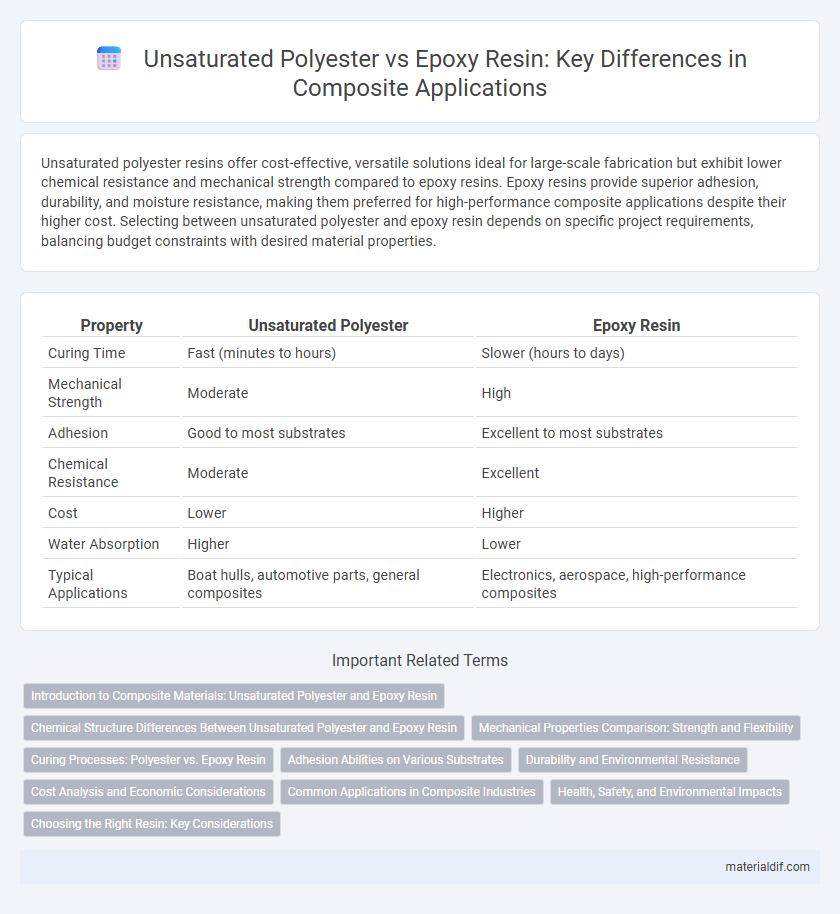
Unsaturated polyester resins offer cost-effective, versatile solutions ideal for large-scale fabrication but exhibit lower chemical resistance and mechanical strength compared to epoxy resins. Epoxy resins provide superior adhesion, durability, and moisture resistance, making them preferred for high-performance composite applications despite their higher cost. Selecting between unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin depends on specific project requirements, balancing budget constraints with desired material properties.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Unsaturated Polyester | Epoxy Resin |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Time | Fast (minutes to hours) | Slower (hours to days) |
| Mechanical Strength | Moderate | High |
| Adhesion | Good to most substrates | Excellent to most substrates |
| Chemical Resistance | Moderate | Excellent |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Water Absorption | Higher | Lower |
| Typical Applications | Boat hulls, automotive parts, general composites | Electronics, aerospace, high-performance composites |
Introduction to Composite Materials: Unsaturated Polyester and Epoxy Resin
Unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin are two widely used matrices in composite materials, each offering distinct chemical properties and mechanical performance. Unsaturated polyester resin is favored for its cost-effectiveness and ease of fabrication, making it suitable for applications requiring moderate strength and durability. Epoxy resin provides superior adhesion, higher mechanical strength, and enhanced chemical resistance, often chosen for high-performance composites in aerospace, automotive, and structural engineering.
Chemical Structure Differences Between Unsaturated Polyester and Epoxy Resin
Unsaturated polyester resins are formed by the polycondensation of diacids and diols, featuring carbon-carbon double bonds (C=C) within the polymer backbone that allow cross-linking during curing. In contrast, epoxy resins consist of epoxide groups (oxirane rings) that undergo ring-opening polymerization with hardeners, resulting in a highly cross-linked three-dimensional network. The presence of unsaturated sites in polyester resins imparts different chemical reactivity and mechanical properties compared to the rigid and thermosetting nature of epoxy resins.
Mechanical Properties Comparison: Strength and Flexibility
Unsaturated polyester resin typically offers moderate tensile strength and good flexural strength, making it suitable for lightweight structural applications, while epoxy resin exhibits superior tensile strength and exceptional impact resistance, resulting in higher durability under mechanical stress. Epoxy's enhanced flexibility and adhesion properties allow it to absorb and dissipate energy more effectively compared to the relatively brittle nature of unsaturated polyester composites. This mechanical advantage makes epoxy resin the preferred choice in high-performance composite manufacturing where strength and flexibility are critical.
Curing Processes: Polyester vs. Epoxy Resin
Unsaturated polyester curing relies on free-radical polymerization initiated by catalysts like methyl ethyl ketone peroxide (MEKP), forming cross-linked thermoset networks rapidly at ambient or elevated temperatures. Epoxy resin curing involves a chemical reaction between epoxy groups and hardeners, such as amines or anhydrides, producing a dense, highly cross-linked structure with superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance. The epoxy curing process typically requires longer curing times and controlled temperature conditions to achieve optimal performance compared to the faster, more exothermic polyester curing.
Adhesion Abilities on Various Substrates
Epoxy resin exhibits superior adhesion abilities on various substrates, including metals, glass, and composites, due to its strong chemical bonding and low shrinkage during curing. Unsaturated polyester resin provides adequate adhesion but generally underperforms epoxy on non-porous surfaces, often requiring surface treatments to enhance bonding. The enhanced interfacial strength of epoxy resin makes it the preferred choice for applications demanding reliable and durable adhesion across diverse materials.
Durability and Environmental Resistance
Unsaturated polyester resin exhibits moderate durability and environmental resistance, performing well in applications with limited exposure to harsh chemicals and UV radiation. Epoxy resin offers superior durability and exceptional resistance to moisture, chemicals, and environmental degradation, making it ideal for demanding structural and marine applications. The choice between these resins largely depends on the specific environmental conditions and longevity requirements of the composite material.
Cost Analysis and Economic Considerations
Unsaturated polyester resins typically cost 30-50% less than epoxy resins, making them a preferred choice for budget-sensitive composite applications. The lower raw material and processing expenses contribute to reduced overall production costs, but epoxy resins offer superior mechanical properties and chemical resistance, often justifying their higher price in high-performance uses. Economic considerations must weigh initial material cost against durability and lifecycle benefits when selecting between unsaturated polyester and epoxy resins.
Common Applications in Composite Industries
Unsaturated polyester resin is widely used in marine, automotive, and construction industries due to its cost-effectiveness and ease of processing for creating fiberglass-reinforced products. Epoxy resin finds common applications in aerospace, sports equipment, and high-performance automotive components, valued for its superior mechanical strength and excellent adhesion properties. Both resins play crucial roles in composites, with unsaturated polyester favored for large-scale, economical production and epoxy preferred where enhanced durability and chemical resistance are required.
Health, Safety, and Environmental Impacts
Unsaturated polyester resins release volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and styrene, posing respiratory and skin irritation risks, while epoxy resins generally emit fewer VOCs but can cause allergic reactions and sensitization. Proper ventilation and personal protective equipment are essential when handling both materials to minimize exposure and hazards. Epoxy resins tend to have a lower environmental impact due to reduced emissions, but waste disposal and curing processes still require careful management to prevent contamination.
Choosing the Right Resin: Key Considerations
Selecting the right resin involves evaluating factors such as mechanical strength, chemical resistance, curing time, and cost-effectiveness. Unsaturated polyester excels in affordability and ease of use with moderate durability, while epoxy resin offers superior adhesion, higher strength, and enhanced resistance to moisture and chemicals. Project requirements like environmental conditions, load-bearing needs, and budget constraints dictate the optimal choice between unsaturated polyester and epoxy resin for composite applications.
Unsaturated Polyester vs Epoxy Resin Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com