DHP copper, or electrolytic tough pitch copper, features higher oxygen content, enhancing its electrical conductivity and making it ideal for electrical wiring and connectors. DLP copper contains low oxygen levels, providing superior strength and corrosion resistance, which suits plumbing and industrial applications. Choosing between DHP and DLP copper depends on the specific requirements for conductivity versus mechanical durability.
Table of Comparison
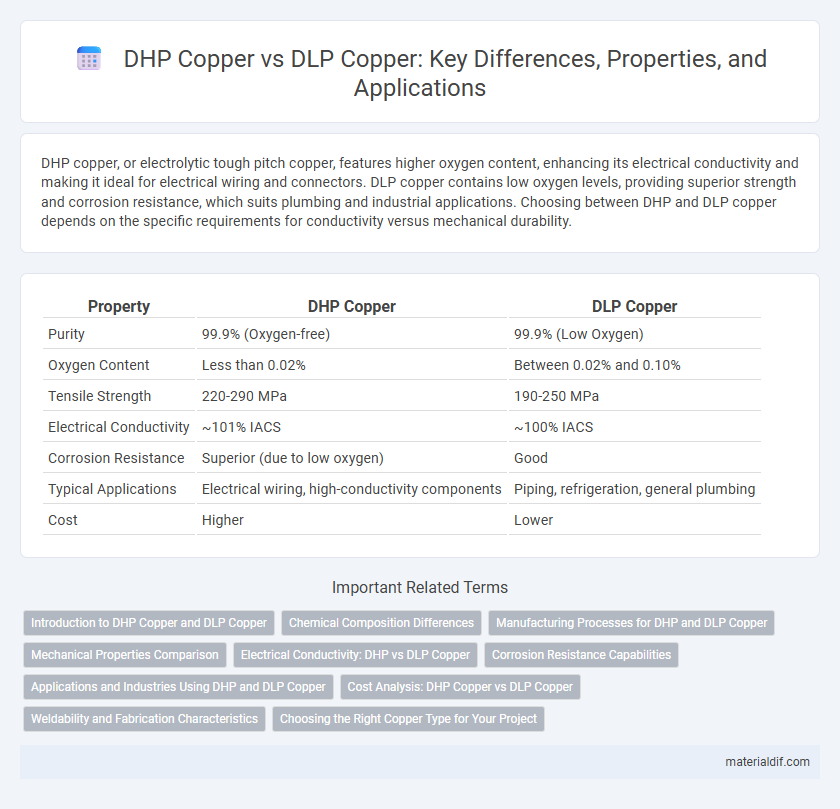
| Property | DHP Copper | DLP Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Purity | 99.9% (Oxygen-free) | 99.9% (Low Oxygen) |
| Oxygen Content | Less than 0.02% | Between 0.02% and 0.10% |
| Tensile Strength | 220-290 MPa | 190-250 MPa |
| Electrical Conductivity | ~101% IACS | ~100% IACS |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior (due to low oxygen) | Good |
| Typical Applications | Electrical wiring, high-conductivity components | Piping, refrigeration, general plumbing |
| Cost | Higher | Lower |
Introduction to DHP Copper and DLP Copper
DHP Copper (Deoxidized High Phosphorus) contains a higher phosphorus content, enhancing its corrosion resistance and making it ideal for plumbing and heat exchanger applications. DLP Copper (Deoxidized Low Phosphorus) has lower phosphorus levels, offering improved ductility and electrical conductivity suited for electrical and HVAC systems. Both types undergo deoxidation processes, but their phosphorus content distinctly influences their mechanical and chemical properties.
Chemical Composition Differences
DHP Copper (Deoxidized High Phosphorus) contains a higher phosphorus content, typically around 0.01-0.04%, which enhances its resistance to hydrogen embrittlement and improves mechanical strength. DLP Copper (Deoxidized Low Phosphorus) has a significantly lower phosphorus level, often below 0.005%, resulting in superior electrical conductivity but reduced mechanical durability compared to DHP Copper. The difference in phosphorus concentration directly influences the copper's suitability for applications requiring either enhanced strength or high electrical performance.
Manufacturing Processes for DHP and DLP Copper
DHP Copper (Deoxidized High Phosphorus) is produced by adding phosphorus during the copper melting process, which acts as a deoxidizer and results in a more uniform grain structure ideal for applications requiring high thermal and electrical conductivity. DLP Copper (Deoxidized Low Phosphorus) involves minimal phosphorus addition, yielding slightly higher electrical conductivity and better ductility, making it suitable for precision manufacturing components. The manufacturing processes for both types emphasize controlled deoxidation and cooling rates to enhance physical properties tailored to specific industrial uses.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
DHP copper (Deoxidized High Phosphorus) exhibits superior mechanical strength and enhanced corrosion resistance compared to DLP copper (Deoxidized Low Phosphorus), making it ideal for heat exchanger applications. DHP copper typically offers higher tensile strength, ranging from 210 to 250 MPa, while DLP copper shows tensile strength around 200 MPa, reflecting its slightly softer character suited for electrical components. The increased phosphorus content in DHP copper improves hardness and wear resistance without compromising ductility, whereas DLP copper prioritizes electrical conductivity with moderate mechanical properties.
Electrical Conductivity: DHP vs DLP Copper
DHP copper (Deoxidized High Phosphorus) offers superior electrical conductivity compared to DLP copper (Deoxidized Low Phosphorus) due to its higher purity and minimal oxygen content, which reduces resistive losses. The phosphorus content in DHP copper acts as a deoxidizer, enhancing conductivity while maintaining excellent mechanical properties for electrical applications. In contrast, DLP copper, with lower phosphorus levels, exhibits slightly reduced conductivity, making DHP copper preferable for high-performance electrical components.
Corrosion Resistance Capabilities
DHP copper, or Deoxidized High Phosphorus copper, exhibits superior corrosion resistance compared to DLP copper due to its higher phosphorus content, which enhances its ability to withstand aggressive environments and reduces susceptibility to dezincification and stress corrosion cracking. DLP copper, or Deoxidized Low Phosphorus copper, while offering good formability and electrical conductivity, tends to have lower corrosion resistance in marine and industrial atmospheres. The phosphorus level in DHP copper forms a protective oxide layer that significantly improves durability in plumbing and heat exchanger applications where corrosion resistance is critical.
Applications and Industries Using DHP and DLP Copper
DHP copper, known for its high phosphorus content, is widely used in brazing applications and heat exchanger manufacturing due to its enhanced corrosion resistance and strength. DLP copper, with lower phosphorus levels, finds extensive use in electrical wiring and plumbing systems where high conductivity and ductility are critical. Industries such as HVAC, automotive, and electronics rely heavily on both DHP and DLP copper grades to meet specific performance requirements in their manufacturing processes.
Cost Analysis: DHP Copper vs DLP Copper
DHP copper, often utilized in plumbing and heat exchanger applications, generally offers a lower cost per unit compared to DLP copper due to its broader availability and less stringent purity requirements. DLP copper, with higher purity and improved conductivity, commands a premium price, impacting overall project budgets when used in high-performance electrical components. Cost analysis between DHP and DLP copper must consider application-specific performance needs, as the initial savings on DHP may result in higher operational expenses or lower efficiency over time.
Weldability and Fabrication Characteristics
DHP Copper, known for its higher phosphorus content (0.02-0.04%), offers superior corrosion resistance and excellent weldability, making it ideal for brazing and soft soldering applications. DLP Copper contains less phosphorus, resulting in slightly lower strength but improved electrical conductivity, with good weldability primarily suited for fusion welding techniques. Fabrication of DHP Copper benefits from enhanced ductility and resistance to hydrogen embrittlement, whereas DLP Copper excels in applications requiring high conductivity with moderate fabrication ease.
Choosing the Right Copper Type for Your Project
DHP copper, with its high purity and excellent conductivity, is ideal for plumbing, heating, and electrical applications requiring superior corrosion resistance and thermal performance. DLP copper, produced via continuous casting, offers consistent ductility and is typically used in manufacturing and industrial processes where cost efficiency and mechanical strength are priorities. Selecting between DHP and DLP copper depends on project-specific factors such as thermal requirements, environmental exposure, and budget constraints to ensure optimal performance and durability.
DHP Copper vs DLP Copper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com