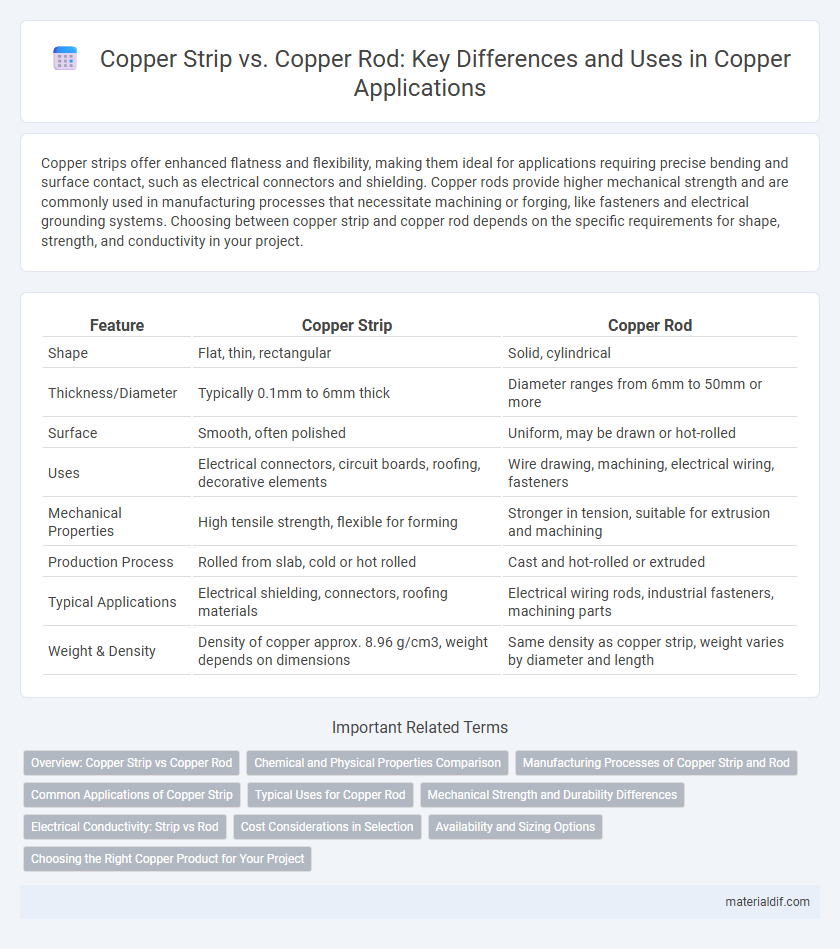
Copper strips offer enhanced flatness and flexibility, making them ideal for applications requiring precise bending and surface contact, such as electrical connectors and shielding. Copper rods provide higher mechanical strength and are commonly used in manufacturing processes that necessitate machining or forging, like fasteners and electrical grounding systems. Choosing between copper strip and copper rod depends on the specific requirements for shape, strength, and conductivity in your project.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Copper Strip | Copper Rod |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Flat, thin, rectangular | Solid, cylindrical |
| Thickness/Diameter | Typically 0.1mm to 6mm thick | Diameter ranges from 6mm to 50mm or more |
| Surface | Smooth, often polished | Uniform, may be drawn or hot-rolled |
| Uses | Electrical connectors, circuit boards, roofing, decorative elements | Wire drawing, machining, electrical wiring, fasteners |
| Mechanical Properties | High tensile strength, flexible for forming | Stronger in tension, suitable for extrusion and machining |
| Production Process | Rolled from slab, cold or hot rolled | Cast and hot-rolled or extruded |
| Typical Applications | Electrical shielding, connectors, roofing materials | Electrical wiring rods, industrial fasteners, machining parts |
| Weight & Density | Density of copper approx. 8.96 g/cm3, weight depends on dimensions | Same density as copper strip, weight varies by diameter and length |
Overview: Copper Strip vs Copper Rod
Copper strips are flat, thin pieces of copper used primarily for electrical grounding, bus bars, and heat exchangers, offering excellent conductivity and flexibility. Copper rods are cylindrical and solid, commonly employed in manufacturing fasteners, electrical wiring, and plumbing, known for their strength and ease of machining. Both forms provide high electrical and thermal conductivity but differ in shape and application suitability, with strips favored for surface-area needs and rods preferred for structural integrity.
Chemical and Physical Properties Comparison
Copper strip exhibits higher surface area and greater flexibility compared to copper rod, making it ideal for applications requiring efficient conductivity and malleability. Chemically, both copper strip and copper rod share similar resistance to corrosion and oxidation due to their high purity copper content, typically above 99.9%. Physically, copper rods have a uniform cross-section and higher tensile strength, whereas copper strips offer enhanced ductility and are easier to shape in thin, flat forms.
Manufacturing Processes of Copper Strip and Rod
Copper strips are produced through a rolling process where copper billets are heated and passed through rollers to achieve precise thickness and flatness, ideal for electrical and industrial applications. Copper rods are typically formed by continuous casting or extrusion, followed by drawing to obtain specific diameters, making them suitable for wire production and machining. Both manufacturing processes emphasize control over grain structure and mechanical properties to ensure optimal conductivity and strength.
Common Applications of Copper Strip
Copper strips are widely used in electrical applications such as busbars, connectors, and grounding systems due to their excellent conductivity and malleability. They also find common usage in roofing, flashing, and cladding in construction for corrosion resistance and aesthetic appeal. In electronics manufacturing, copper strips serve as critical components in circuit boards, springs, and shielding materials.
Typical Uses for Copper Rod
Copper rods are typically used in electrical wiring, construction, and plumbing due to their excellent conductivity and mechanical strength. They serve as raw materials for manufacturing wire, fasteners, and various hardware components where precise dimensions and durability are essential. Copper rods also find applications in automotive parts and industrial machinery for their corrosion resistance and thermal conductivity.
Mechanical Strength and Durability Differences
Copper strips exhibit higher tensile strength and enhanced durability compared to copper rods due to their flat, thin geometry which allows for better resistance to bending and fatigue. Copper rods, while offering excellent conductivity and ease of machining, typically have lower mechanical strength and are more prone to deformation under stress. The choice between copper strip and rod depends on the application requirements where mechanical strength and long-term durability are critical factors.
Electrical Conductivity: Strip vs Rod
Copper strips exhibit higher electrical conductivity per unit area compared to copper rods due to their flat, thin geometry that facilitates better current flow and heat dissipation. Copper rods, while offering robust mechanical strength, generally have lower surface area-to-volume ratios, which can limit their conductivity efficiency in certain electrical applications. Selecting between copper strip and rod depends on balancing conductivity requirements with mechanical durability and installation constraints.
Cost Considerations in Selection
Copper strips generally offer a lower cost per unit compared to copper rods due to their manufacturing process and material efficiency. Copper rods, while typically more expensive, provide enhanced strength and conductivity suited for high-stress applications, justifying the higher price in performance-critical projects. Evaluating budget constraints alongside application requirements is crucial for optimizing cost-effectiveness when selecting between copper strips and rods.
Availability and Sizing Options
Copper strips offer a wide range of thicknesses and widths, making them ideal for applications requiring precise sizing and flexibility. Copper rods are typically available in standard diameters, catering to structural and manufacturing needs with consistent round profiles. Availability of copper strips generally spans custom cut lengths, while copper rods are supplied in longer, uniform bars, influencing selection based on project requirements.
Choosing the Right Copper Product for Your Project
Copper strips offer excellent flexibility and are ideal for applications requiring flat, thin conductive materials, such as electrical grounding and bus bars. Copper rods provide superior mechanical strength and are better suited for manufacturing, machining, and heavy-duty electrical components. Selecting the right copper product depends on project requirements like conductivity, shape, and mechanical stress tolerance.
Copper Strip vs Copper Rod Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com