Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing dry fiber preforms, resulting in high-quality, complex composite parts with consistent fiber placement. Vacuum-Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM) uses vacuum pressure to draw resin into the fiber reinforcement, allowing for larger, more cost-effective production with reduced tooling expenses. Both methods offer strong mechanical properties, but RTM typically delivers superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy compared to the more flexible and scalable VARTM process.
Table of Comparison
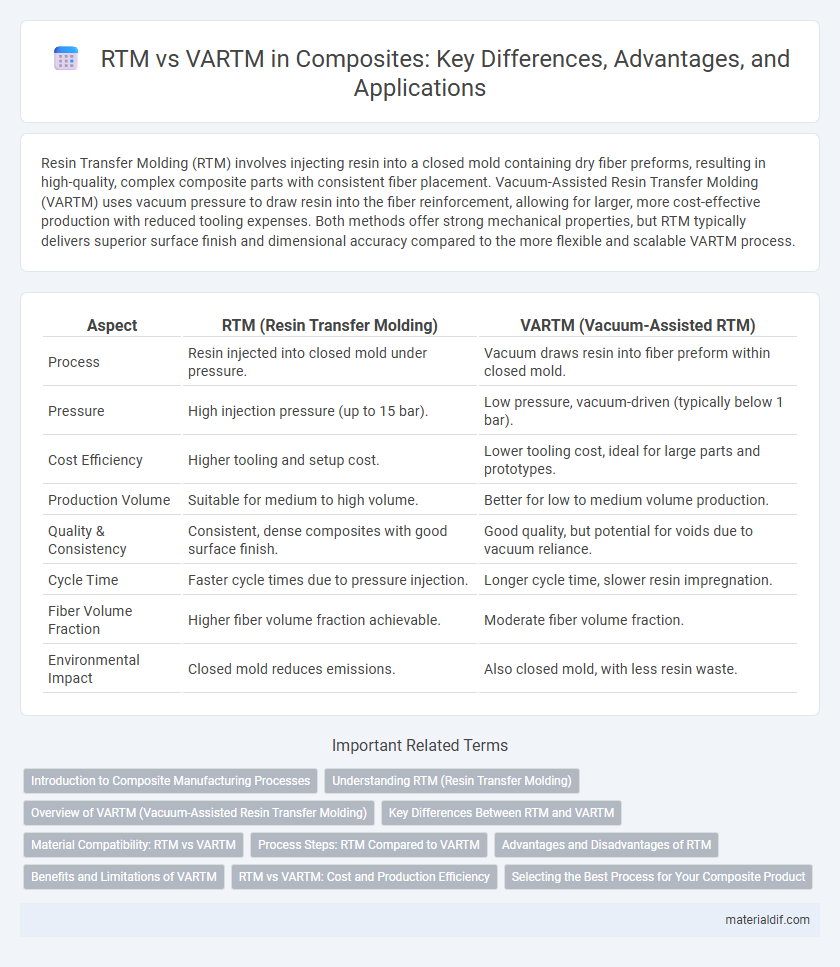
| Aspect | RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) | VARTM (Vacuum-Assisted RTM) |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Resin injected into closed mold under pressure. | Vacuum draws resin into fiber preform within closed mold. |
| Pressure | High injection pressure (up to 15 bar). | Low pressure, vacuum-driven (typically below 1 bar). |
| Cost Efficiency | Higher tooling and setup cost. | Lower tooling cost, ideal for large parts and prototypes. |
| Production Volume | Suitable for medium to high volume. | Better for low to medium volume production. |
| Quality & Consistency | Consistent, dense composites with good surface finish. | Good quality, but potential for voids due to vacuum reliance. |
| Cycle Time | Faster cycle times due to pressure injection. | Longer cycle time, slower resin impregnation. |
| Fiber Volume Fraction | Higher fiber volume fraction achievable. | Moderate fiber volume fraction. |
| Environmental Impact | Closed mold reduces emissions. | Also closed mold, with less resin waste. |
Introduction to Composite Manufacturing Processes
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM) are critical composite manufacturing processes commonly used in aerospace and automotive industries for producing high-strength, lightweight components. RTM involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing dry fiber preforms under pressure, ensuring uniform resin distribution and minimal void content. VARTM enhances this process by using vacuum pressure to pull resin through the fiber reinforcement, offering cost-effective tooling and improved control over resin flow for large and complex composite structures.
Understanding RTM (Resin Transfer Molding)
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) is a closed-mold composite fabrication process where resin is injected into a mold containing a dry fiber preform, ensuring high fiber volume fraction and consistent part quality. RTM provides superior control over fiber placement and resin distribution compared to vacuum-assisted RTM (VARTM), resulting in composites with excellent dimensional accuracy and mechanical properties. Optimal RTM parameters, such as injection pressure and mold temperature, are critical to achieving defect-free laminates suitable for aerospace and automotive applications.
Overview of VARTM (Vacuum-Assisted Resin Transfer Molding)
VARTM (Vacuum-Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) is an advanced composite manufacturing process that uses vacuum pressure to infuse resin into fiber reinforcements within a sealed mold. This technique enables efficient resin flow and thorough impregnation while reducing void content and improving laminate quality. VARTM is favored for producing large, complex composite structures with enhanced mechanical properties and cost-effective tooling compared to traditional RTM methods.
Key Differences Between RTM and VARTM
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) involves injecting resin into a closed mold with a pre-placed dry fiber preform, resulting in high precision and consistent part quality. VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) differs by using vacuum pressure to draw resin through the fiber preform, allowing for larger, more complex parts at lower cost but with potentially less control over resin flow. Key differences include mold complexity, pressure application (injection vs. vacuum), and part size capabilities, impacting production speed and cost efficiency in composite manufacturing.
Material Compatibility: RTM vs VARTM
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) and VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) differ significantly in material compatibility, where RTM accommodates a wider range of higher-viscosity resins ideal for complex, high-performance composites. VARTM relies on lower-viscosity resins to ensure thorough impregnation under vacuum pressure, making it suitable for larger, less intricate parts and more cost-effective materials. Material compatibility in RTM supports advanced fibers and hybrid reinforcements, while VARTM excels in processing large, flexible fabrics with moderate resin systems.
Process Steps: RTM Compared to VARTM
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) involves injecting resin into a closed mold containing dry fiber preforms under moderate pressure, ensuring complete impregnation and higher fiber volume fraction. VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) uses vacuum pressure to draw resin through the fiber preform placed under a single-sided mold, typically resulting in longer cycle times and lower injection pressures. The RTM process offers better control over resin flow and fiber wet-out, leading to improved mechanical properties compared to VARTM.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RTM
Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) offers high-quality surface finishes and precise fiber placement, making it ideal for complex composite parts with tight tolerances. However, RTM requires expensive, rigid molds and has longer cycle times compared to Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM), limiting its cost-effectiveness for large-scale production. The closed mold process in RTM reduces emissions and improves material consistency but demands higher initial investment and complex tooling.
Benefits and Limitations of VARTM
Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM) offers significant benefits including lower tooling costs and the ability to produce large, complex composite parts with reduced void content and improved fiber wet-out compared to traditional Resin Transfer Molding (RTM). VARTM enables better control of resin flow through vacuum suction, enhancing laminate quality and reducing environmental emissions by minimizing volatile organic compounds (VOCs). Limitations include longer cure cycles and potential challenges in achieving uniform resin distribution in thick or highly reinforced parts, which may impact structural performance and repeatability.
RTM vs VARTM: Cost and Production Efficiency
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) generally incurs higher tooling and equipment costs compared to VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding), making VARTM more cost-effective for low to medium production volumes. VARTM offers greater production efficiency with lower energy consumption and simpler setups, suitable for large, complex composite structures requiring high fiber volume fractions. RTM excels in repeatability and surface finish quality but demands longer cycle times and higher capital investment, impacting overall production speed and scalability.
Selecting the Best Process for Your Composite Product
RTM (Resin Transfer Molding) offers high precision and consistent fiber volume fractions, making it ideal for complex, high-performance composite parts requiring tight dimensional tolerances. VARTM (Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding) provides cost-effective manufacturing for large, less complex structures with good surface finish and reduced tooling expenses. Choosing between RTM and VARTM depends on part complexity, production volume, mechanical performance requirements, and budget constraints to optimize quality and manufacturing efficiency.
RTM vs VARTM Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com