Closed mold processing offers superior precision and reduced emissions compared to open mold processing, making it ideal for complex composite parts. This method utilizes two matched mold halves, ensuring better dimensional control and surface finish. In contrast, open mold processing exposes the composite materials to the environment, leading to higher emissions and potential inconsistencies in part quality.
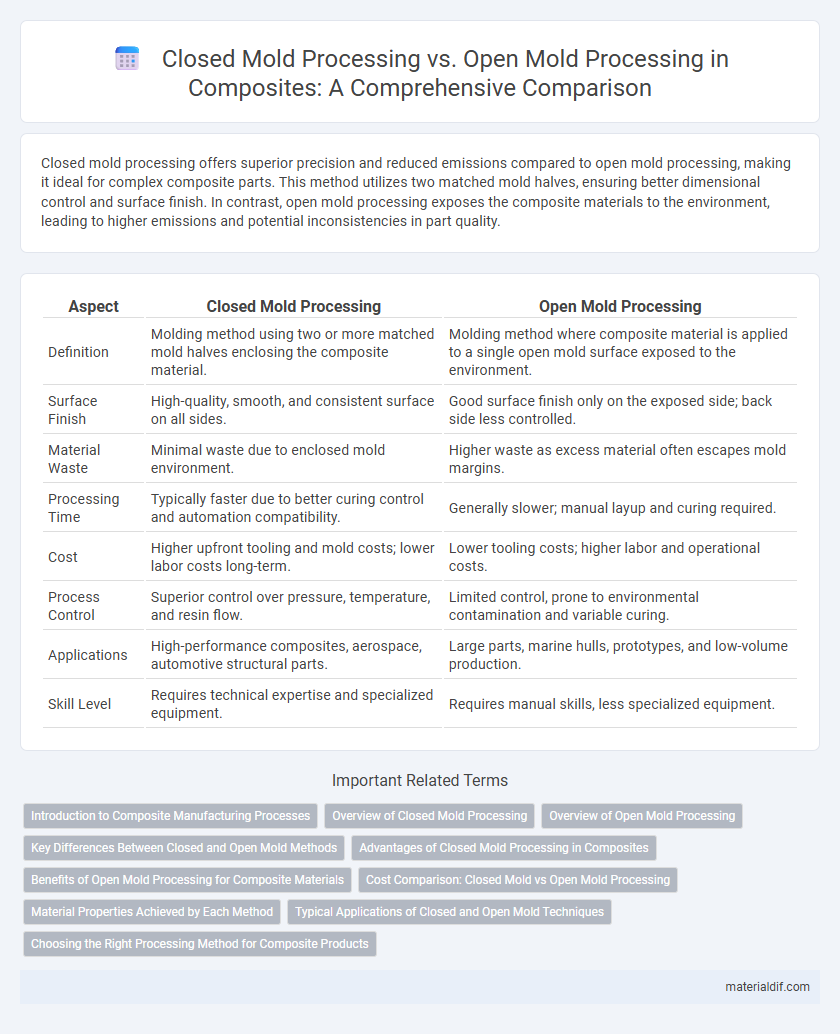
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Closed Mold Processing | Open Mold Processing |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Molding method using two or more matched mold halves enclosing the composite material. | Molding method where composite material is applied to a single open mold surface exposed to the environment. |
| Surface Finish | High-quality, smooth, and consistent surface on all sides. | Good surface finish only on the exposed side; back side less controlled. |
| Material Waste | Minimal waste due to enclosed mold environment. | Higher waste as excess material often escapes mold margins. |
| Processing Time | Typically faster due to better curing control and automation compatibility. | Generally slower; manual layup and curing required. |
| Cost | Higher upfront tooling and mold costs; lower labor costs long-term. | Lower tooling costs; higher labor and operational costs. |
| Process Control | Superior control over pressure, temperature, and resin flow. | Limited control, prone to environmental contamination and variable curing. |
| Applications | High-performance composites, aerospace, automotive structural parts. | Large parts, marine hulls, prototypes, and low-volume production. |
| Skill Level | Requires technical expertise and specialized equipment. | Requires manual skills, less specialized equipment. |
Introduction to Composite Manufacturing Processes
Closed mold processing in composite manufacturing enhances material efficiency and surface finish by using sealed molds to shape composites under controlled pressure and temperature. Open mold processing involves laying composite materials into an open cavity mold, offering greater design flexibility but higher risk of defects and lower consistency. Selecting between closed and open mold methods depends on production volume, part complexity, and desired mechanical properties of the composite component.
Overview of Closed Mold Processing
Closed mold processing involves injecting resin into a mold cavity that is sealed, ensuring precise control over resin distribution and reducing emissions. This method enhances product consistency, minimizes waste, and supports complex geometries with high structural integrity. Common closed mold techniques include Resin Transfer Molding (RTM) and Vacuum Assisted Resin Transfer Molding (VARTM), widely used in aerospace and automotive composite manufacturing.
Overview of Open Mold Processing
Open mold processing involves applying composite materials onto a single mold surface, allowing air to escape freely during curing, which results in lower tooling costs and simpler manufacturing setups. This technique is commonly used for large, less complex parts such as automotive panels and boat hulls, making it ideal for lower production volumes. Despite its advantages in cost and flexibility, open mold processing generally yields components with lower surface finish quality and structural consistency compared to closed mold methods.
Key Differences Between Closed and Open Mold Methods
Closed mold processing offers superior control over resin flow, resulting in higher-quality composite parts with consistent thickness and reduced void content, while open mold processing typically leads to greater material waste and less uniformity. Closed mold methods, such as resin transfer molding (RTM), utilize sealed molds that enhance part reproducibility and allow automation, whereas open mold techniques, including hand lay-up and spray-up, rely heavily on manual labor with longer cycle times. The environmental impact also differs, as closed mold processing minimizes emissions and overspray, making it more suitable for high-volume, precision composite manufacturing.
Advantages of Closed Mold Processing in Composites
Closed mold processing in composites offers superior control over resin flow and fiber placement, resulting in higher quality and more consistent parts with reduced porosity and void content. This method enhances worker safety by minimizing exposure to volatile organic compounds and dust, and improves environmental sustainability through lower emissions and material waste. The precision of closed mold techniques allows for faster cycle times and better integration of complex geometries, making it ideal for high-performance composite manufacturing.
Benefits of Open Mold Processing for Composite Materials
Open mold processing offers greater design flexibility and faster production times ideal for large composite structures. This method reduces tooling costs and allows for easier adjustments during fabrication, making it cost-effective for low to medium volume manufacturing. Additionally, open mold processing enables simpler visual inspection and quality control throughout the composite curing process.
Cost Comparison: Closed Mold vs Open Mold Processing
Closed mold processing typically incurs higher initial costs due to expensive tooling and equipment but offers lower labor expenses and reduced waste, resulting in more cost-efficient large-scale production. Open mold processing requires less upfront investment in molds and machinery, making it more suitable for low-volume or custom composites, yet it demands higher manual labor and generates more material waste. Overall, closed mold processes like resin transfer molding (RTM) provide better long-term cost savings compared to traditional open mold techniques such as hand lay-up and spray-up, especially for complex or high-volume composite parts.
Material Properties Achieved by Each Method
Closed mold processing enhances composite material properties by ensuring uniform resin distribution and reducing void content, resulting in higher strength and improved surface finish. Open mold processing often leads to greater porosity and less consistent fiber wet-out, which can compromise mechanical performance and durability. Material strength, stiffness, and overall quality are typically superior in closed mold composites due to controlled environmental conditions and pressure application during curing.
Typical Applications of Closed and Open Mold Techniques
Closed mold processing is typically used in automotive parts manufacturing, aerospace components, and high-volume production of complex composites due to its superior surface finish and dimensional accuracy. Open mold processing finds common applications in large-scale marine structures, architectural elements, and custom or low-volume parts where flexibility and lower tooling costs are prioritized. Each technique caters to specific industry demands, balancing production efficiency with design complexity and material properties.
Choosing the Right Processing Method for Composite Products
Closed mold processing offers superior surface finish quality and higher production efficiency for composite products, making it ideal for complex, high-volume manufacturing. Open mold processing provides versatility and cost-effectiveness for prototypes or low-volume runs, particularly when intricate molds are unnecessary. Selecting the right method depends on factors such as production volume, part complexity, and desired surface properties to optimize both performance and manufacturing costs.
Closed Mold Processing vs Open Mold Processing Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com