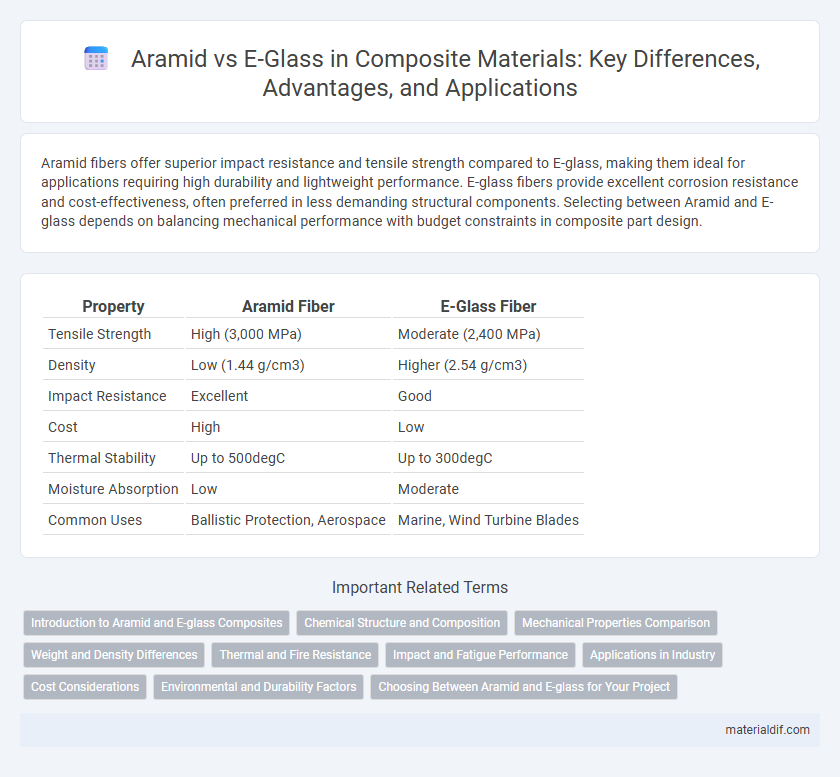
Aramid fibers offer superior impact resistance and tensile strength compared to E-glass, making them ideal for applications requiring high durability and lightweight performance. E-glass fibers provide excellent corrosion resistance and cost-effectiveness, often preferred in less demanding structural components. Selecting between Aramid and E-glass depends on balancing mechanical performance with budget constraints in composite part design.
Table of Comparison
| Property | Aramid Fiber | E-Glass Fiber |
|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | High (3,000 MPa) | Moderate (2,400 MPa) |
| Density | Low (1.44 g/cm3) | Higher (2.54 g/cm3) |
| Impact Resistance | Excellent | Good |
| Cost | High | Low |
| Thermal Stability | Up to 500degC | Up to 300degC |
| Moisture Absorption | Low | Moderate |
| Common Uses | Ballistic Protection, Aerospace | Marine, Wind Turbine Blades |
Introduction to Aramid and E-glass Composites
Aramid and E-glass composites are widely used in high-performance applications due to their unique mechanical properties and durability. Aramid fibers, known for their exceptional tensile strength and impact resistance, are often utilized in ballistic protection and aerospace components. E-glass fibers offer excellent corrosion resistance, electrical insulation, and cost-effectiveness, making them ideal for automotive parts, marine structures, and industrial applications.
Chemical Structure and Composition
Aramid fibers consist of aromatic polyamide chains with strong amide linkages, providing exceptional tensile strength and thermal stability, while E-glass fibers are composed primarily of silica, alumina, and calcium oxide, forming a borosilicate glass with high chemical resistance and electrical insulation properties. The chemical structure of aramid features rigid, planar molecular chains that enhance resistance to abrasion and impact, contrasting with the amorphous, inorganic glass network of E-glass, which excels in stiffness and corrosion resistance. These differences in chemical composition result in aramid composites being more flexible and resistant to chemical degradation, whereas E-glass composites offer superior compressive strength and cost-effectiveness.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Aramid fibers exhibit a tensile strength of around 3,620 MPa and a density of 1.44 g/cm3, making them significantly stronger and lighter than E-glass fibers, which typically have a tensile strength of 2,900 MPa and a density of 2.54 g/cm3. The elastic modulus of Aramid ranges between 70-125 GPa, offering better flexibility, while E-glass has a higher modulus of about 73 GPa, resulting in increased stiffness but reduced impact resistance. Impact resistance and elongation at break favor Aramid composites, making them ideal for applications requiring high toughness and energy absorption.
Weight and Density Differences
Aramid fibers exhibit a significantly lower density of approximately 1.44 g/cm3 compared to E-glass fibers, which have a density around 2.54 g/cm3, resulting in lighter composite materials when aramid is used. This reduced density translates to substantial weight savings in aerospace and automotive components where minimizing mass enhances performance and fuel efficiency. The lower weight of aramid-based composites provides a critical advantage over E-glass composites in applications demanding high strength-to-weight ratios.
Thermal and Fire Resistance
Aramid fibers exhibit superior thermal stability and flame resistance compared to E-glass, maintaining structural integrity at temperatures exceeding 500degC. E-glass fibers typically degrade around 250degC, limiting their application in high-temperature environments. The enhanced thermal and fire-resistant properties of Aramid composites make them ideal for aerospace and defense applications requiring robust heat shielding.
Impact and Fatigue Performance
Aramid fibers exhibit superior impact resistance due to their high toughness and energy absorption capabilities compared to E-glass fibers, which are more brittle under sudden loading. Fatigue performance of aramid composites remains stable over extended cyclic loading, making them ideal for applications with repetitive stress, whereas E-glass composites tend to accumulate micro-cracks leading to earlier fatigue failure. The combination of aramid's lower density and enhanced fatigue durability provides significant advantages in aerospace and defense composite structures.
Applications in Industry
Aramid fibers are widely used in aerospace and military industries due to their high strength-to-weight ratio and exceptional impact resistance, making them ideal for ballistic armor and aircraft components. E-glass fibers dominate in automotive, marine, and construction sectors by offering cost-effective reinforcement with excellent tensile strength and corrosion resistance for applications like boat hulls, wind turbine blades, and structural panels. Both materials serve vital roles in composites, with aramid preferred for high-performance, safety-critical products and E-glass favored for economical, large-scale manufacturing.
Cost Considerations
Aramid fibers typically exhibit higher costs compared to E-glass due to their superior strength-to-weight ratio and enhanced durability in composite applications. E-glass offers a more cost-effective solution for large-scale manufacturing, making it a preferred choice where budget constraints dominate. The trade-off between initial material expense and long-term performance benefits is critical in selecting either aramid or E-glass composites.
Environmental and Durability Factors
Aramid fibers exhibit superior environmental resistance compared to E-glass, offering excellent resistance to moisture, chemicals, and UV degradation, which significantly enhances the longevity of composites in harsh conditions. E-glass fibers, while cost-effective, are more susceptible to moisture absorption leading to reduced mechanical properties and potential fiber-matrix debonding over time. The inherent durability of aramid composites in corrosive environments and their resistance to impact and fatigue make them ideal for long-term applications where environmental factors are critical.
Choosing Between Aramid and E-glass for Your Project
When choosing between Aramid and E-glass for your composite project, consider Aramid's superior impact resistance and high tensile strength, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and toughness. E-glass offers excellent electrical insulation, cost-effectiveness, and good tensile properties, suitable for less demanding structural components. Project-specific factors such as mechanical load, environmental conditions, and budget constraints will determine the optimal fiber choice.
Aramid vs E-glass Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com