Copper clad steel offers a cost-effective alternative by combining the strength of a steel core with the electrical conductivity of a copper exterior, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and conductivity. Copper core cables, in contrast, provide superior electrical performance and corrosion resistance, making them preferred for high-frequency signal transmission and critical electronic uses. Selecting between copper clad steel and copper core depends on balancing mechanical strength needs with electrical efficiency requirements.
Table of Comparison
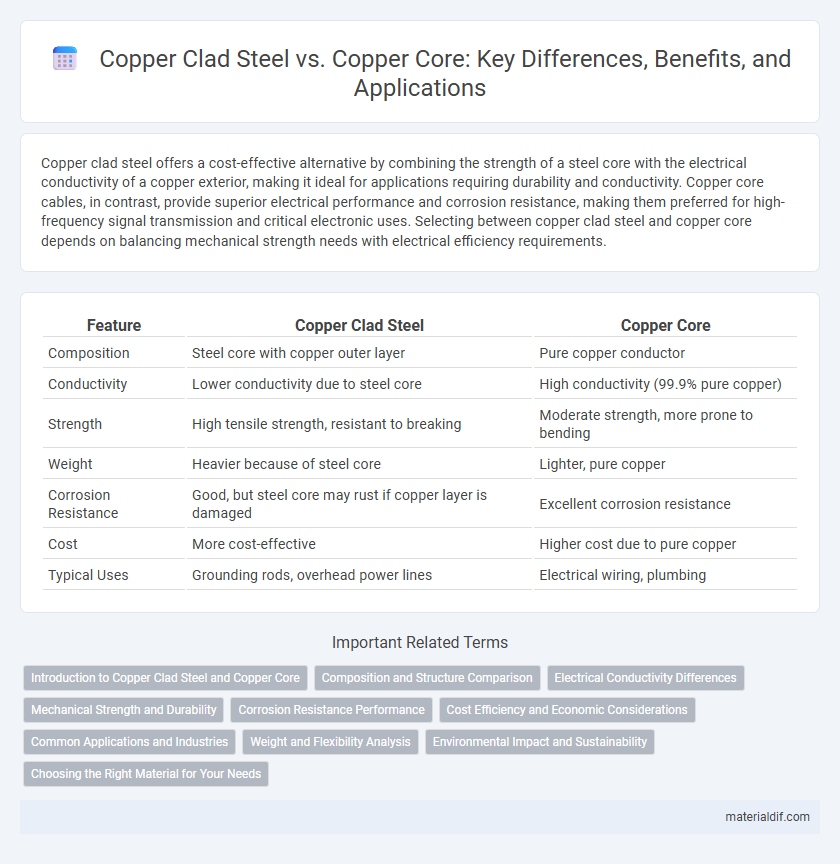
| Feature | Copper Clad Steel | Copper Core |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Steel core with copper outer layer | Pure copper conductor |
| Conductivity | Lower conductivity due to steel core | High conductivity (99.9% pure copper) |
| Strength | High tensile strength, resistant to breaking | Moderate strength, more prone to bending |
| Weight | Heavier because of steel core | Lighter, pure copper |
| Corrosion Resistance | Good, but steel core may rust if copper layer is damaged | Excellent corrosion resistance |
| Cost | More cost-effective | Higher cost due to pure copper |
| Typical Uses | Grounding rods, overhead power lines | Electrical wiring, plumbing |
Introduction to Copper Clad Steel and Copper Core
Copper Clad Steel (CCS) features a steel core with a copper outer layer, combining high tensile strength and electrical conductivity while reducing material costs. Copper Core wires consist entirely of pure copper, offering superior electrical conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to CCS. Choosing between Copper Clad Steel and Copper Core depends on application requirements such as strength, conductivity, weight, and budget constraints.
Composition and Structure Comparison
Copper clad steel consists of a steel core coated with a thin layer of copper, combining the tensile strength of steel with copper's excellent electrical conductivity. Copper core cables feature a solid or stranded pure copper conductor, offering superior conductivity and corrosion resistance compared to copper clad steel. The structural difference influences mechanical durability and electrical performance, making copper core ideal for high-frequency applications while copper clad steel balances cost and strength.
Electrical Conductivity Differences
Copper clad steel combines a steel core with a thin copper layer to offer improved tensile strength but exhibits lower electrical conductivity compared to a pure copper core. Copper core cables provide superior electrical conductivity due to the homogeneous copper material, allowing for better signal transmission and reduced resistance. This conductivity difference makes copper core preferred for applications requiring efficient power and signal delivery, while copper clad steel is chosen where mechanical strength is critical.
Mechanical Strength and Durability
Copper Clad Steel (CCS) combines a steel core with a copper outer layer, offering superior mechanical strength and enhanced durability compared to pure Copper Core conductors. The steel core provides higher tensile strength, making CCS ideal for applications requiring resistance to physical stress and environmental wear. Copper Core conductors excel in electrical conductivity but lack the robust mechanical properties of Copper Clad Steel, limiting their durability under mechanical strain.
Corrosion Resistance Performance
Copper clad steel wires offer enhanced mechanical strength but are more susceptible to corrosion compared to pure copper core conductors, which exhibit superior corrosion resistance due to their homogeneous copper composition. The copper core material forms a stable oxide layer that effectively protects against environmental degradation, making it ideal for applications requiring long-term durability in harsh conditions. In contrast, the steel core beneath a thin copper cladding can corrode if the coating is damaged, reducing the overall lifespan and performance of the wire.
Cost Efficiency and Economic Considerations
Copper clad steel offers significant cost efficiency by combining the conductivity of copper with the strength and lower price of steel, making it an economical choice for grounding and electrical applications. Copper core cables provide superior conductivity and corrosion resistance but come with higher material and manufacturing costs, impacting overall budget allocation. Selecting copper clad steel reduces upfront expenses and maintenance, optimizing economic considerations for large-scale infrastructure projects.
Common Applications and Industries
Copper clad steel combines the strength and durability of steel with the excellent conductivity and corrosion resistance of copper, making it ideal for telecommunications, grounding systems, and grounding electrodes in power distribution. Copper core conducts electricity more efficiently and is widely used in electrical wiring, circuit boards, and transformers across electronics, automotive, and electrical power industries. Both materials are crucial in applications requiring a balance between mechanical strength and electrical performance, with copper clad steel favored in high-strength environments and copper core preferred for maximum conductivity.
Weight and Flexibility Analysis
Copper clad steel offers significant weight reduction compared to a solid copper core due to its steel core, making it ideal for applications where lightweight materials are crucial. The steel core in copper clad steel enhances tensile strength but reduces flexibility relative to pure copper, which remains highly malleable and easier to bend without fracturing. In electrical wiring, copper core cables provide superior flexibility, while copper clad steel cables balance durability and weight savings for more demanding mechanical environments.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability
Copper clad steel cables combine a steel core with a thin copper outer layer, reducing the overall copper usage and lowering environmental extraction impacts. Pure copper core cables offer superior conductivity but require more extensive mining, contributing to higher resource depletion and energy consumption. Recycling rates for copper clad steel are lower compared to pure copper, making sustainability management crucial for minimizing landfill waste and promoting circular economy practices.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Needs
Copper clad steel offers enhanced tensile strength and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and cost-effectiveness, such as grounding and overhead power lines. Copper core provides superior electrical conductivity and flexibility, preferred in high-performance electrical wiring and electronics where efficient current flow is critical. Selecting between copper clad steel and copper core depends on balancing factors like mechanical strength, conductivity requirements, and budget constraints to suit specific project needs.
Copper Clad Steel vs Copper Core Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com