Unidirectional tape offers superior strength and stiffness in a single direction, making it ideal for applications requiring high tensile performance along the fiber orientation. Woven fabric provides enhanced multi-directional strength and better impact resistance due to the interlaced fiber structure. Choosing between unidirectional tape and woven fabric depends on the specific load distribution and performance requirements of the composite part.
Table of Comparison
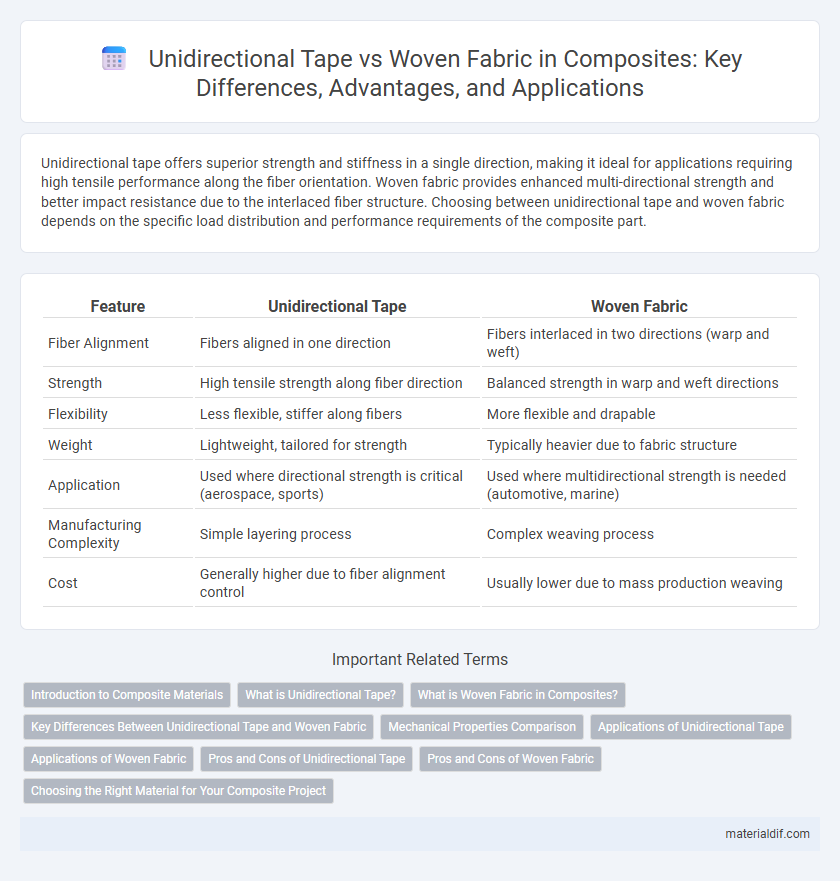
| Feature | Unidirectional Tape | Woven Fabric |
|---|---|---|
| Fiber Alignment | Fibers aligned in one direction | Fibers interlaced in two directions (warp and weft) |
| Strength | High tensile strength along fiber direction | Balanced strength in warp and weft directions |
| Flexibility | Less flexible, stiffer along fibers | More flexible and drapable |
| Weight | Lightweight, tailored for strength | Typically heavier due to fabric structure |
| Application | Used where directional strength is critical (aerospace, sports) | Used where multidirectional strength is needed (automotive, marine) |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Simple layering process | Complex weaving process |
| Cost | Generally higher due to fiber alignment control | Usually lower due to mass production weaving |
Introduction to Composite Materials
Unidirectional tape in composite materials consists of fibers aligned in a single direction, providing superior strength and stiffness along the fiber axis, which optimizes load-bearing capacity. Woven fabric, composed of interlaced fibers in multiple directions, offers balanced mechanical properties and enhanced damage tolerance due to its multidirectional reinforcement. Understanding these differences is critical for selecting appropriate composite materials in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods applications where tailored performance is essential.
What is Unidirectional Tape?
Unidirectional tape in composites consists of continuous fibers aligned in a single direction, providing high strength and stiffness along the fiber axis. This tape enhances load-bearing capacity and minimizes weight, making it ideal for aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods applications. Compared to woven fabric, unidirectional tape allows for precise fiber orientation, optimizing mechanical performance for specific engineering requirements.
What is Woven Fabric in Composites?
Woven fabric in composites consists of fibers interlaced in a crisscross pattern, providing balanced strength and flexibility in multiple directions. This structure enhances damage tolerance and impact resistance compared to unidirectional tape, making it ideal for applications requiring durability and multidirectional load bearing. Woven fabrics are commonly made from materials like carbon, glass, or aramid fibers, optimizing mechanical performance in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries.
Key Differences Between Unidirectional Tape and Woven Fabric
Unidirectional tape features fibers aligned in a single direction, offering superior tensile strength and stiffness along that axis, while woven fabric has fibers interlaced at right angles, providing balanced mechanical properties and enhanced dimensional stability. The manufacturing process of unidirectional tape allows precise fiber orientation, optimizing load transfer in composite structures, whereas woven fabric facilitates ease of handling and draping over complex shapes due to its flexible weave. These distinctions influence the composite's performance in applications requiring directional strength versus multidirectional load resistance.
Mechanical Properties Comparison
Unidirectional tape offers superior tensile strength and stiffness along the fiber direction due to aligned continuous fibers, enhancing load-bearing capacity in composite structures. Woven fabric exhibits balanced mechanical properties with improved impact resistance and resistance to delamination, attributed to interlaced fibers providing multidirectional reinforcement. The choice between unidirectional tape and woven fabric depends on specific mechanical requirements, where unidirectional tape excels in axial loading while woven fabric delivers better durability and damage tolerance.
Applications of Unidirectional Tape
Unidirectional tape in composites is primarily used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods industries due to its superior tensile strength along a single axis, making it ideal for load-bearing components. Unlike woven fabrics, unidirectional tape allows precise fiber alignment, enhancing stiffness and strength where directional properties are critical. This targeted reinforcement improves performance in structural parts such as aircraft wings, race car monocoques, and high-performance bicycle frames.
Applications of Woven Fabric
Woven fabric composites are widely used in aerospace, automotive, and sporting goods due to their superior tensile strength and impact resistance. Their interlaced fiber architecture provides excellent dimensional stability and damage tolerance, making them ideal for load-bearing components and structural reinforcements. These fabrics enable improved fatigue performance and enhanced durability in high-stress environments compared to unidirectional tape composites.
Pros and Cons of Unidirectional Tape
Unidirectional tape in composites offers superior strength and stiffness along the fiber direction, making it ideal for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity. Its main limitation is reduced performance in transverse directions due to the lack of fiber reinforcement across fibers, leading to potential weaknesses in multi-directional stress scenarios. Compared to woven fabric, unidirectional tape enables more precise fiber alignment and better consolidation, but at the cost of reduced impact resistance and damage tolerance.
Pros and Cons of Woven Fabric
Woven fabric in composites offers superior dimensional stability and impact resistance, making it ideal for structural applications requiring strength and toughness. However, its heavier weight and lower flexibility compared to unidirectional tape can limit performance in designs where minimal mass and high conformability are critical. The interlaced fiber architecture also introduces potential points for resin-rich zones, which may affect fatigue resistance and overall laminate uniformity.
Choosing the Right Material for Your Composite Project
Unidirectional tape provides superior strength and stiffness along a single axis, making it ideal for applications requiring high load-bearing capacity in one direction. Woven fabric offers balanced mechanical properties with enhanced impact resistance and dimensional stability, suitable for components subjected to multi-directional stresses. Selecting the right composite reinforcement depends on load orientation, mechanical performance criteria, and application-specific demands to optimize structural integrity and durability.
Unidirectional Tape vs Woven Fabric Infographic
 materialdif.com
materialdif.com