Phosphor bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance and good fatigue resistance, making it ideal for marine and electrical applications. Beryllium copper delivers superior strength, electrical and thermal conductivity, along with non-magnetic properties, favored in high-performance electronics and aerospace components. Both alloys provide exceptional wear resistance but differ in performance characteristics suited to specific industrial demands.
Table of Comparison
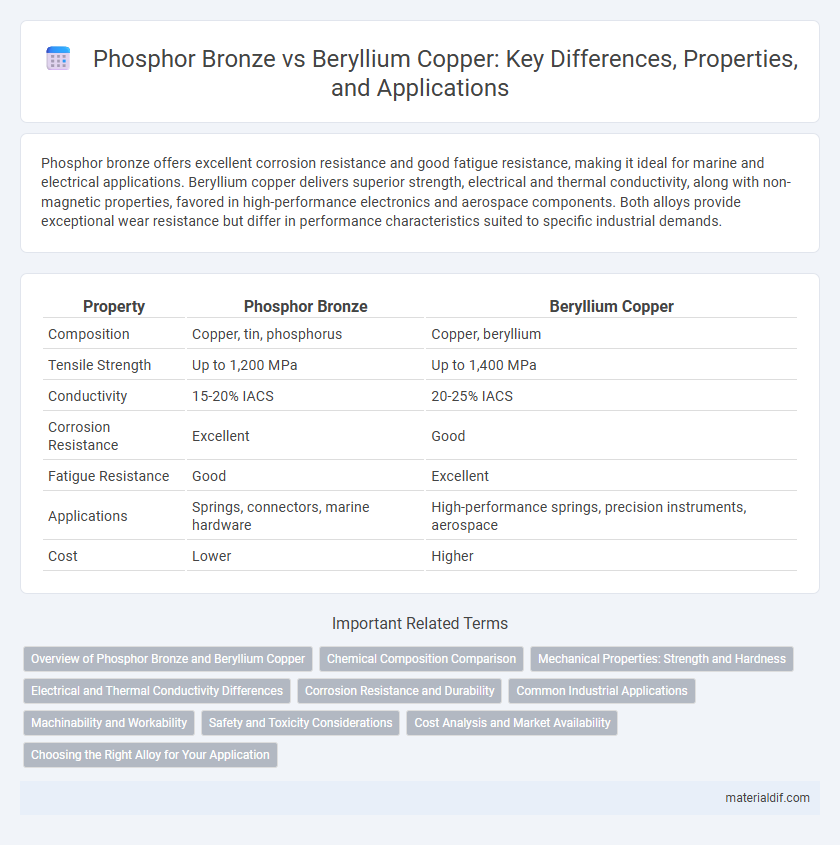
| Property | Phosphor Bronze | Beryllium Copper |
|---|---|---|
| Composition | Copper, tin, phosphorus | Copper, beryllium |
| Tensile Strength | Up to 1,200 MPa | Up to 1,400 MPa |
| Conductivity | 15-20% IACS | 20-25% IACS |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Fatigue Resistance | Good | Excellent |
| Applications | Springs, connectors, marine hardware | High-performance springs, precision instruments, aerospace |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
Overview of Phosphor Bronze and Beryllium Copper
Phosphor bronze is an alloy primarily composed of copper with 0.5-11% tin and 0.01-0.35% phosphorus, known for its excellent wear resistance, low friction, and high fatigue resistance, making it ideal for springs, bearings, and electrical connectors. Beryllium copper contains 0.5-3% beryllium and offers superior strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance while maintaining excellent electrical and thermal conductivity, widely used in aerospace, telecommunications, and precision instruments. Both alloys provide distinct advantages with phosphor bronze excelling in durability and beryllium copper in strength and conductivity, depending on application requirements.
Chemical Composition Comparison
Phosphor bronze primarily consists of copper with 0.5-11% tin and 0.01-0.35% phosphorus, enhancing strength and corrosion resistance. Beryllium copper contains about 0.5-3% beryllium, significantly improving hardness and electrical conductivity while maintaining copper's ductility. The phosphorus in phosphor bronze acts as a deoxidizing agent, whereas beryllium in beryllium copper forms a precipitation-hardened alloy with superior mechanical properties.
Mechanical Properties: Strength and Hardness
Phosphor bronze offers a balanced combination of high strength and excellent hardness, making it suitable for applications requiring durability and wear resistance. Beryllium copper surpasses phosphor bronze in strength and hardness, with tensile strengths reaching up to 1,400 MPa and exceptional fatigue resistance, ideal for demanding mechanical and electrical components. Both alloys exhibit superior mechanical properties compared to pure copper, but beryllium copper's enhanced hardness and strength make it the preferred choice in high-performance environments.
Electrical and Thermal Conductivity Differences
Phosphor bronze exhibits moderate electrical conductivity, typically around 15-22% IACS (International Annealed Copper Standard), and thermal conductivity near 60 W/m*K, making it suitable for applications requiring good corrosion resistance and moderate conductivity. Beryllium copper, on the other hand, offers superior mechanical strength with electrical conductivity ranging from 20-30% IACS and thermal conductivity approximately 105 W/m*K, enabling enhanced performance in electrical connectors and thermal management components. The higher conductivity and thermal transfer capabilities of beryllium copper make it preferable for precision electrical applications demanding both durability and efficient heat dissipation.
Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Phosphor bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance in marine and industrial environments due to its high phosphorus content, which enhances its durability and wear resistance. Beryllium copper provides superior strength and fatigue resistance, maintaining durability under high-stress applications, but it is more susceptible to corrosion without proper protective coatings. Both alloys exhibit good corrosion resistance, yet phosphor bronze outperforms in harsh, wet conditions, while beryllium copper excels in mechanical durability and electrical conductivity.
Common Industrial Applications
Phosphor bronze is widely used in electrical connectors, springs, and bearings due to its excellent corrosion resistance and good fatigue properties. Beryllium copper is preferred for precision instruments, aerospace components, and oilfield tools because of its high strength, electrical conductivity, and non-magnetic qualities. Both alloys serve critical roles in industrial sectors where durability and performance are essential under varying mechanical and environmental conditions.
Machinability and Workability
Phosphor Bronze offers excellent machinability due to its fine grain structure and high strength, making it ideal for precision components requiring good wear resistance. Beryllium Copper outperforms in workability, exhibiting superior elasticity and fatigue resistance, which is beneficial for springs and electrical connectors. While Phosphor Bronze provides easier machining, Beryllium Copper's enhanced mechanical properties enable more complex shaping and forming processes without compromising performance.
Safety and Toxicity Considerations
Phosphor bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance and is generally considered safe for use in various industrial applications due to its low toxicity. Beryllium copper, while exhibiting superior strength and conductivity, poses significant health risks during machining or welding because of beryllium dust and fumes, which can cause chronic berylliosis. Proper ventilation, protective equipment, and rigorous safety protocols are essential when handling beryllium copper to prevent harmful exposure.
Cost Analysis and Market Availability
Phosphor bronze typically costs less than beryllium copper due to lower raw material expenses and simpler manufacturing processes, making it more economically feasible for large-scale applications. Beryllium copper commands a premium price, driven by its superior strength, electrical conductivity, and resistance to fatigue, but its supply is restricted, influencing market availability and price volatility. Industries prioritize phosphor bronze for cost-sensitive projects, while beryllium copper is reserved for high-performance applications despite higher costs and limited availability.
Choosing the Right Alloy for Your Application
Phosphor bronze offers excellent corrosion resistance and good fatigue strength, making it ideal for marine and electrical applications requiring durability and flexibility. Beryllium copper provides superior hardness, high electrical conductivity, and non-sparking properties, well-suited for precision instruments and aerospace components. Selecting the right alloy depends on balancing mechanical strength, corrosion resistance, and conductivity based on specific application requirements.
Phosphor Bronze vs Beryllium Copper Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com