Copper wiring remains a prevalent choice for electrical and data transmission due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation, offering reliable performance over short distances. Fiber optic cables surpass copper in bandwidth and signal quality, enabling faster data transfer with minimal interference and significantly longer transmission ranges. For modern high-speed internet and telecommunications infrastructure, fiber optics present a superior solution despite higher initial costs and installation complexity.
Table of Comparison
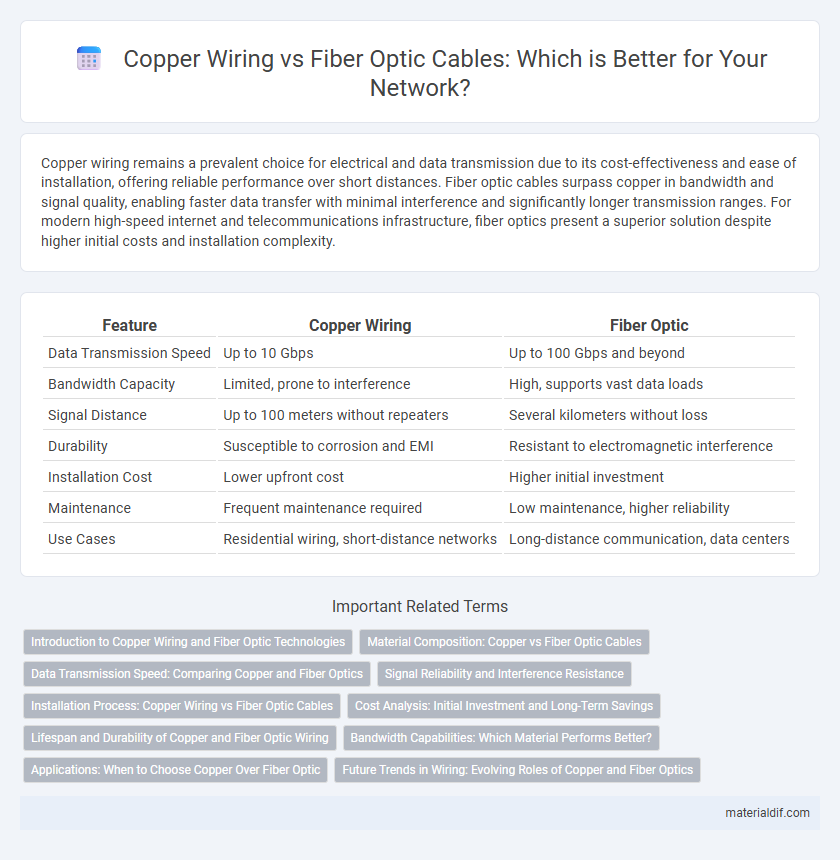
| Feature | Copper Wiring | Fiber Optic |
|---|---|---|
| Data Transmission Speed | Up to 10 Gbps | Up to 100 Gbps and beyond |
| Bandwidth Capacity | Limited, prone to interference | High, supports vast data loads |
| Signal Distance | Up to 100 meters without repeaters | Several kilometers without loss |
| Durability | Susceptible to corrosion and EMI | Resistant to electromagnetic interference |
| Installation Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Maintenance | Frequent maintenance required | Low maintenance, higher reliability |
| Use Cases | Residential wiring, short-distance networks | Long-distance communication, data centers |
Introduction to Copper Wiring and Fiber Optic Technologies
Copper wiring transmits electrical signals using conductive metal, primarily copper, which offers durability and ease of installation in traditional telecommunications and electrical systems. Fiber optic technology employs strands of glass or plastic fibers to transmit data as pulses of light, enabling higher bandwidth and faster transmission over longer distances without electromagnetic interference. Both technologies serve critical roles in communication infrastructure, with copper wiring favored for local connections and fiber optics ideal for high-speed, long-range data transfer.
Material Composition: Copper vs Fiber Optic Cables
Copper wiring consists of conductive copper metal strands that transmit electrical signals through electron flow, offering durability and flexibility in various applications. Fiber optic cables are composed of glass or plastic fibers that transmit data as pulses of light, enabling higher bandwidth and faster data transfer over longer distances without electromagnetic interference. The fundamental material differences impact installation cost, signal quality, and susceptibility to environmental factors in telecommunications infrastructure.
Data Transmission Speed: Comparing Copper and Fiber Optics
Fiber optic cables provide significantly higher data transmission speeds compared to copper wiring, reaching up to 100 Gbps or more in modern implementations. Copper wiring, often using twisted-pair or coaxial cables, typically supports speeds up to 10 Gbps but suffers from signal degradation over longer distances. The superior bandwidth and minimal interference of fiber optics make it the preferred choice for high-speed internet and data communication networks.
Signal Reliability and Interference Resistance
Copper wiring transmits signals via electrical currents, making it susceptible to electromagnetic interference and signal degradation over long distances, which reduces overall reliability. Fiber optic cables use light to transmit data, providing superior resistance to electromagnetic interference and maintaining signal integrity across extended spans. This makes fiber optic wiring the preferred choice for high-speed, stable connections in environments with significant electrical noise.
Installation Process: Copper Wiring vs Fiber Optic Cables
Copper wiring installation involves pulling and securing metal conductors inside insulated sheaths, often requiring careful handling to avoid electrical interference and corrosion issues. Fiber optic cable installation demands precision in laying fragile glass fibers within protective cladding, necessitating specialized tools for splicing and connectors to maintain signal integrity. Compared to copper, fiber optic cables offer faster data transmission with less signal degradation but require more skilled labor and stringent handling protocols during installation.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-Term Savings
Copper wiring generally requires a lower initial investment compared to fiber optic cables due to cheaper materials and established installation practices. However, fiber optic technology offers significant long-term savings through reduced maintenance costs, higher durability, and increased bandwidth capacity that supports future upgrades without extensive infrastructure changes. The total cost of ownership often favors fiber optics, particularly for large-scale or data-intensive network deployments.
Lifespan and Durability of Copper and Fiber Optic Wiring
Copper wiring typically offers a lifespan of 30 to 50 years, with high resistance to mechanical stress but vulnerability to corrosion and electromagnetic interference. Fiber optic cables, made from glass or plastic fibers, boast lifespans exceeding 25 years and superior durability against environmental factors, including moisture, temperature fluctuations, and electromagnetic interference. The inherently corrosion-resistant nature and immunity to electrical disturbances make fiber optic wiring a more robust solution for long-term, high-performance communication infrastructure.
Bandwidth Capabilities: Which Material Performs Better?
Copper wiring supports bandwidths typically up to 10 Gbps over shorter distances, limited by electrical interference and signal attenuation. Fiber optic cables deliver vastly superior bandwidth capabilities, exceeding 100 Gbps over much longer distances without signal degradation. For high-speed data transmission and future-proof network infrastructure, fiber optics outperform copper wiring significantly.
Applications: When to Choose Copper Over Fiber Optic
Copper wiring offers superior performance in short-distance applications such as home networking, telephone lines, and legacy data centers due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of installation. It is preferable in environments with existing copper infrastructure where electromagnetic interference is manageable and power over Ethernet (PoE) is required. Fiber optic is better suited for long-distance, high-bandwidth needs, but copper remains the practical choice for cost-sensitive, low-to-moderate data rate, and power-delivery scenarios.
Future Trends in Wiring: Evolving Roles of Copper and Fiber Optics
Copper wiring remains essential for power delivery and short-distance data transmission due to its durability and cost-efficiency, while fiber optic technology dominates long-haul, high-speed internet infrastructure with superior bandwidth and minimal signal degradation. Emerging hybrid systems integrate copper and fiber to optimize performance and cost, supporting the transition toward 5G networks and smart grid applications. Advancements in materials and installation techniques enhance copper's viability in IoT ecosystems, ensuring its continued relevance alongside rapidly evolving fiber optic innovations.
Copper Wiring vs Fiber Optic Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com