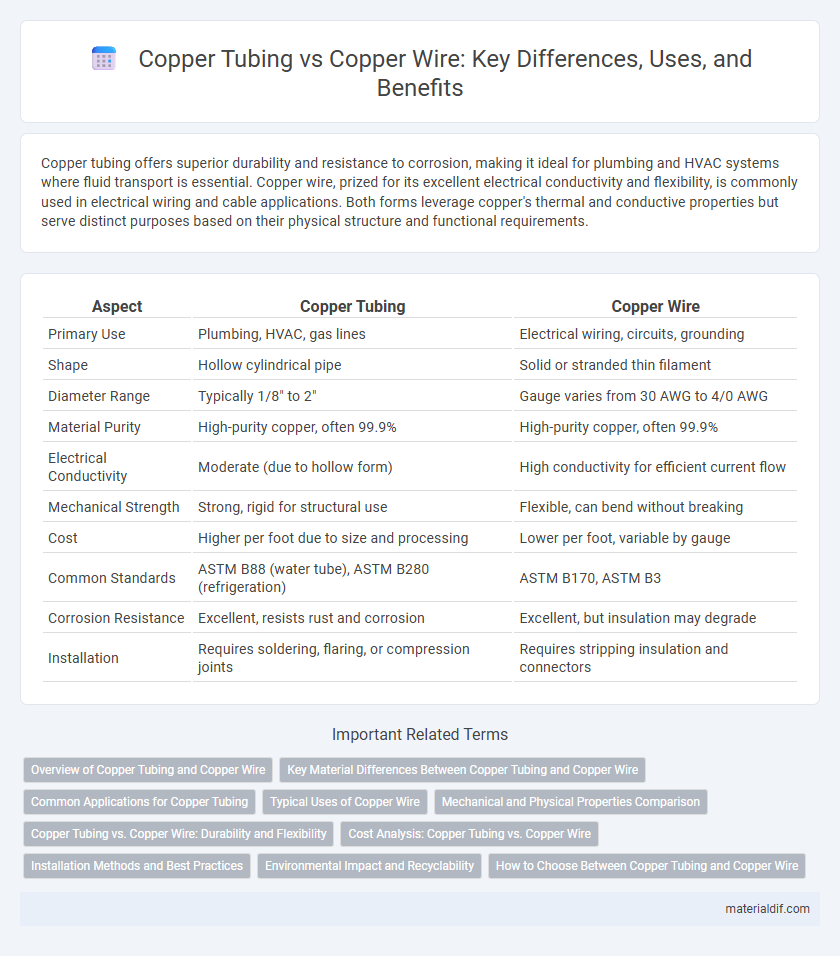
| Aspect | Copper Tubing | Copper Wire |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use | Plumbing, HVAC, gas lines | Electrical wiring, circuits, grounding |
| Shape | Hollow cylindrical pipe | Solid or stranded thin filament |
| Diameter Range | Typically 1/8" to 2" | Gauge varies from 30 AWG to 4/0 AWG |
| Material Purity | High-purity copper, often 99.9% | High-purity copper, often 99.9% |
| Electrical Conductivity | Moderate (due to hollow form) | High conductivity for efficient current flow |
| Mechanical Strength | Strong, rigid for structural use | Flexible, can bend without breaking |
| Cost | Higher per foot due to size and processing | Lower per foot, variable by gauge |
| Common Standards | ASTM B88 (water tube), ASTM B280 (refrigeration) | ASTM B170, ASTM B3 |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent, resists rust and corrosion | Excellent, but insulation may degrade |
| Installation | Requires soldering, flaring, or compression joints | Requires stripping insulation and connectors |
Overview of Copper Tubing and Copper Wire
Copper tubing is a hollow cylindrical product primarily used in plumbing, refrigeration, and HVAC systems due to its corrosion resistance and excellent thermal conductivity. Copper wire consists of solid or stranded copper strands that provide exceptional electrical conductivity, commonly used in electrical wiring and electronic components. Both copper tubing and wire leverage copper's durability and conductivity but serve distinct functions in construction and electrical applications.
Key Material Differences Between Copper Tubing and Copper Wire
Copper tubing is primarily designed for fluid transport and features a hollow cylindrical shape with varying wall thicknesses to withstand pressure and corrosion. Copper wire is solid or stranded, optimized for electrical conductivity and flexibility in wiring applications, with insulation often applied for safety. The key material differences include tubing's emphasis on strength and corrosion resistance, while wire prioritizes electrical conductivity and mechanical flexibility.
Common Applications for Copper Tubing
Copper tubing is widely used in plumbing systems for water supply and refrigerant lines in HVAC applications due to its corrosion resistance and flexibility. It is essential in medical gas delivery and natural gas transportation systems, where safety and durability are critical. Copper tubing is also preferred in fire sprinkler systems and solar thermal installations for efficient heat transfer and reliability.
Typical Uses of Copper Wire
Copper wire is primarily used in electrical wiring due to its excellent conductivity and flexibility, making it ideal for power transmission, telecommunications, and electronic circuits. It is commonly found in residential and commercial building wiring, electrical motors, transformers, and printed circuit boards. Copper wire's high thermal and electrical conductivity also ensures efficient performance in automotive wiring and grounding systems.
Mechanical and Physical Properties Comparison
Copper tubing exhibits superior rigidity and durability compared to copper wire, making it ideal for plumbing and HVAC applications requiring structural stability and resistance to deformation. Copper wire offers higher flexibility and excellent electrical conductivity, which is essential for electrical wiring and electronic components where bending and twisting are frequent. The tensile strength of copper tubing typically surpasses that of copper wire, while copper wire's annealed condition provides enhanced ductility for efficient current transmission.
Copper Tubing vs. Copper Wire: Durability and Flexibility
Copper tubing offers superior durability due to its thicker walls and resistance to corrosion, making it ideal for plumbing and HVAC applications. Copper wire provides greater flexibility, allowing it to bend and twist easily for electrical wiring and intricate installations. The choice between copper tubing and copper wire depends on the required balance between structural strength and adaptability in specific projects.
Cost Analysis: Copper Tubing vs. Copper Wire
Copper tubing generally incurs higher material and manufacturing costs compared to copper wire due to its thicker walls and required precision in bending and joining. Copper wire, being thinner and more flexible, often offers lower installation and transportation expenses, making it more cost-effective for electrical applications. However, the total cost analysis should also consider application-specific factors such as durability, conductivity requirements, and long-term maintenance.
Installation Methods and Best Practices
Copper tubing installation requires precise cutting, deburring, and fitting to ensure leak-free joints, often using soldering or compression fittings to secure connections. Copper wire installation emphasizes proper gauge selection, insulation stripping without damaging the conductor, and secure terminal connections to maintain electrical conductivity and safety. Best practices include following local codes, ensuring tight connections, and avoiding mechanical stress that could damage either tubing or wiring during installation.
Environmental Impact and Recyclability
Copper tubing and copper wire both offer high recyclability, with copper achieving nearly 100% reuse rates, significantly reducing the demand for new mining and associated environmental degradation. Copper tubing, often used in plumbing and HVAC systems, typically contains fewer impurities than copper wire used in electrical applications, enhancing its recyclability quality and reducing potential waste. The environmental impact of copper wire can be higher if insulation materials complicate recycling processes, whereas bare copper tubing simplifies recycling, minimizing landfill accumulation and promoting circular economy practices.
How to Choose Between Copper Tubing and Copper Wire
Choosing between copper tubing and copper wire depends on the intended application and performance requirements. Copper tubing is ideal for fluid transport and HVAC systems due to its corrosion resistance and ease of bending, while copper wire excels in electrical conductivity for wiring and circuitry. Consider factors such as mechanical flexibility, conductivity standards, and regulatory compliance to select the appropriate copper form for your project.
Copper Tubing vs Copper Wire Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com